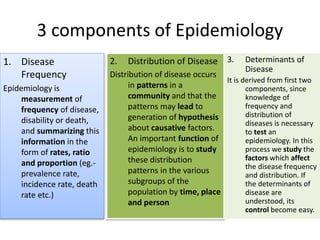
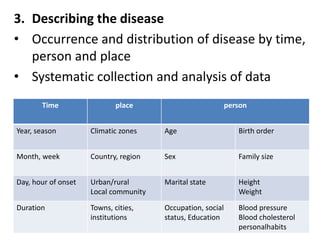
Epidemiology is the study of the distribution and determinants of health and disease in populations. It has three main aims: to describe disease distribution and frequency, identify risk factors, and provide data to plan, implement, and evaluate disease prevention and control services. Descriptive epidemiology involves observing disease distribution by time, place, and person to measure disease frequency and form hypotheses about potential causes. Key aspects include defining the population and disease, systematically collecting data on time trends, geographic variations, and characteristics of individuals with the disease. This allows comparison to other populations and formulation of testable hypotheses about disease etiology.