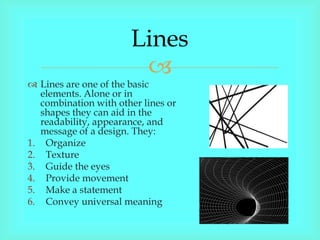
The document discusses key design elements including lines, shape, form, color, texture, depth, light, direction, mass, tone, value, space, balance, emphasis, proportion, repetition, unity, contrast, harmony, proximity, and variety. It describes how each element can be used alone or combined with other elements to achieve different effects in visual design works.