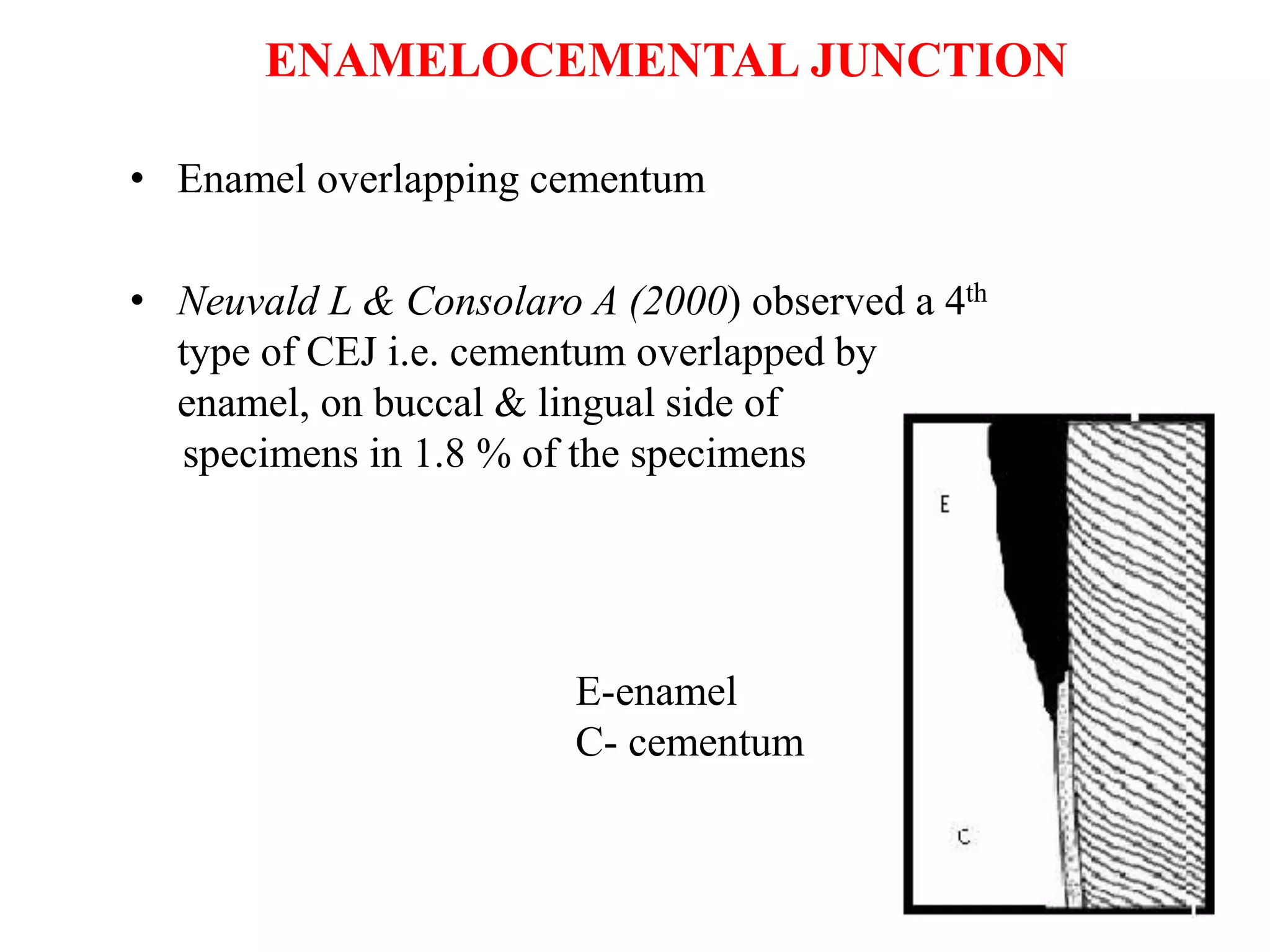
Cementum is the calcified tissue covering the roots of teeth. It has both acellular and cellular varieties. Acellular cementum lacks cementocytes and is laid down slowly with closely spaced incremental lines. Cellular cementum contains cementocytes within lacunae and canaliculi and is deposited more rapidly with wider spaced lines. Cementum is produced by cementoblasts, which are derived from the dental follicle or Hertwig's epithelial root sheath. Cementoblasts secrete cementum, while cementocytes are embedded within it and cementoclasts resorb it. Cementum provides anchorage for periodontal ligament fibers and adapts the tooth for function.