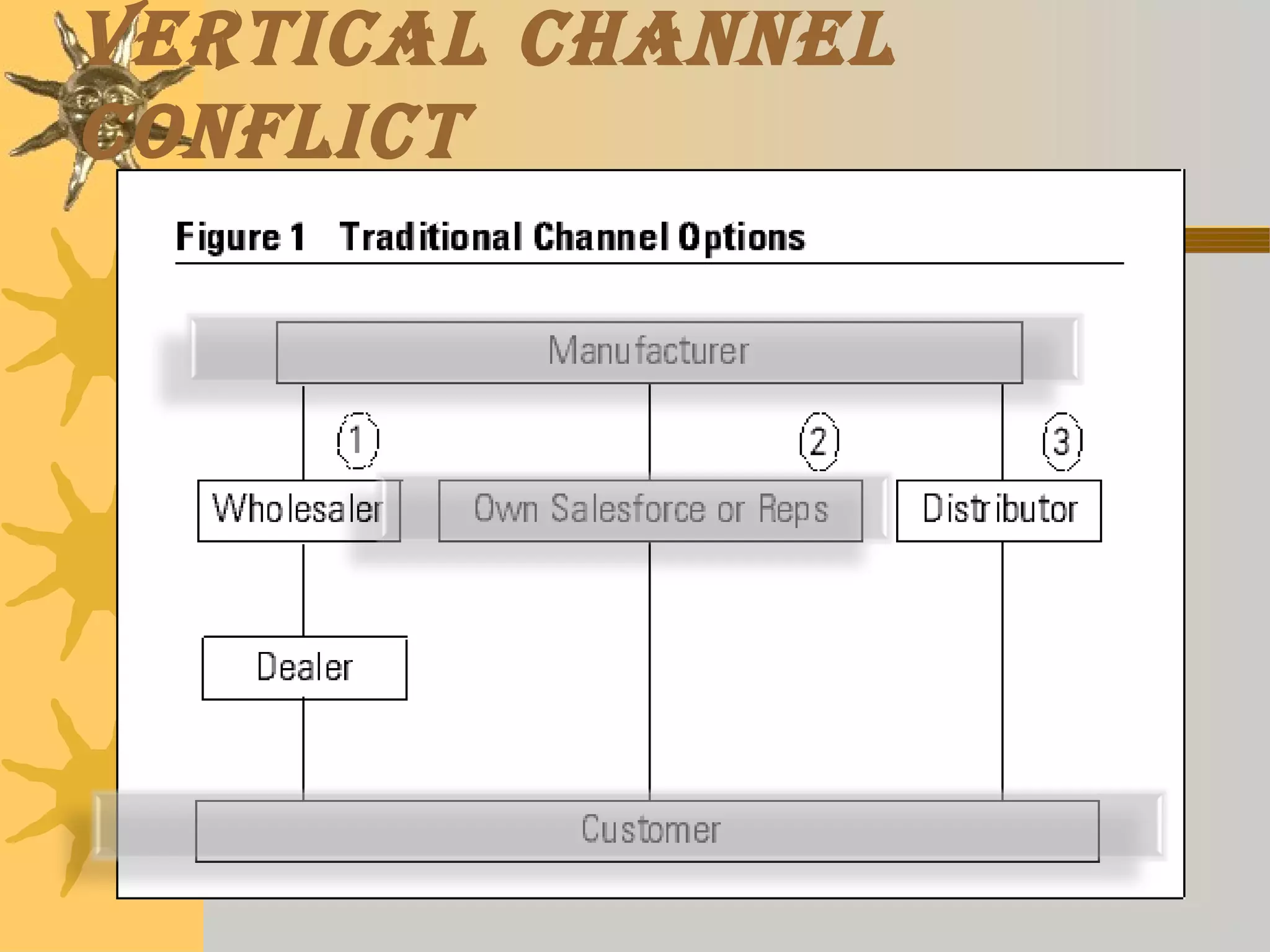
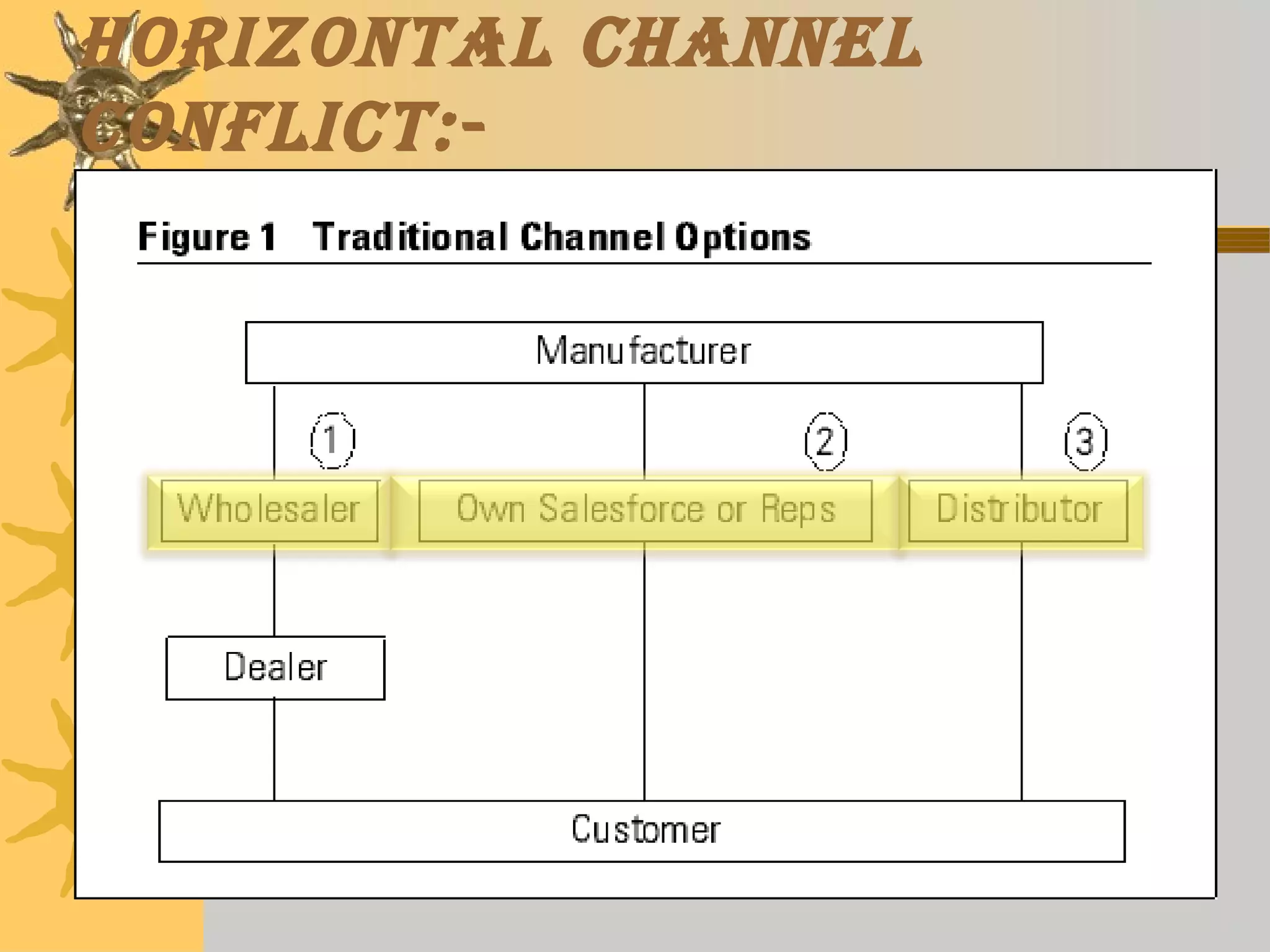
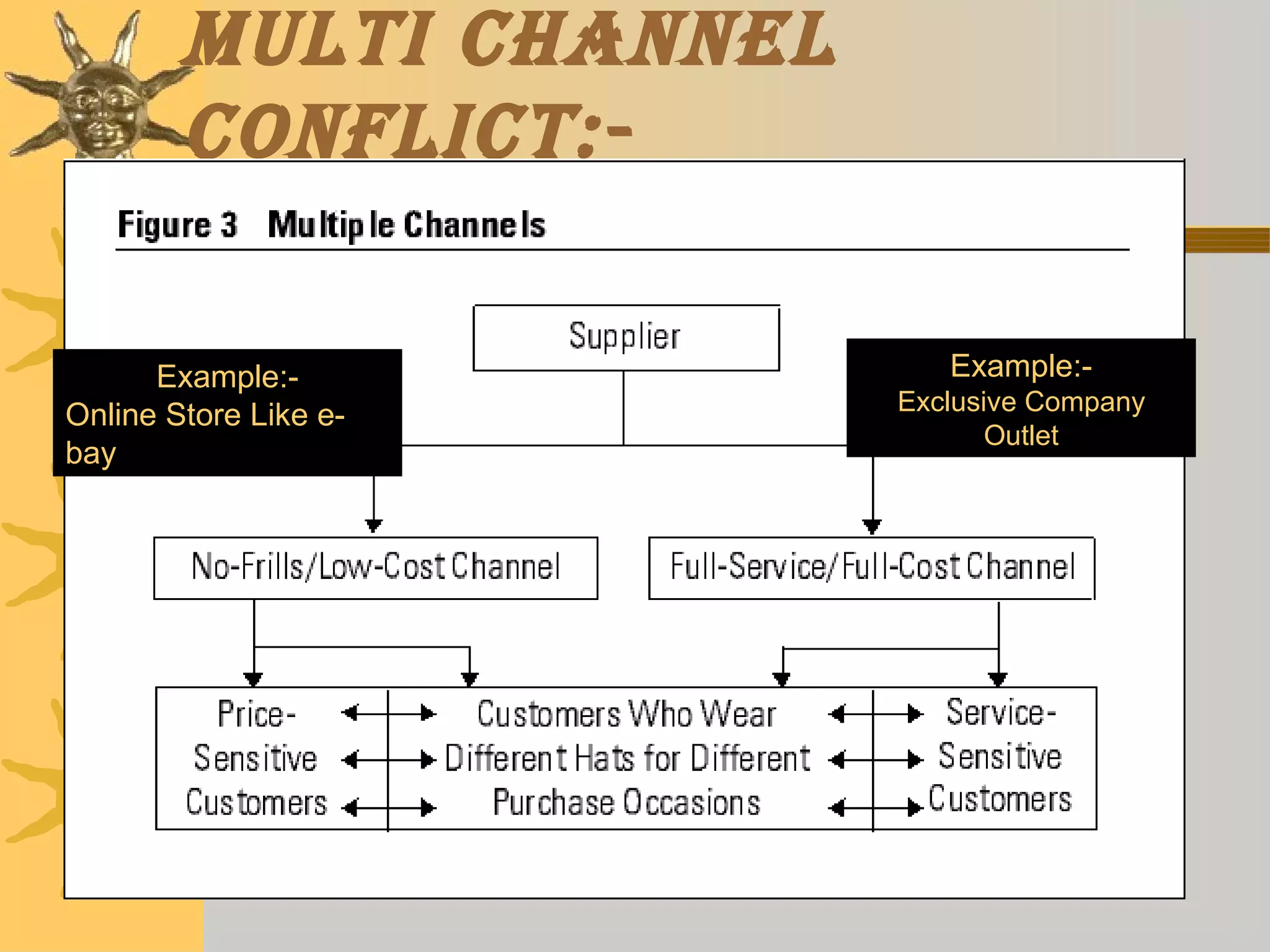
