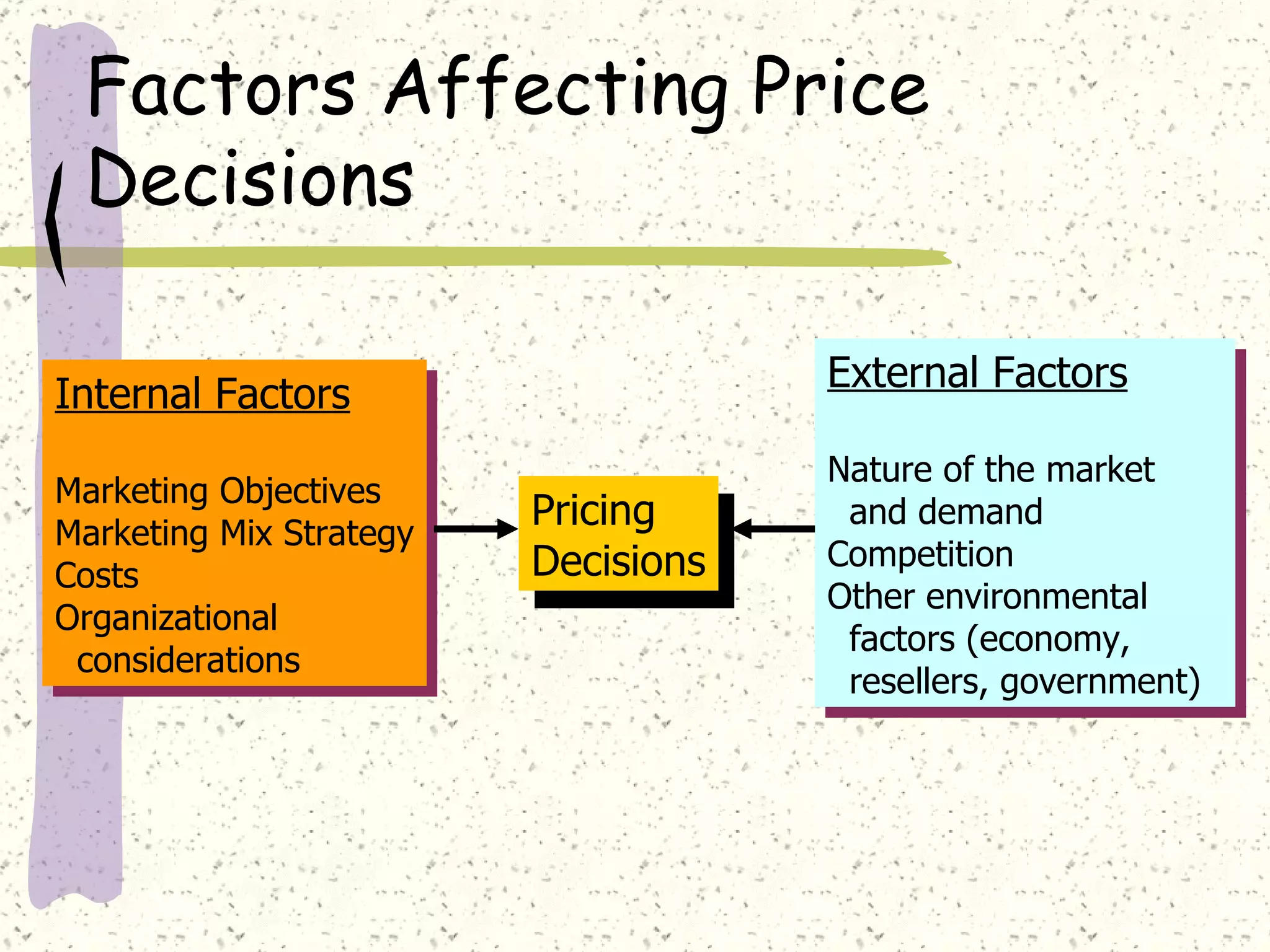
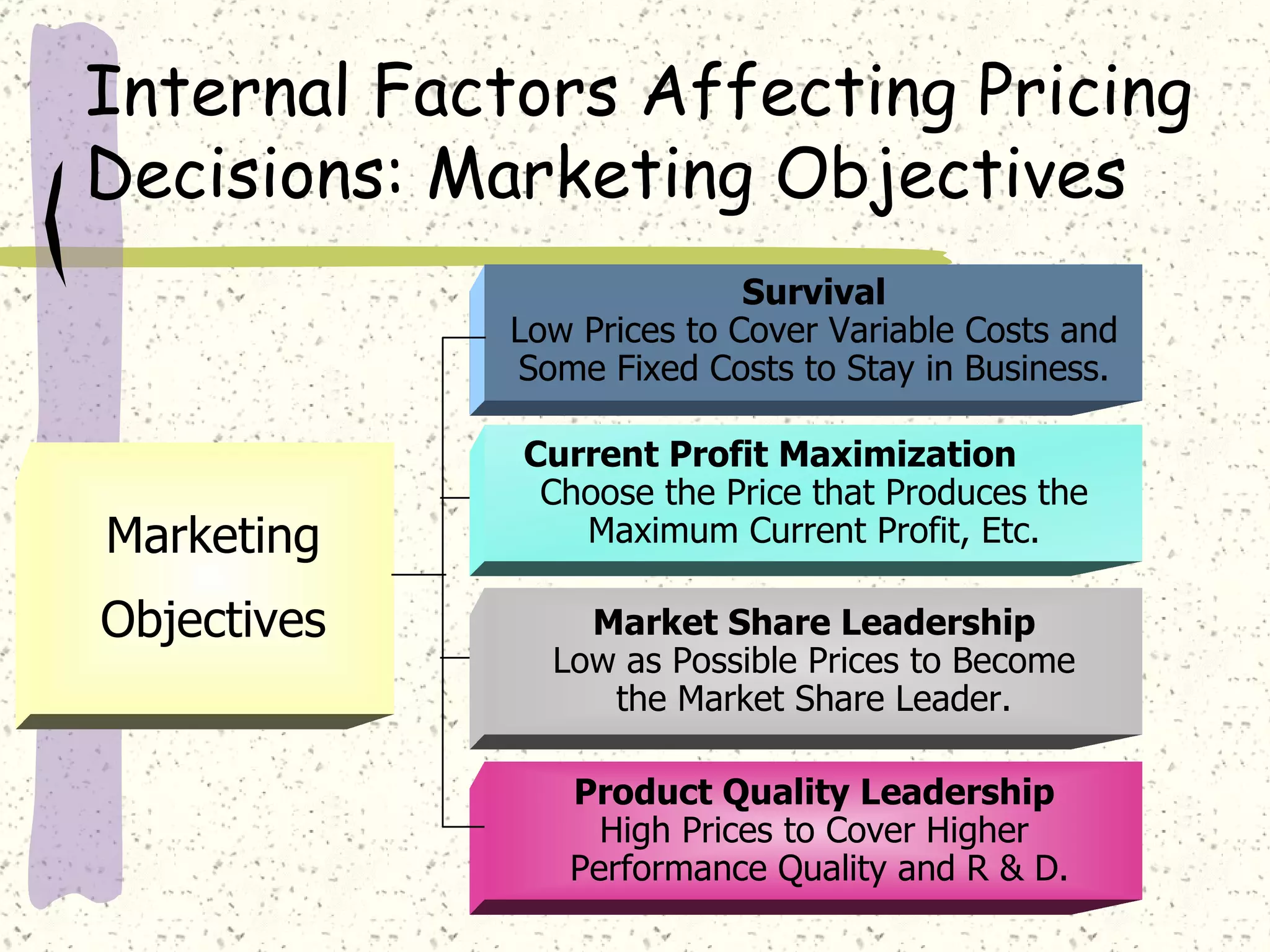
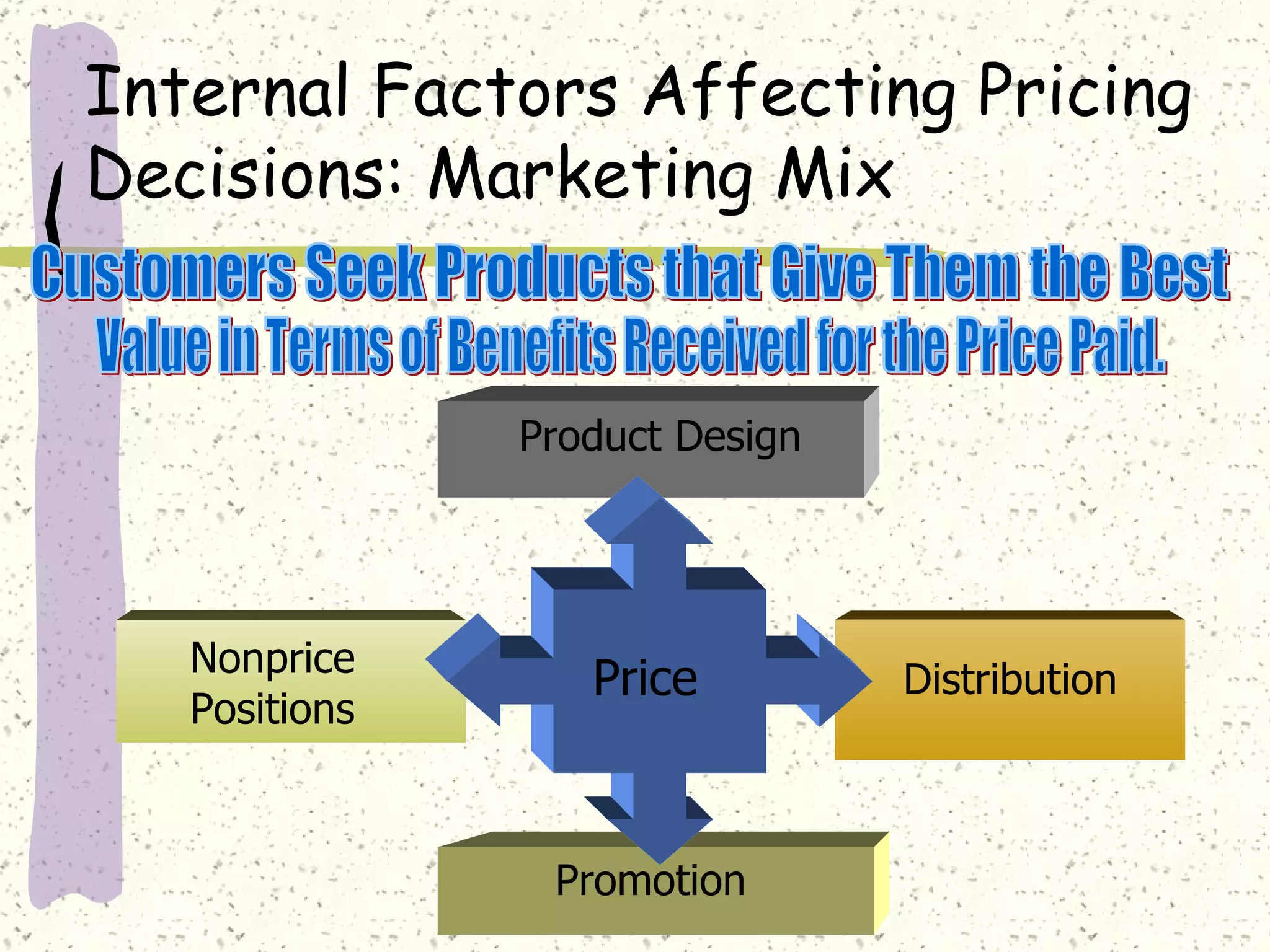
