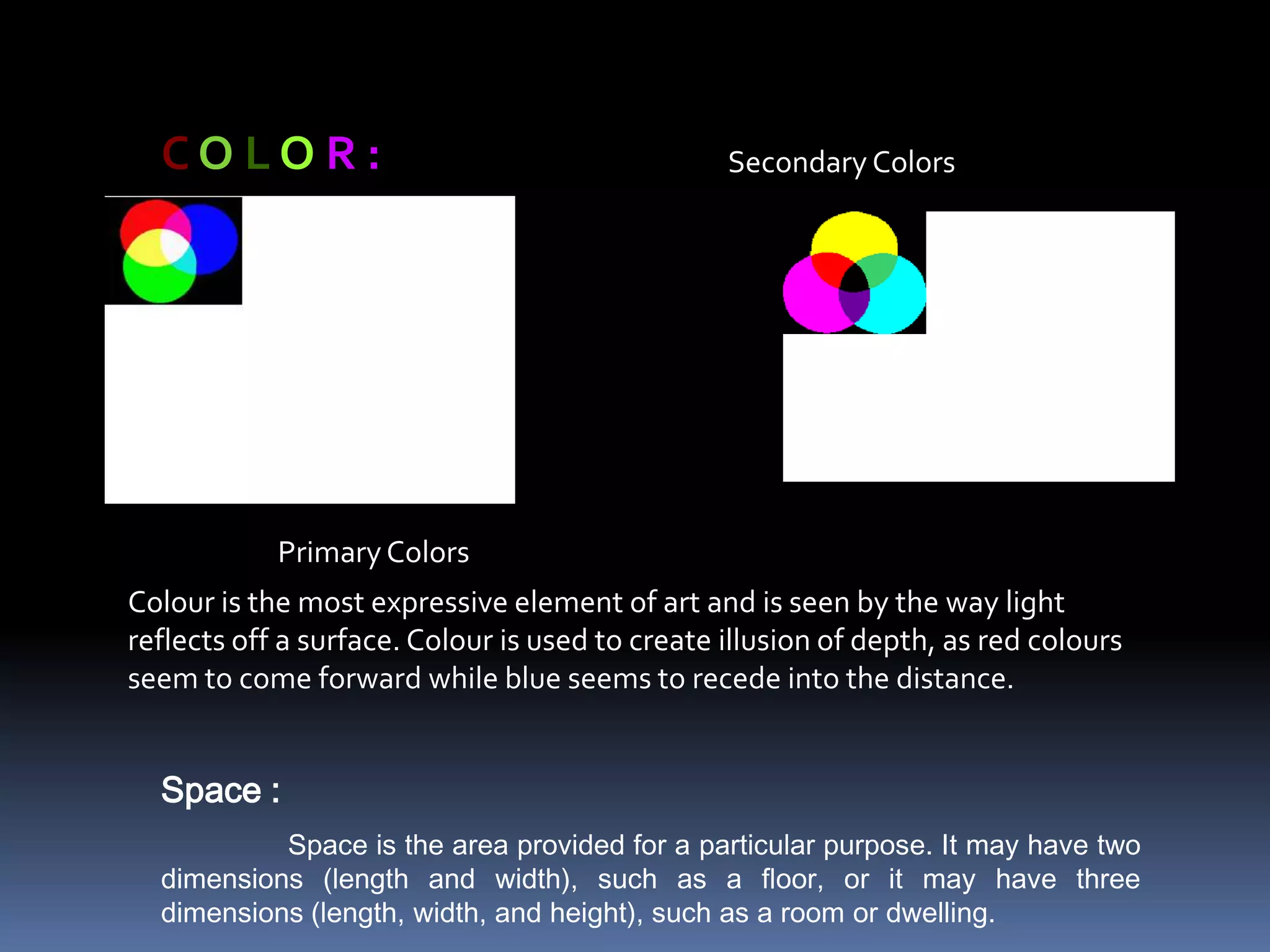
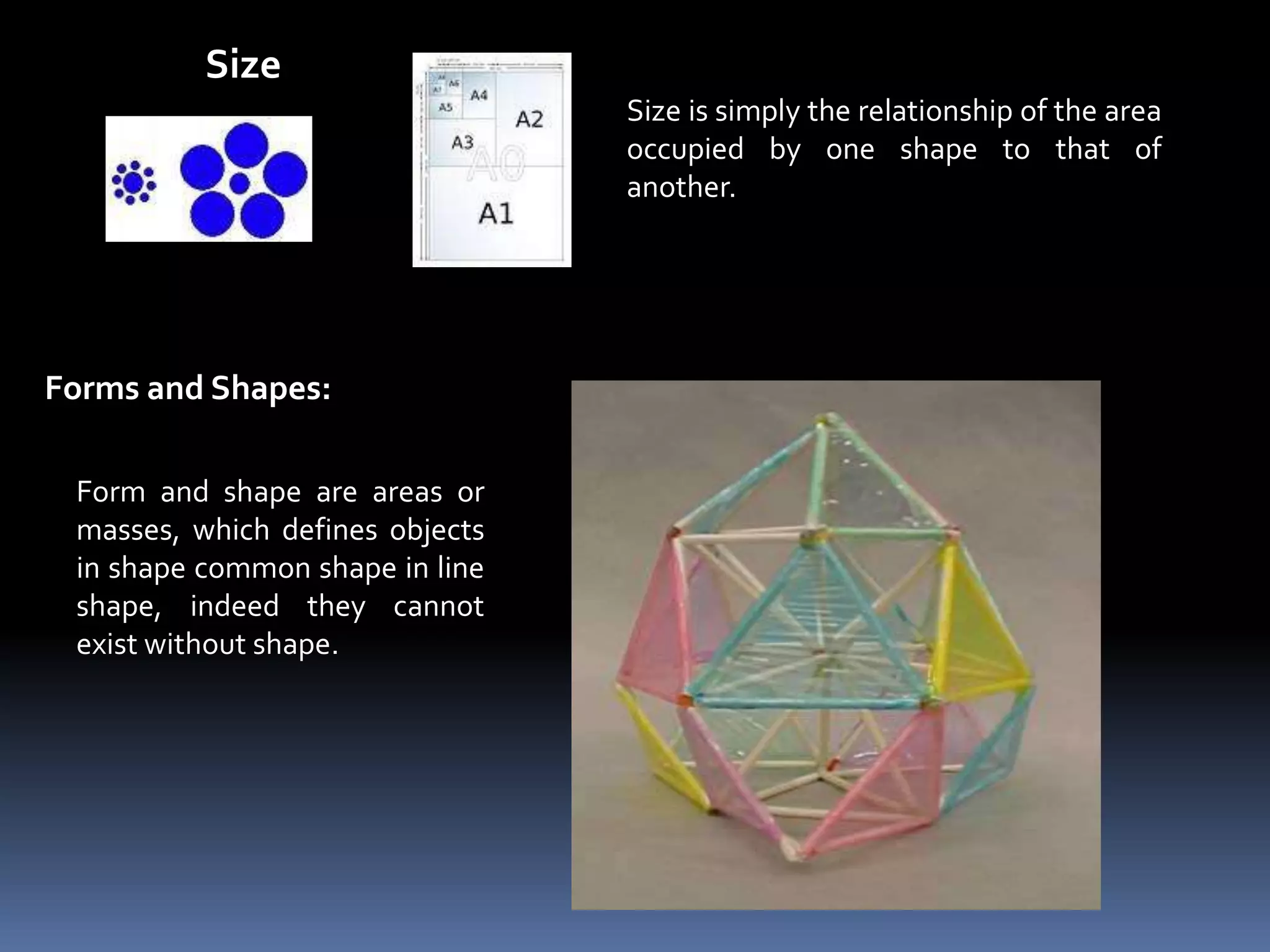
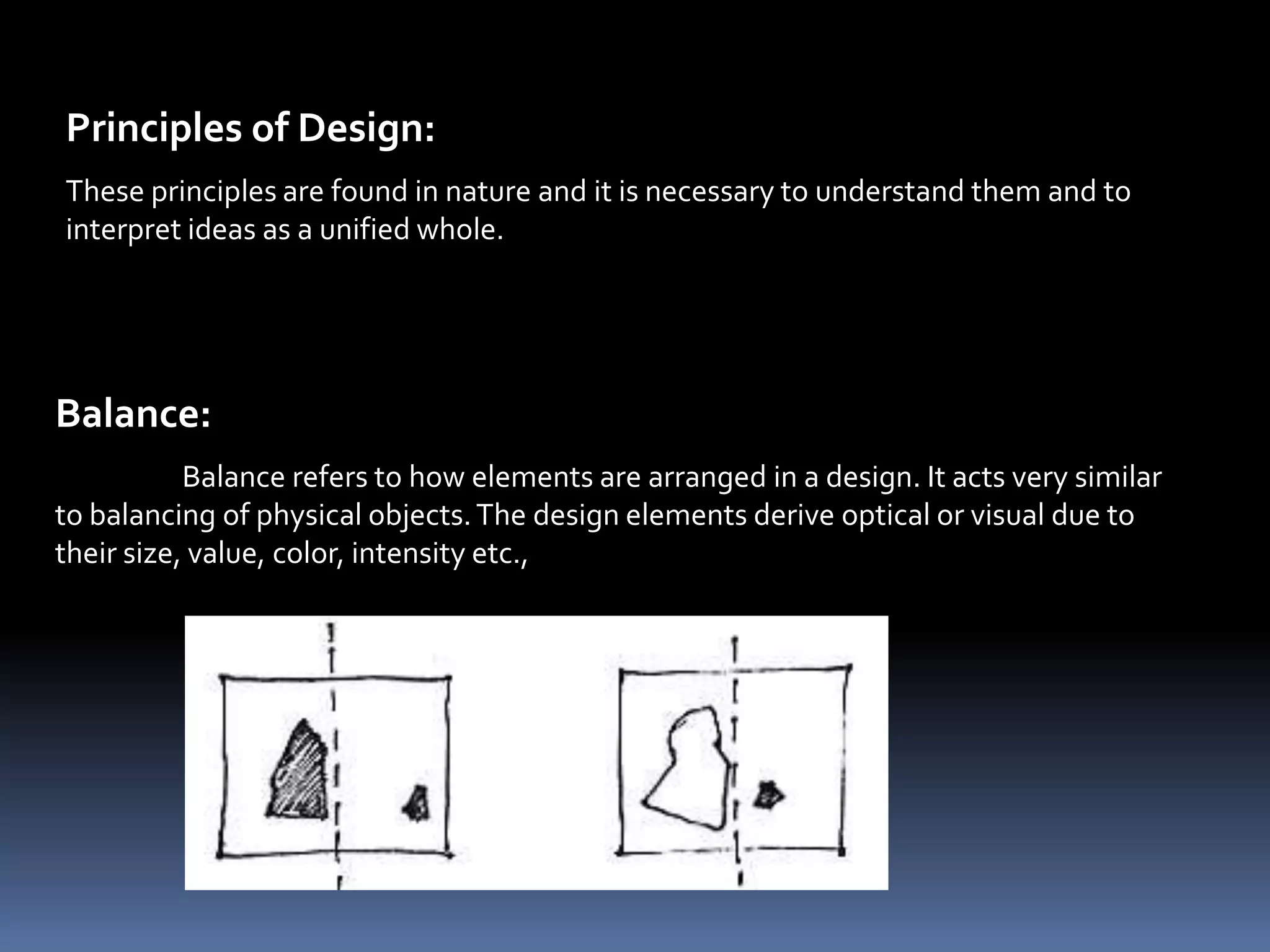
