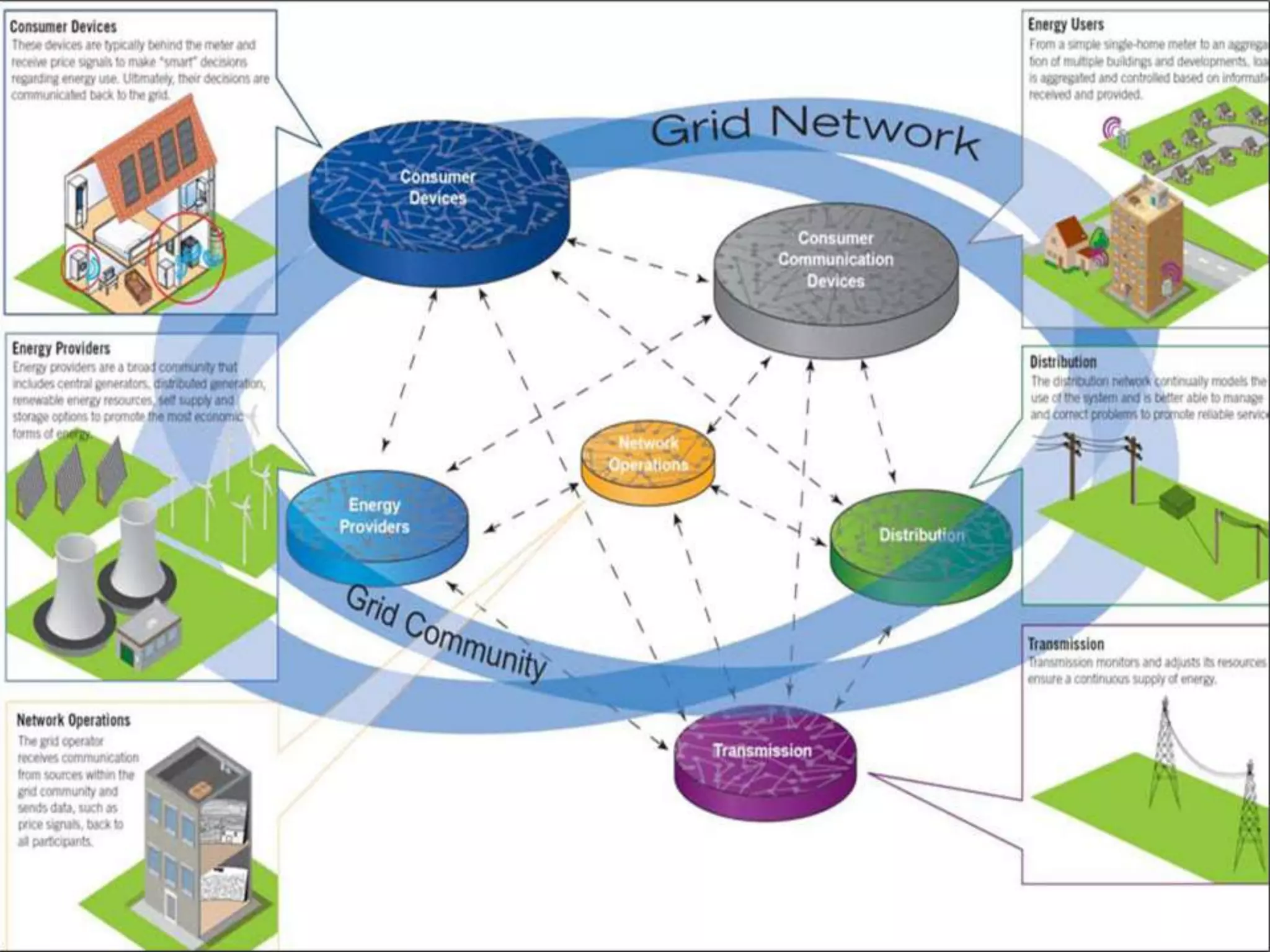