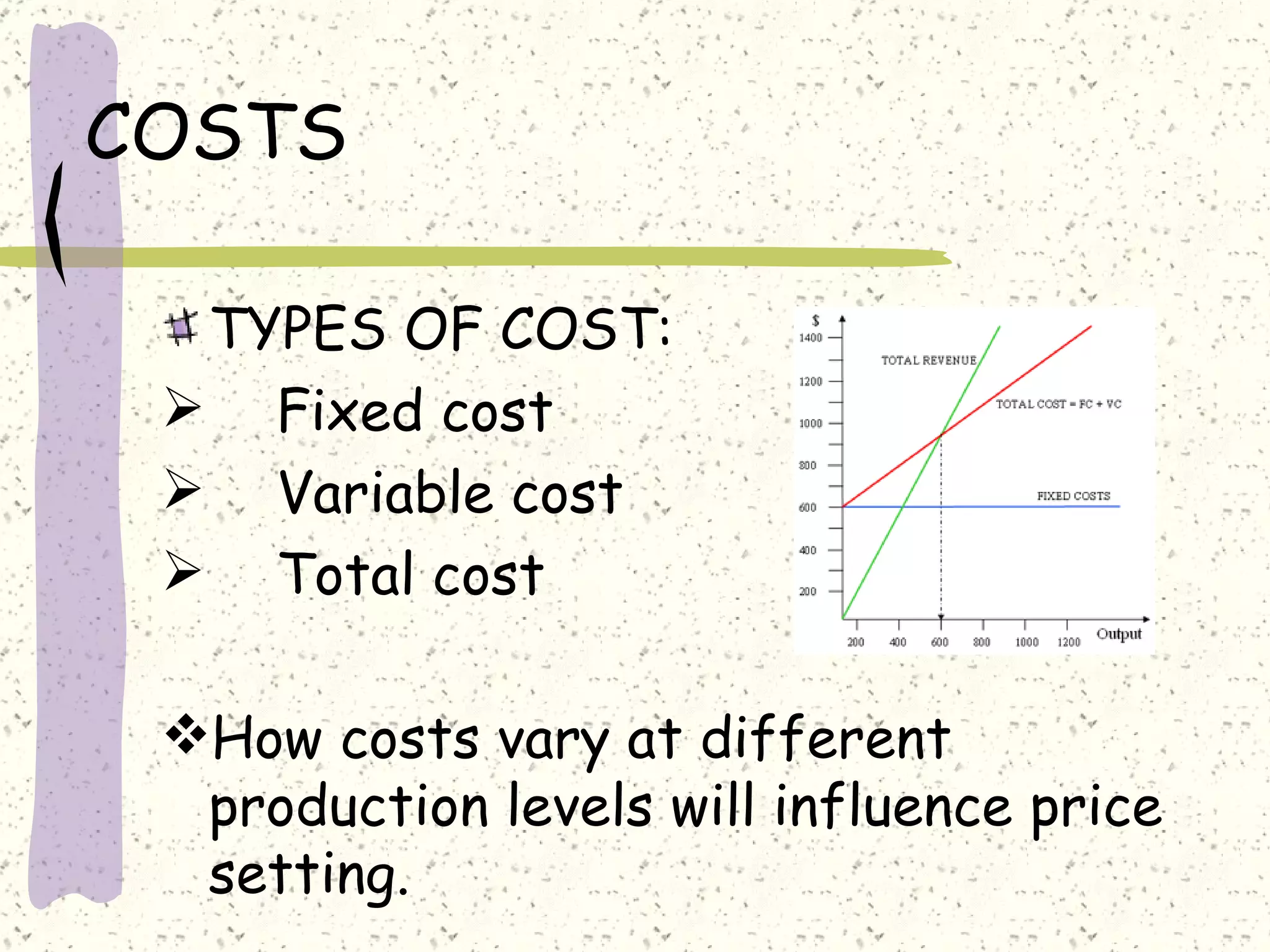
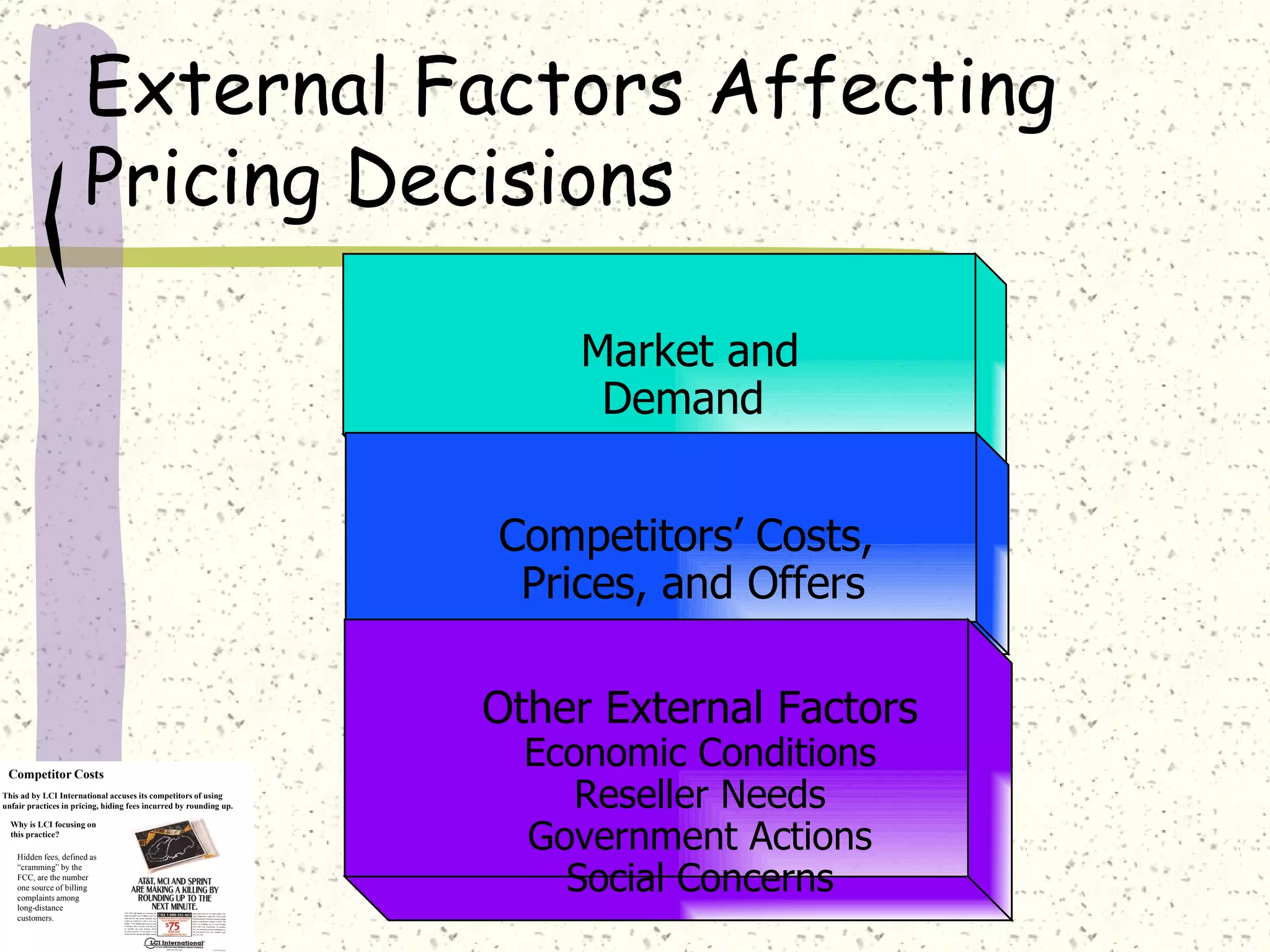
