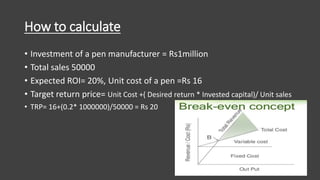
This document discusses various methods of pricing, including cost-oriented and market-oriented approaches. It describes mark-up pricing, absorption cost pricing, target-return pricing, perceived value pricing, going rate pricing, and auction-type pricing. For each method, it provides examples of industries that use that approach and explains how to calculate pricing using that method. The key methods discussed are mark-up pricing based on desired profit margins, absorption cost pricing which includes all costs, and target-return pricing where the profit margin is set based on desired return on investment.