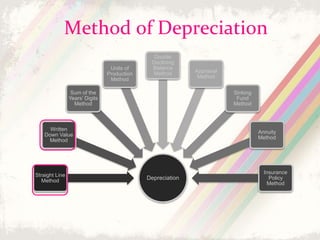
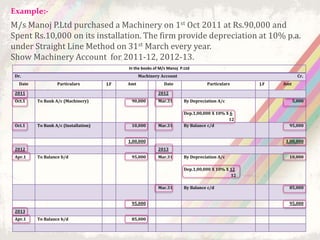
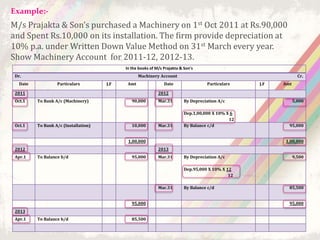
This document discusses depreciation, which refers to the reduction in value of fixed assets over time due to usage and age. It defines depreciation and lists assets that are depreciated, such as machinery, furniture, vehicles, and electronics used for business. The objectives and causes of depreciation are outlined. Several depreciation methods are presented, including the straight-line method and written down value method. Examples are provided to illustrate how to calculate depreciation using each method. The advantages and disadvantages of the straight-line and written down value methods are also summarized.