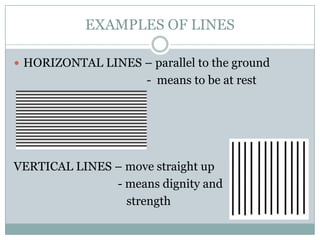
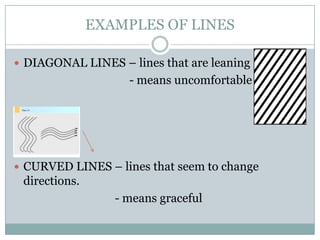
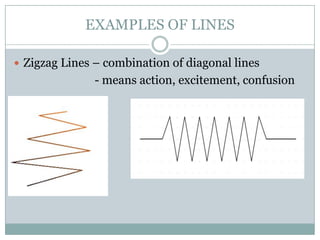
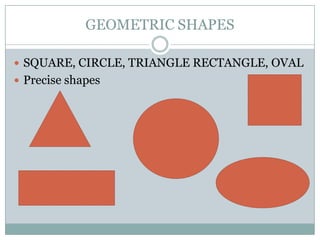
The document defines the key elements of art as lines, texture, form, space, color, and shape. It provides examples and descriptions of each element. Lines can be horizontal, vertical, diagonal, curved or zigzag. Texture can be tactile, artificial or visual. Form refers to 3D objects with height, width and depth. Space includes positive space of subjects and negative space around them. Color has properties of hue, value and intensity and can be primary, secondary or complementary. Shapes can be geometric or organic.