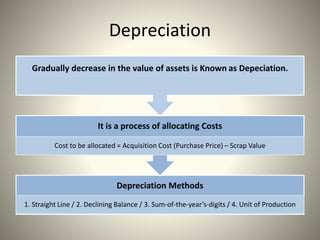
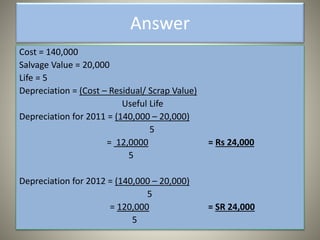
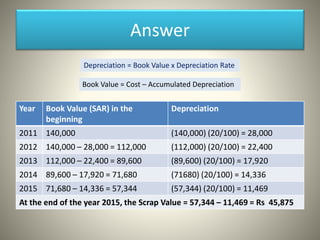
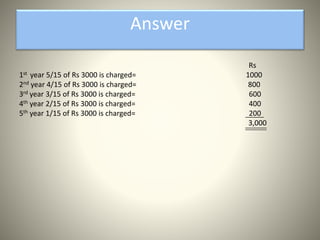
This document discusses various depreciation methods including straight line, declining balance, sum-of-the-years digits, unit of production, depletion, and machine hour methods. Depreciation is the process of allocating the cost of an asset over its useful life. It is calculated by taking the original cost minus the scrap value and dividing by the number of years or other relevant unit of the asset's life. Examples are provided for calculating depreciation under different methods.