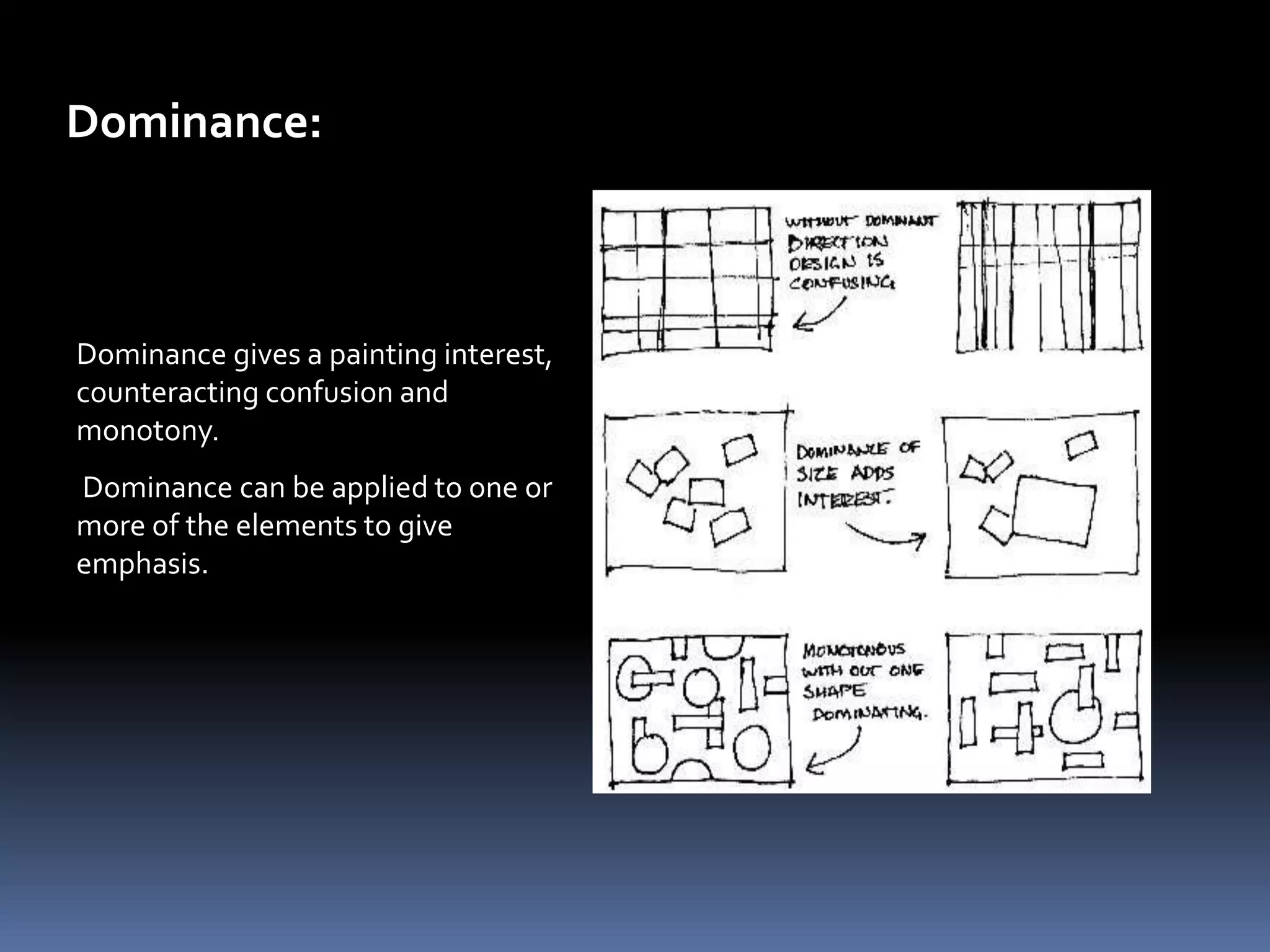
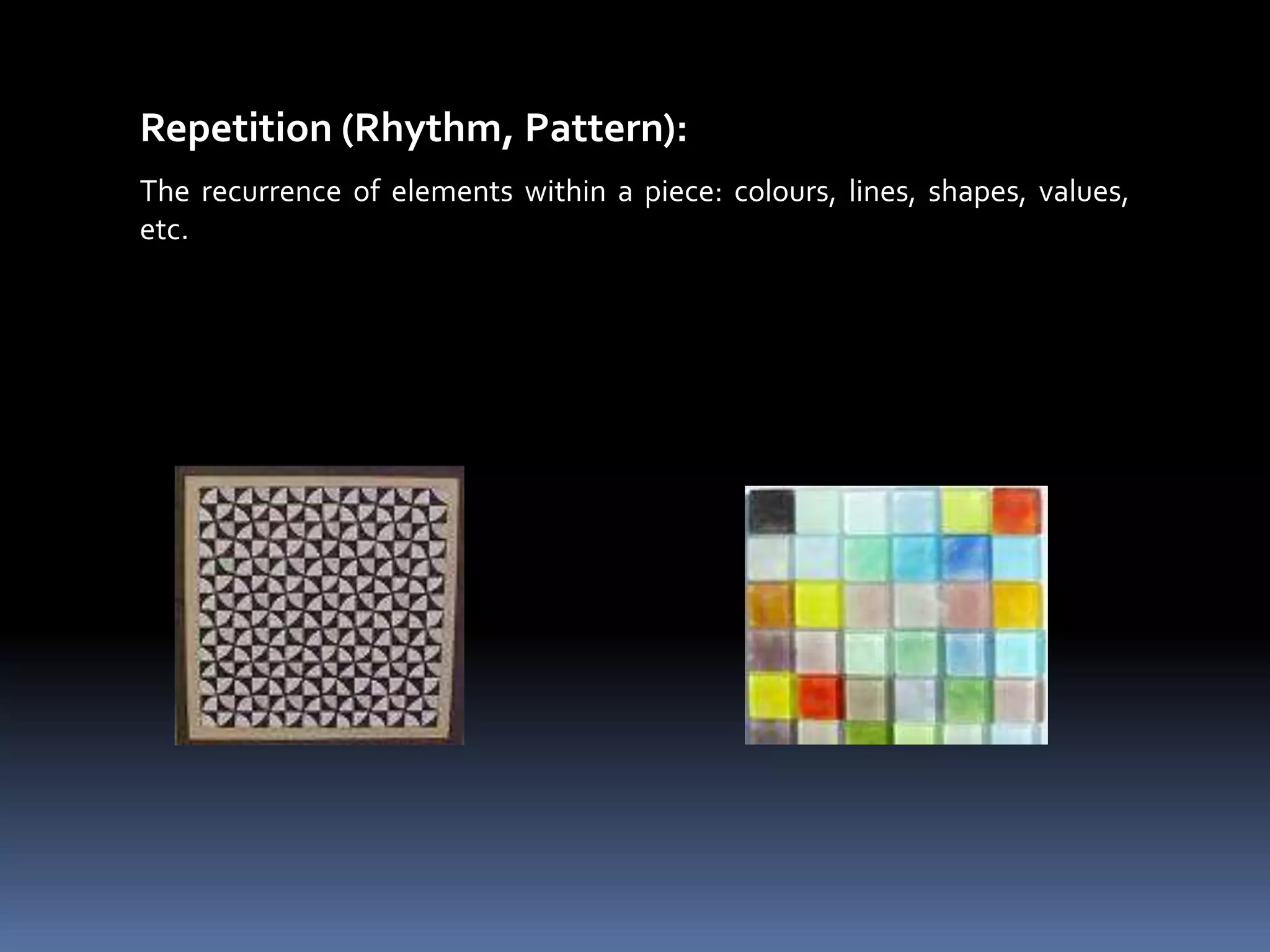
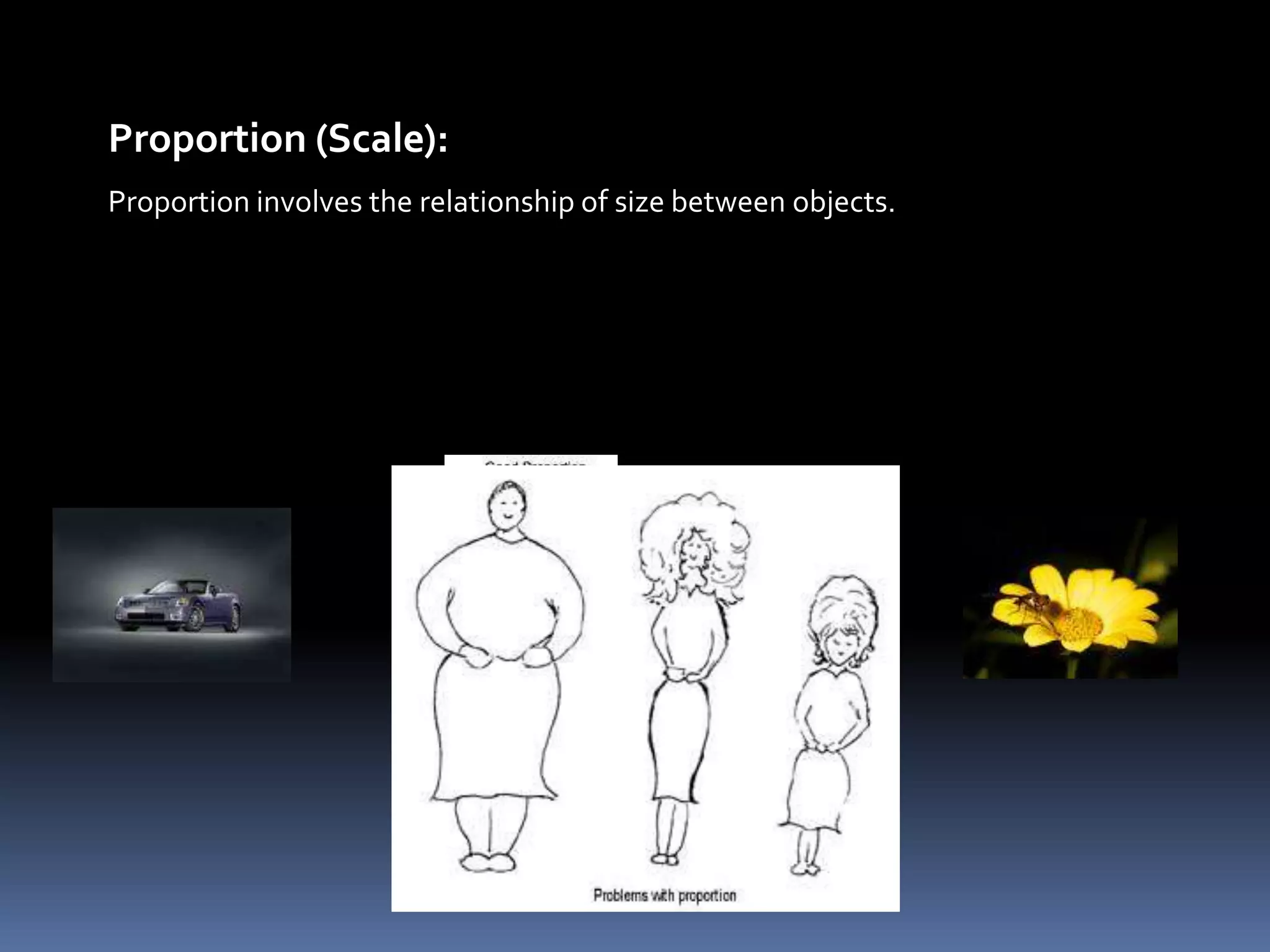
Design involves planning and organizing elements to create objects and systems. Key elements of design include line, color, space, texture, value, shape, type, direction, size, forms, and principles like balance, dominance, unity, harmony, contrast, repetition, variety, proportion, proximity, and gradation. Effective design is economical, customer-friendly, attractive, appealing, convincing, new, and technological. The design process includes analyzing needs, planning the design, organizing elements, and presenting the final design.