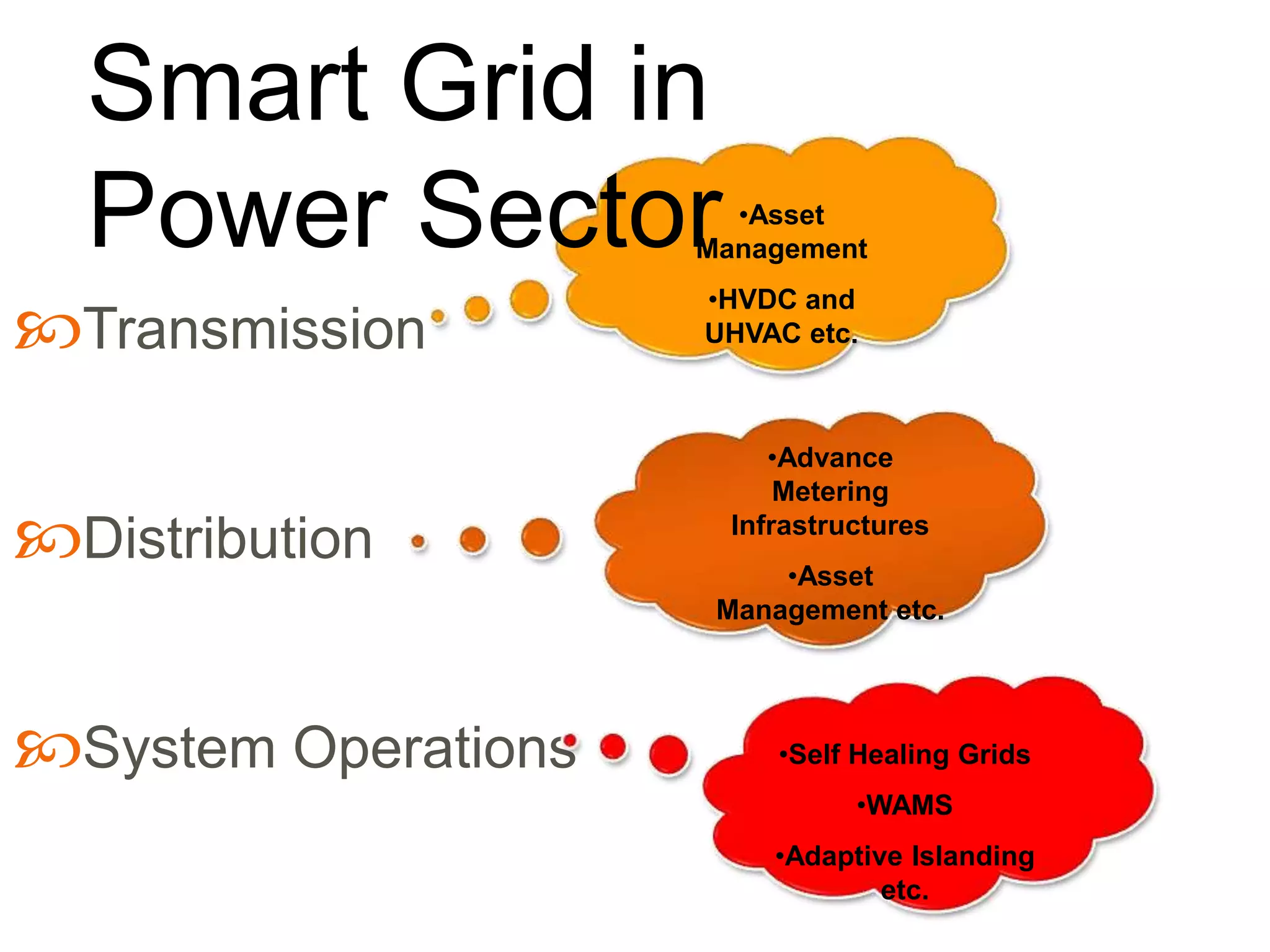