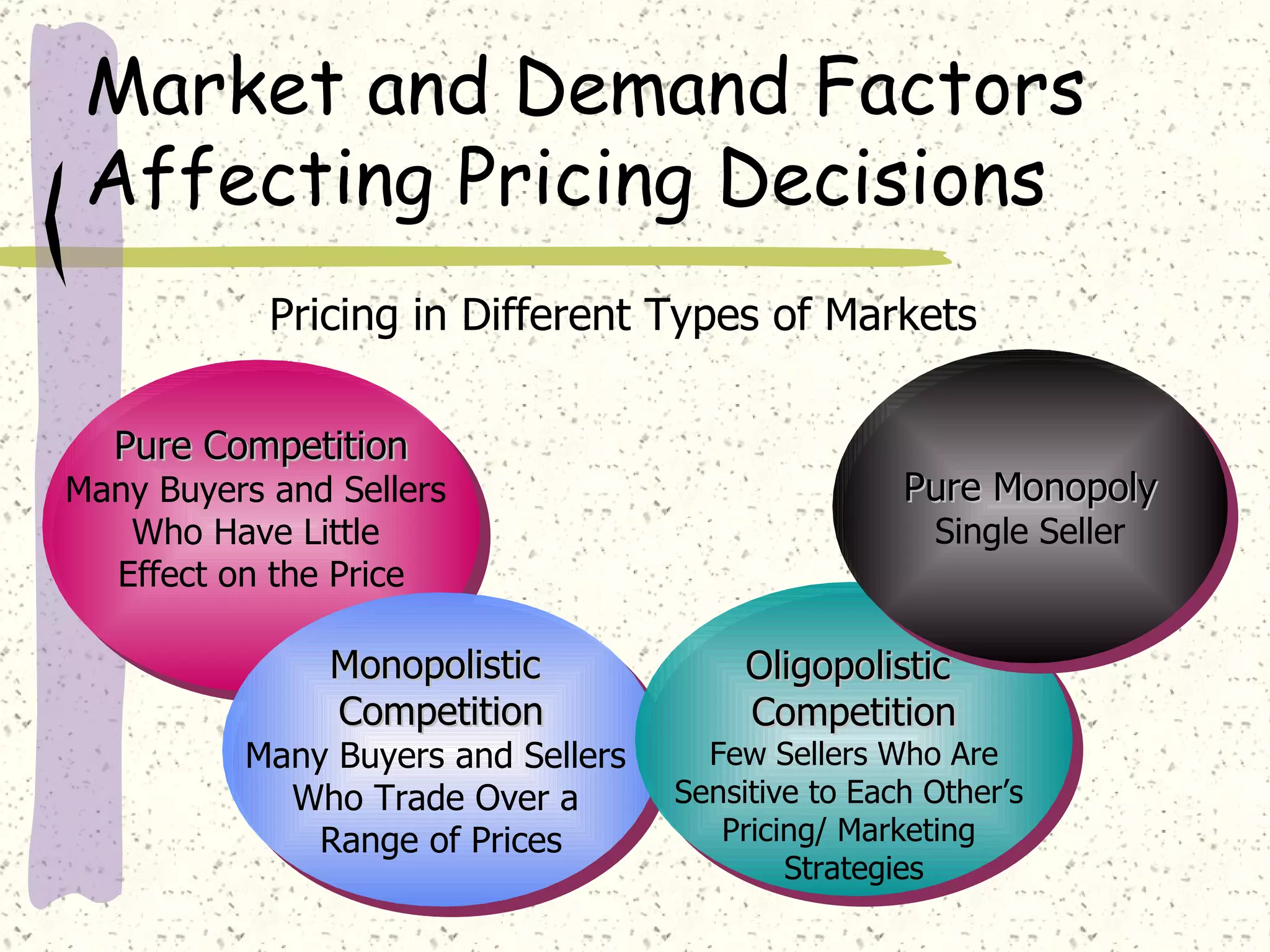
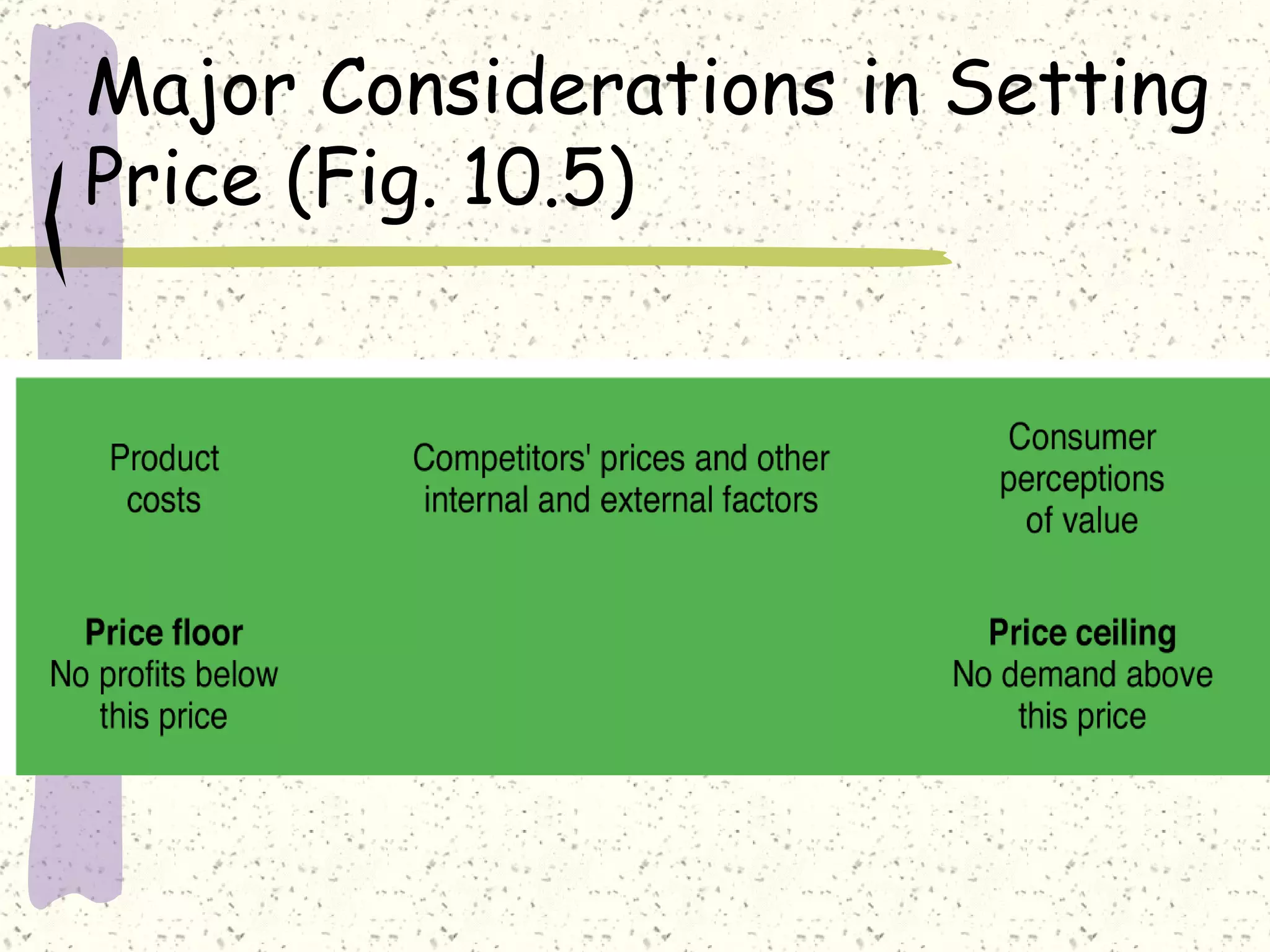
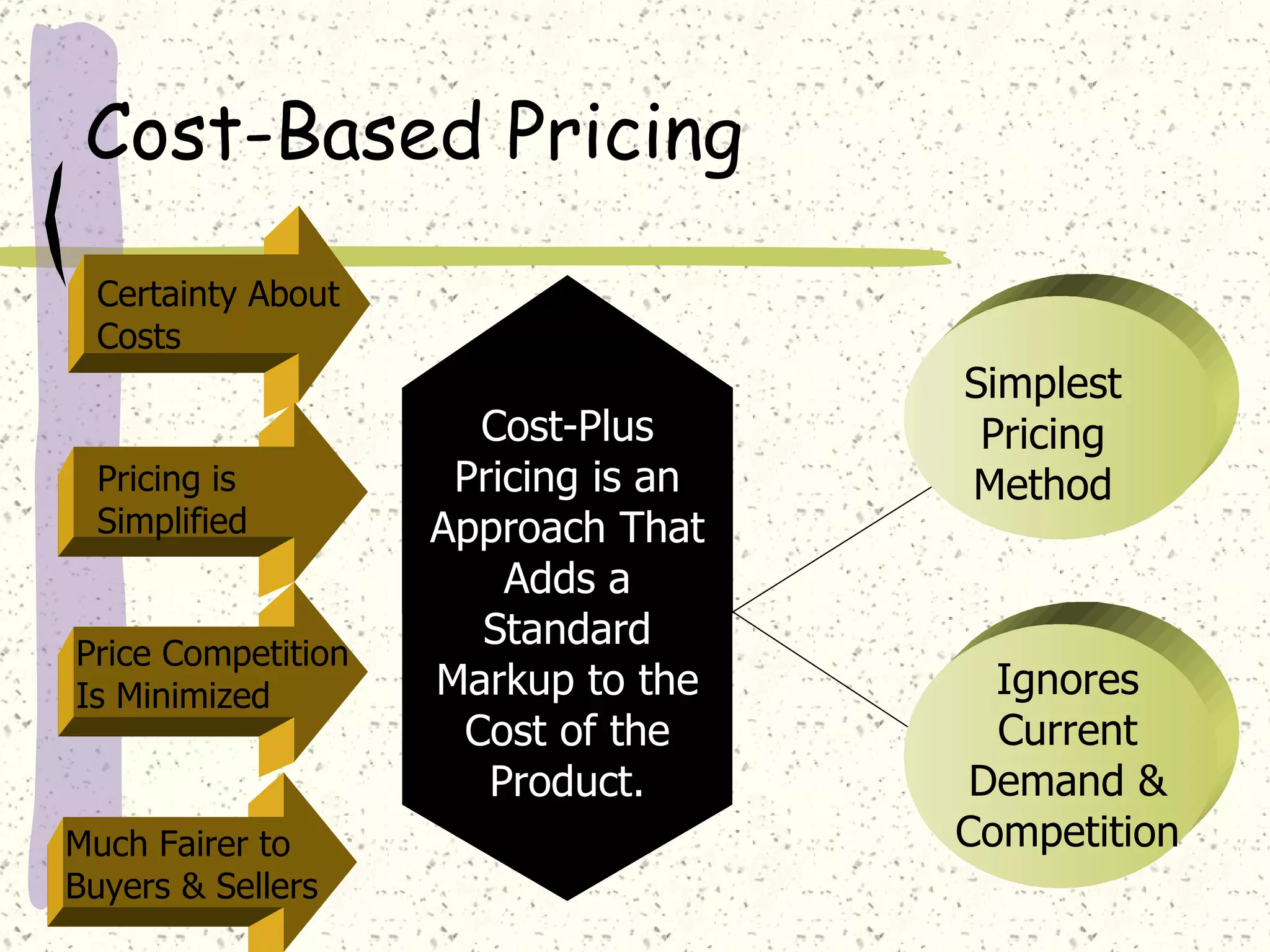
