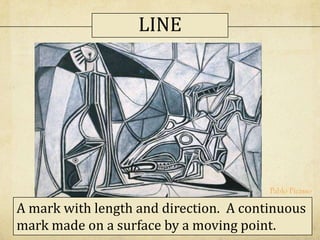
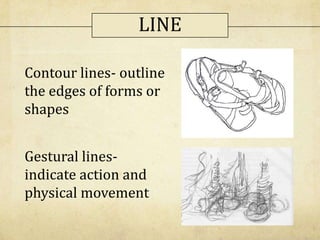
This document discusses the elements of art and principles of design. It defines the seven elements of art as line, color, value, shape, form, space, and texture. It then defines and provides examples for each element. The document also defines the seven principles of design as balance, emphasis, contrast, movement and rhythm, unity, variety, and proportion. It provides definitions and examples for each principle. The purpose of the document is to provide information about the building blocks and organizational tools used in visual art to the reader.