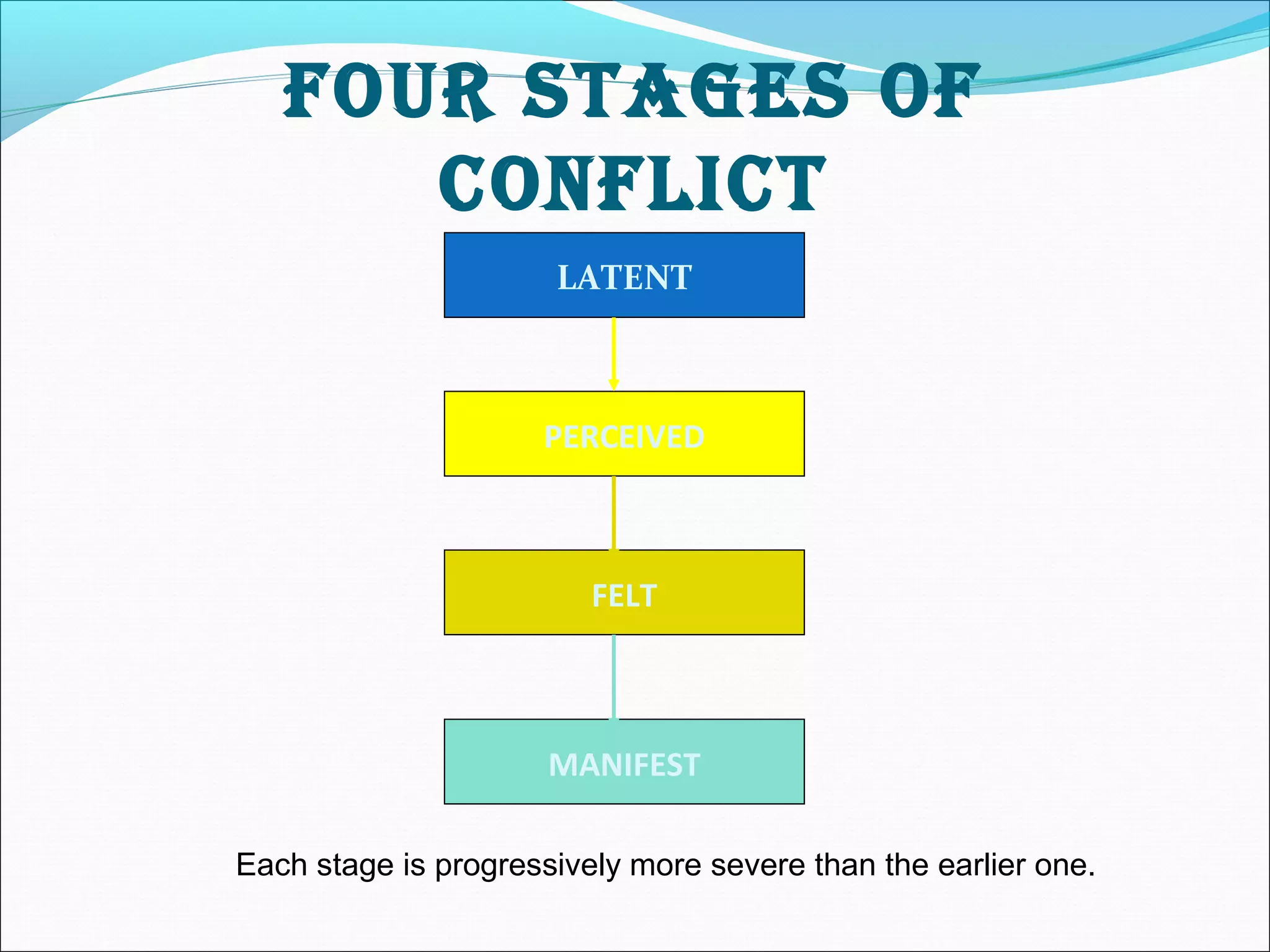
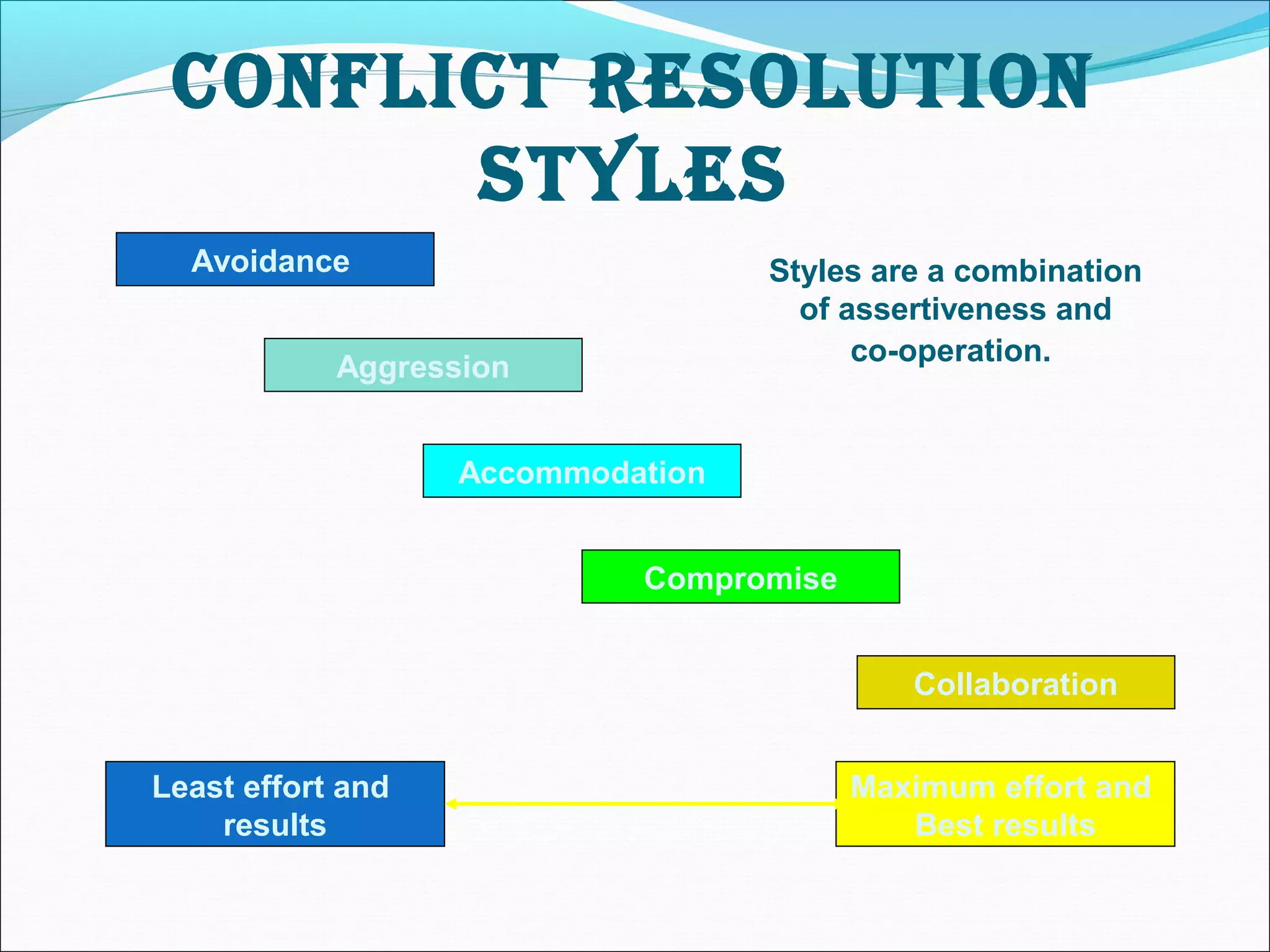
This document discusses different types of channel conflicts that can occur in marketing channels, including vertical conflicts between manufacturers and retailers, horizontal conflicts between retailers, and multi-channel conflicts when multiple distribution strategies are used. It also describes the stages of conflicts from latent to manifest, and strategies for resolving conflicts such as avoidance, aggression, accommodation, compromise, and collaboration.