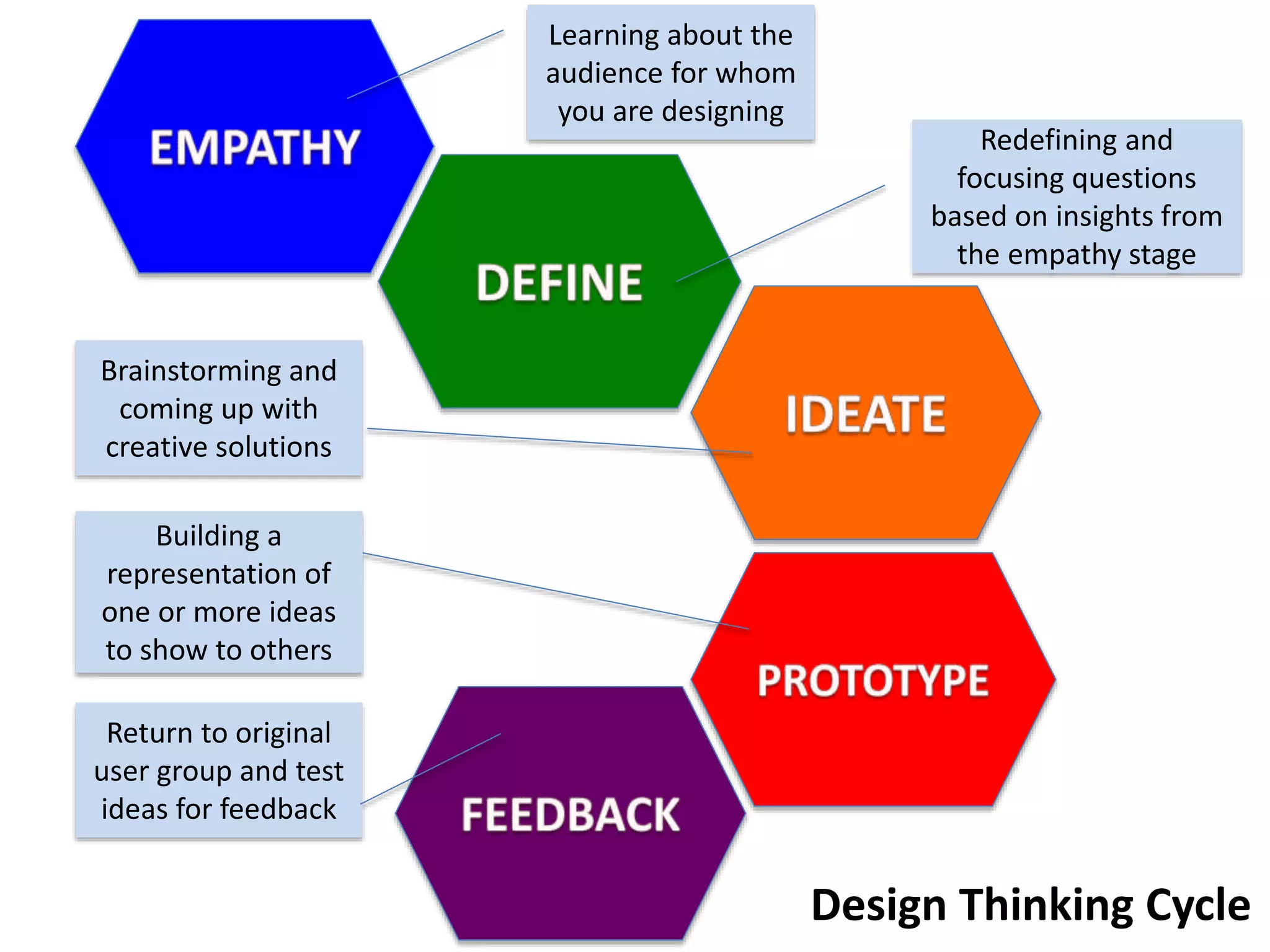
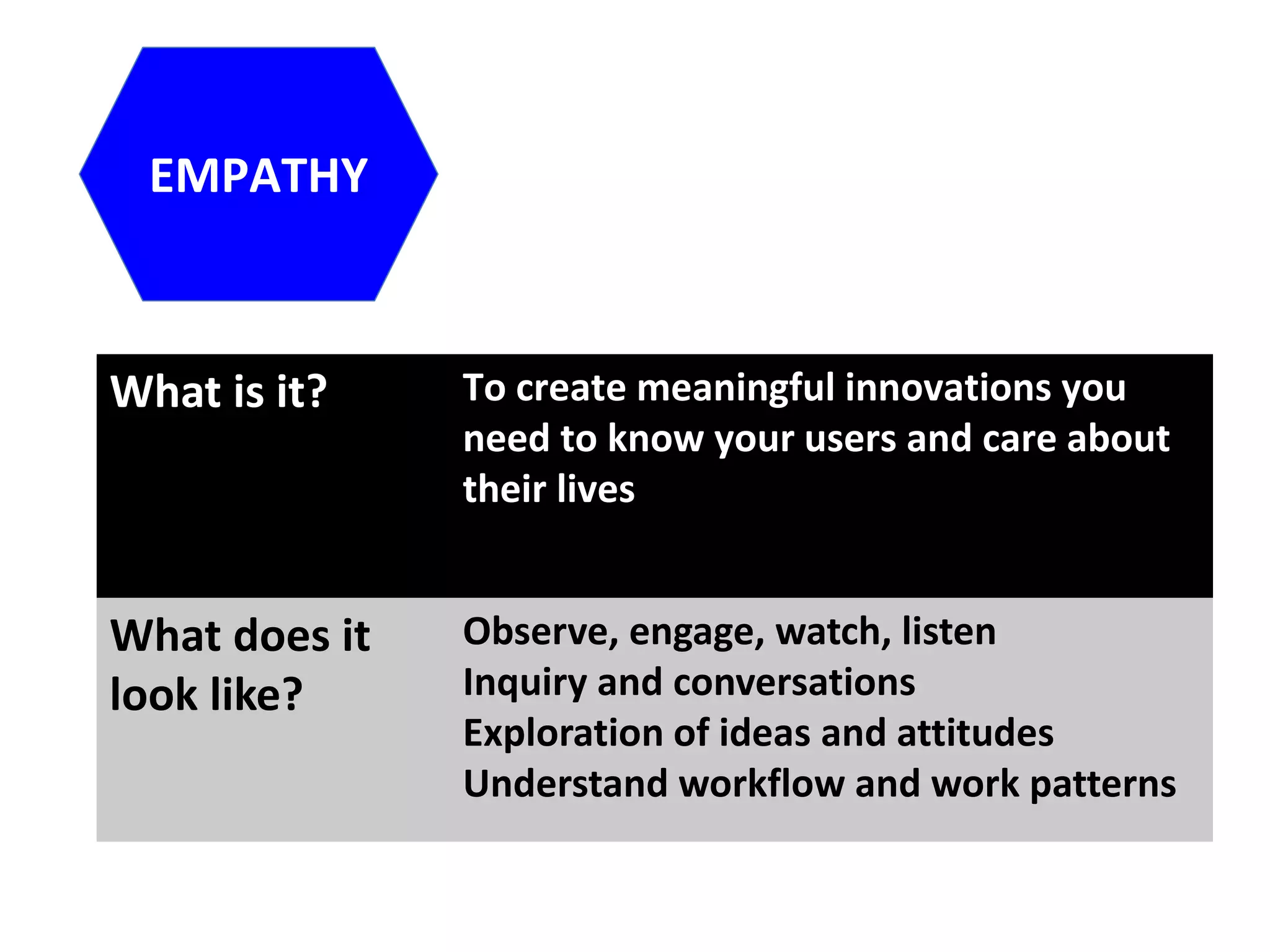
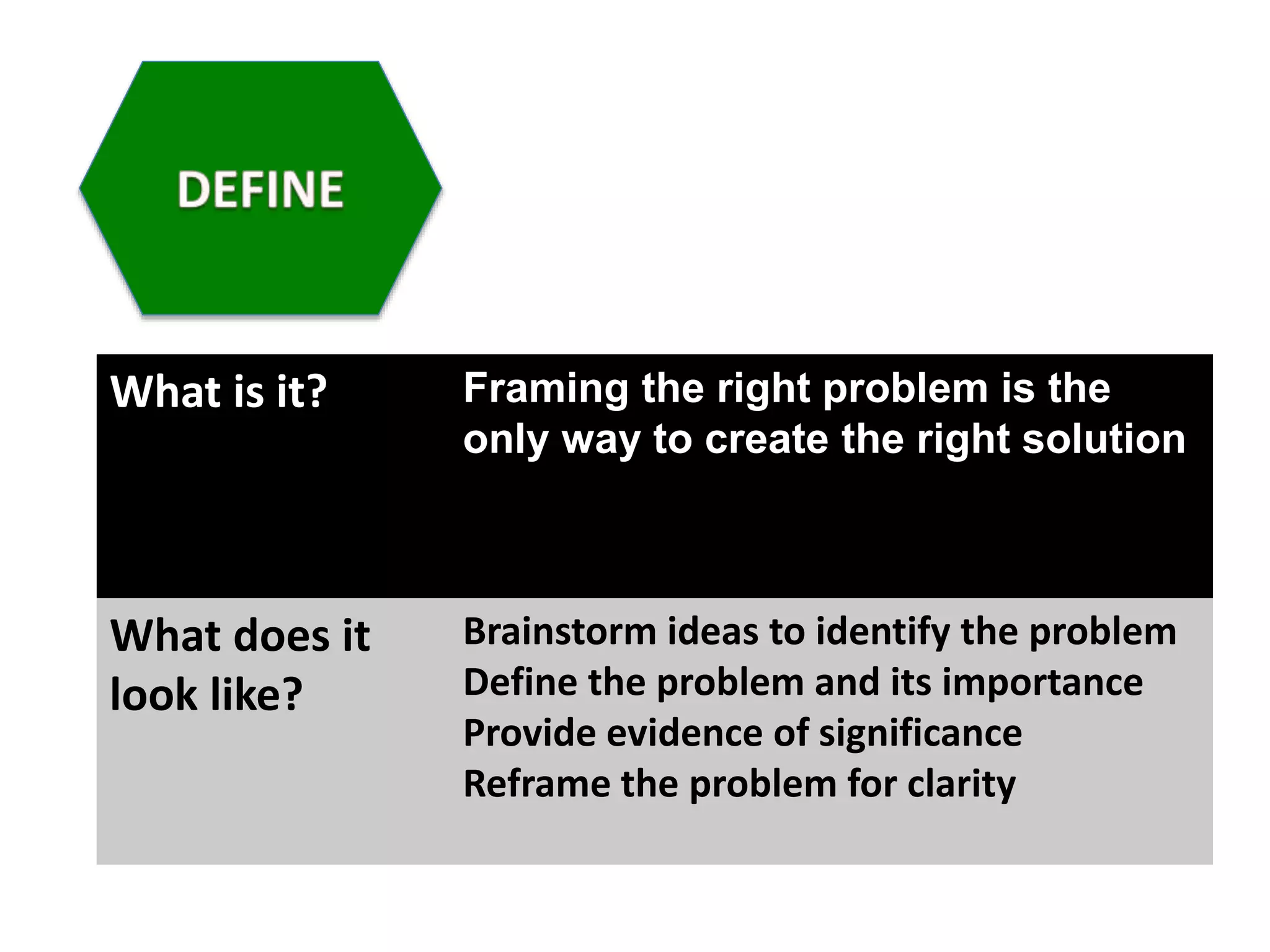
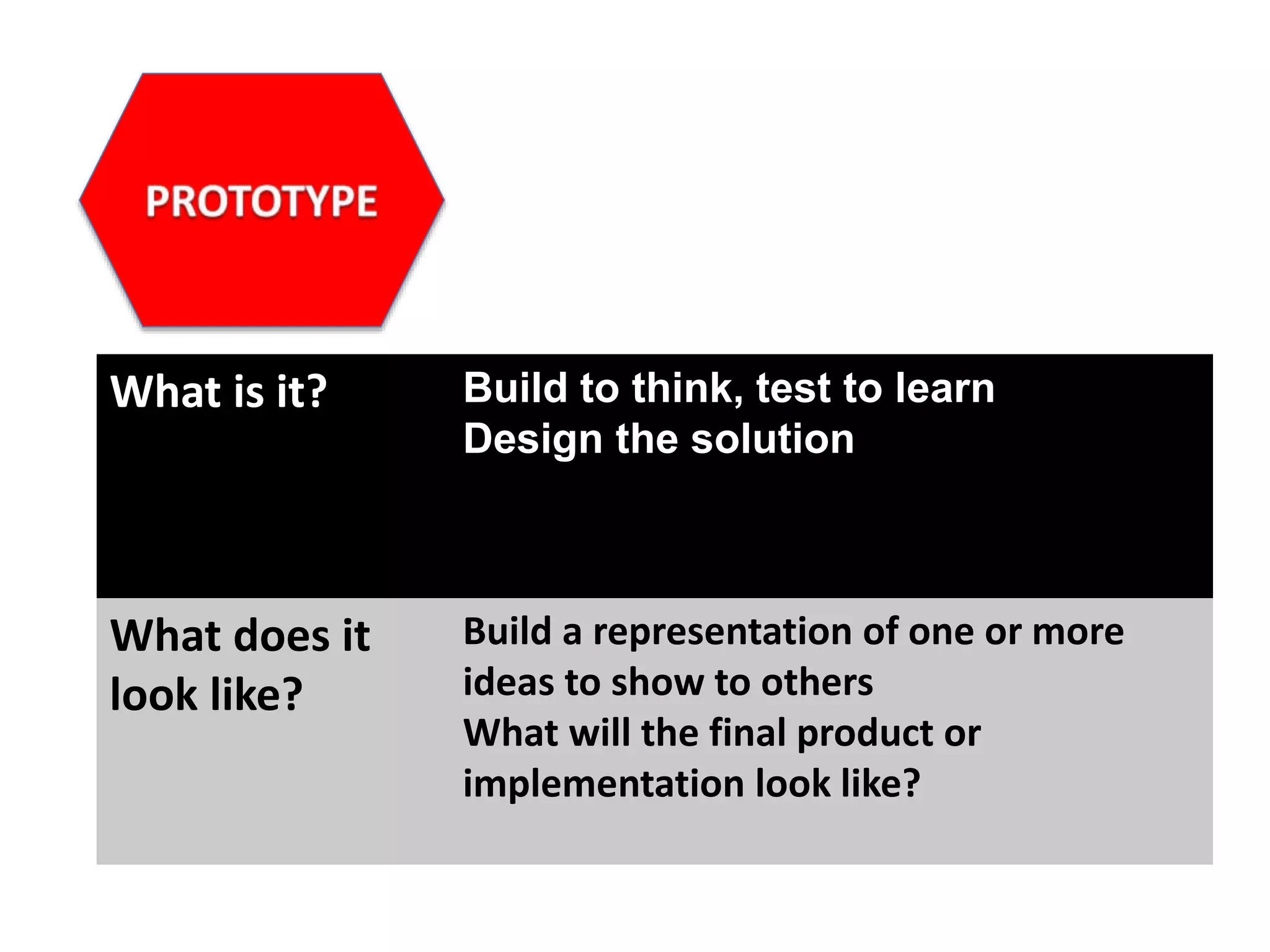
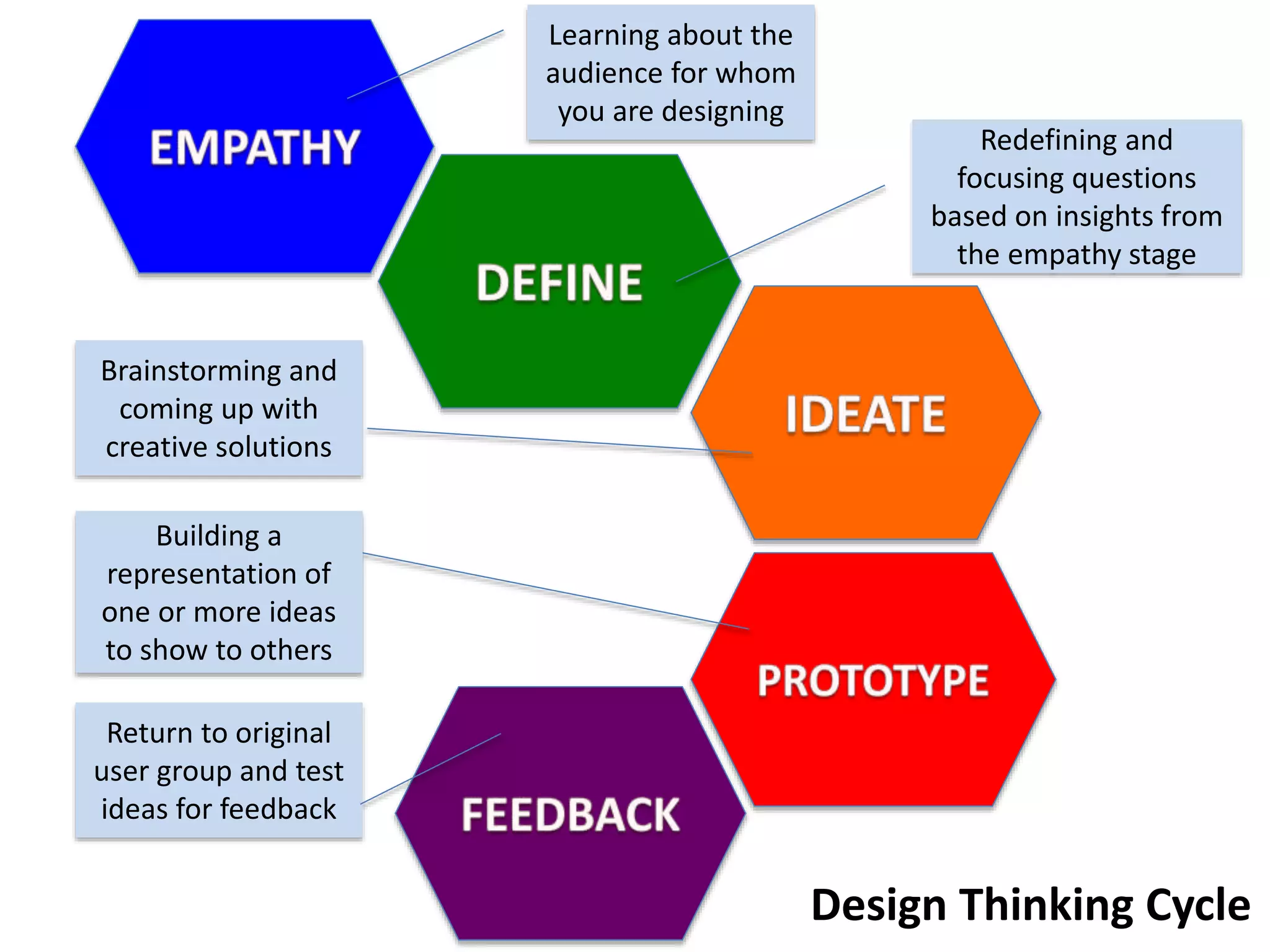
The document discusses how design thinking can facilitate workplace change by fostering empathy, collaboration, and communication among stakeholders through digital technologies. It outlines a structured approach encompassing empathy building, problem definition, brainstorming solutions, and generating feedback in design processes. Julie Lindsay emphasizes the importance of understanding user needs and employing collaborative methods to create meaningful innovations.














![“[C]ollaborative production is simple:
no one person can take credit for
what gets created, and the project
could not come into being without
the participation of many.”
Clay Shirky, Here comes everybody](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/julielindsaydesignthinkingforworkplacechange-150622002522-lva1-app6891/75/Design-thinking-for-workplace-change-15-2048.jpg)