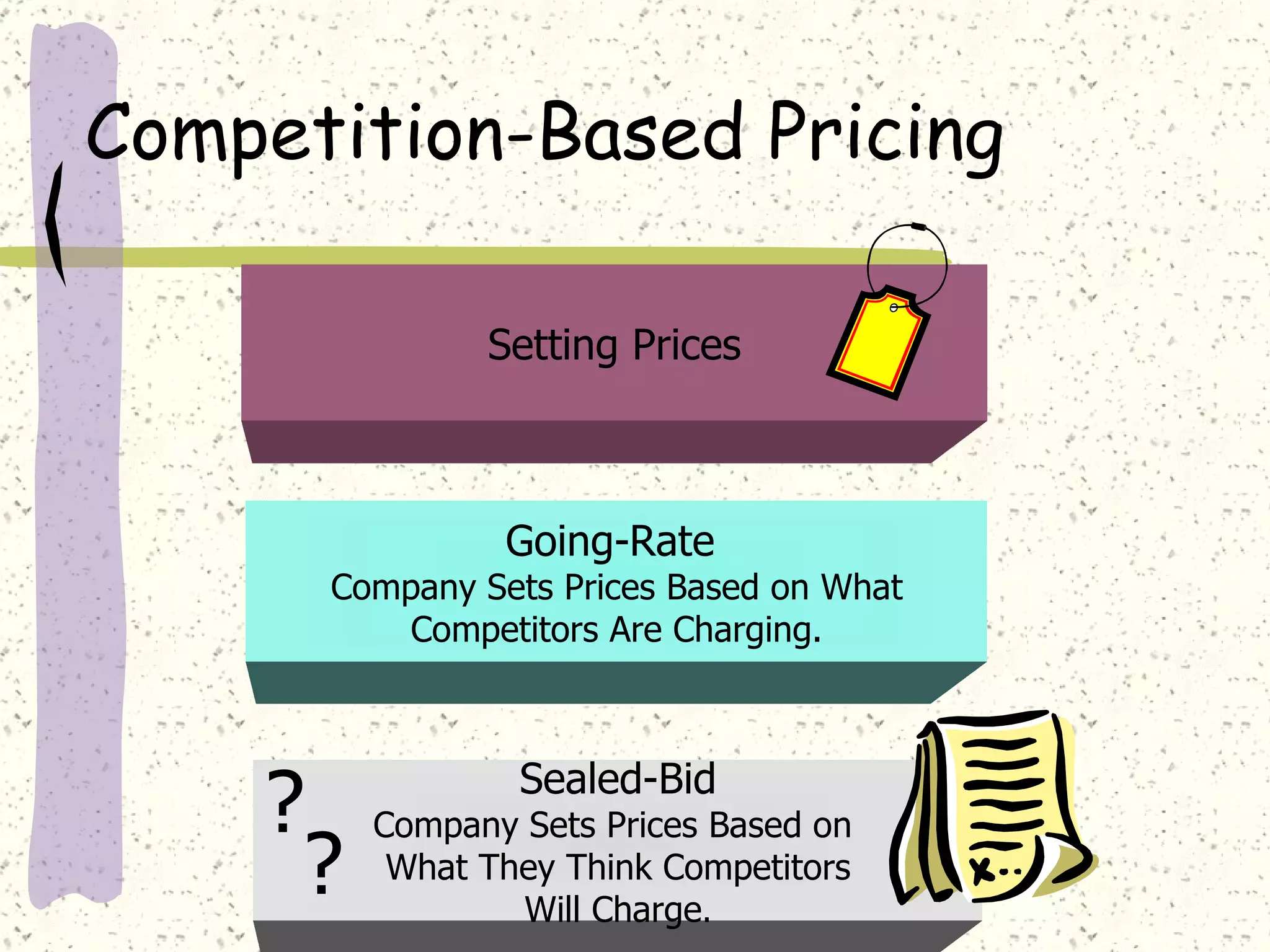
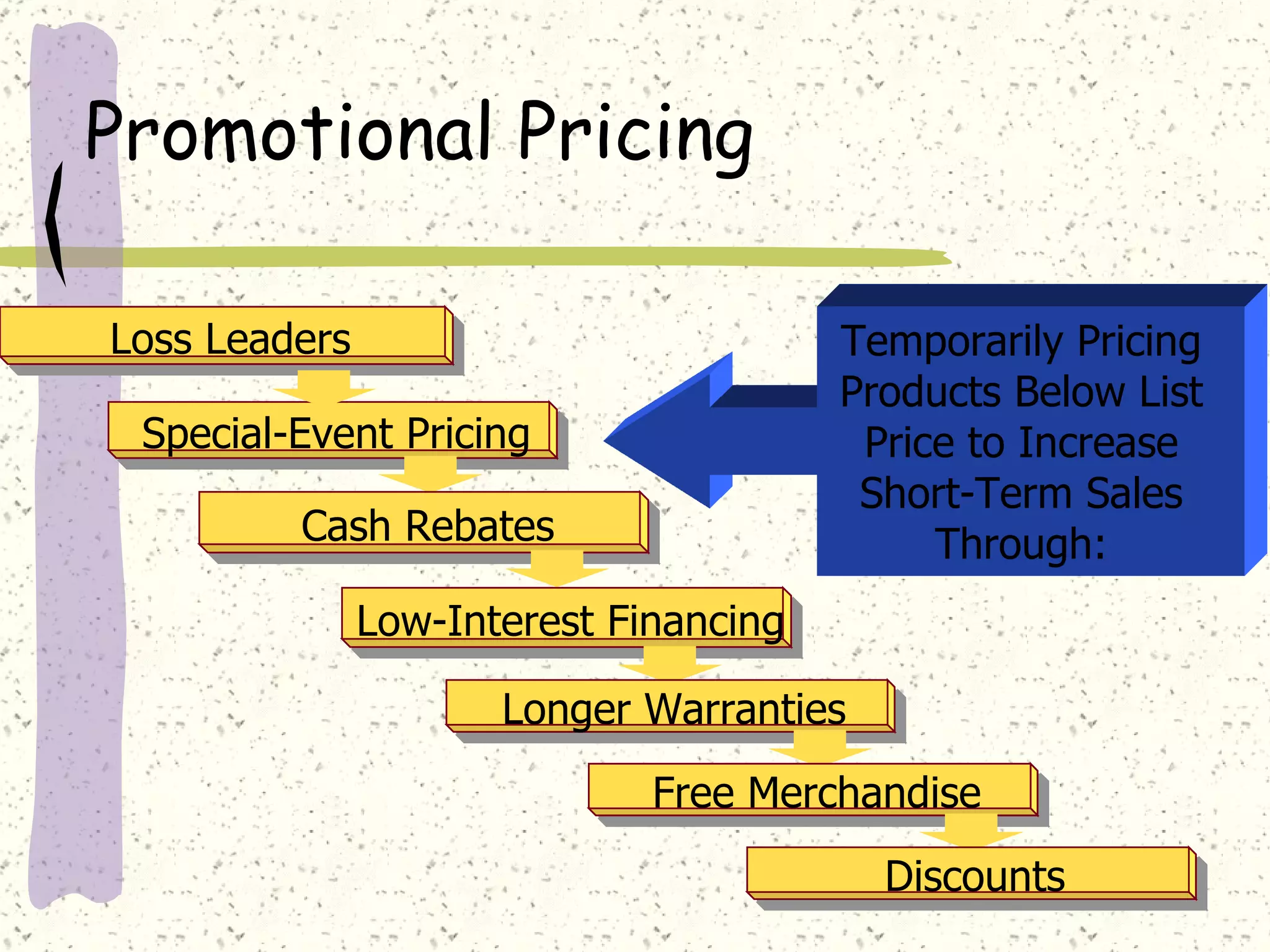
There are internal and external factors that determine price. Internal factors include marketing objectives, costs, and organizational considerations. External factors include market demand, competition, economic conditions, and government actions. When setting price, companies consider costs, value to customers, competition, and promotional strategies. The optimal pricing strategy depends on the product, market conditions, and business objectives.