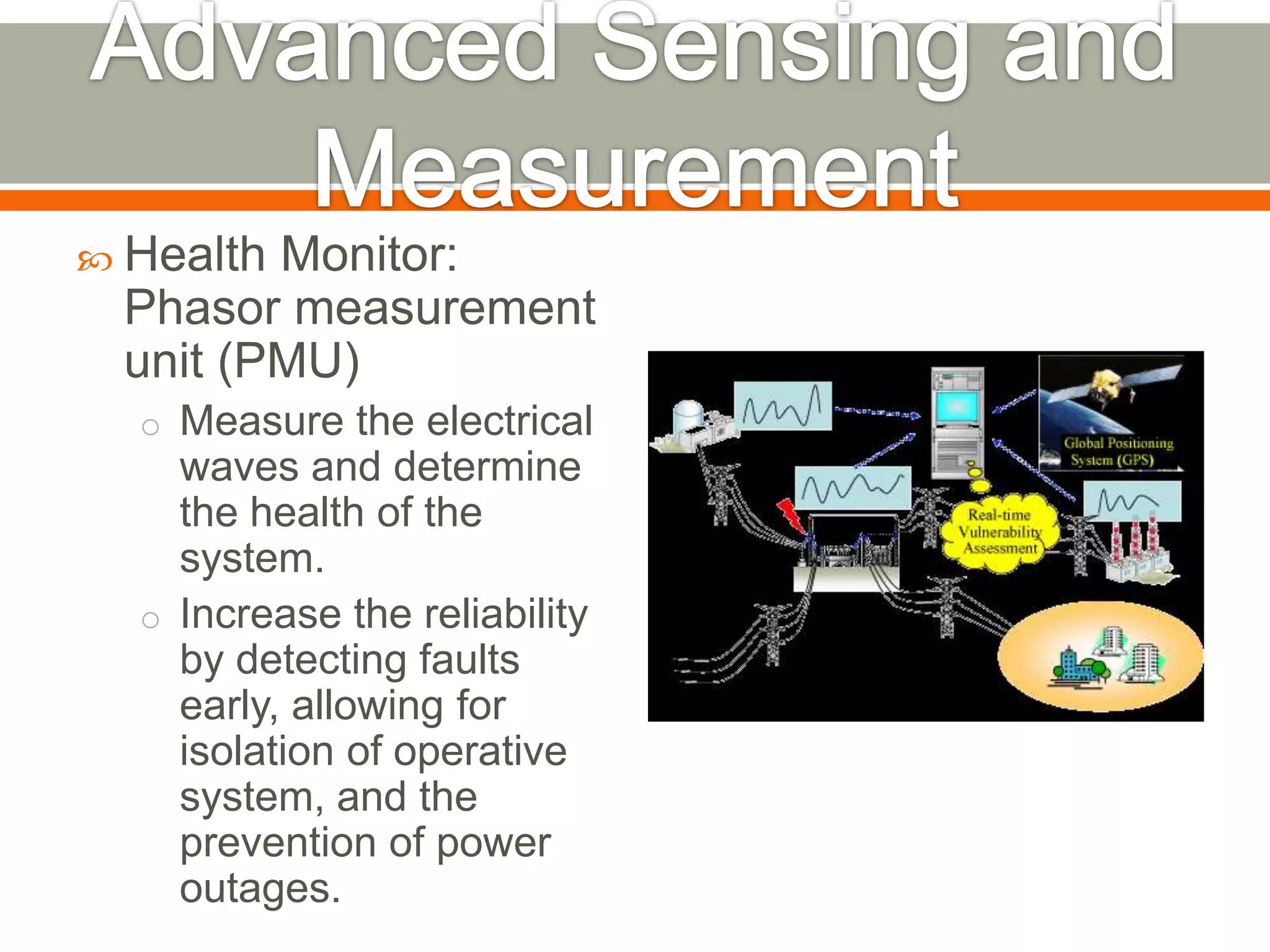
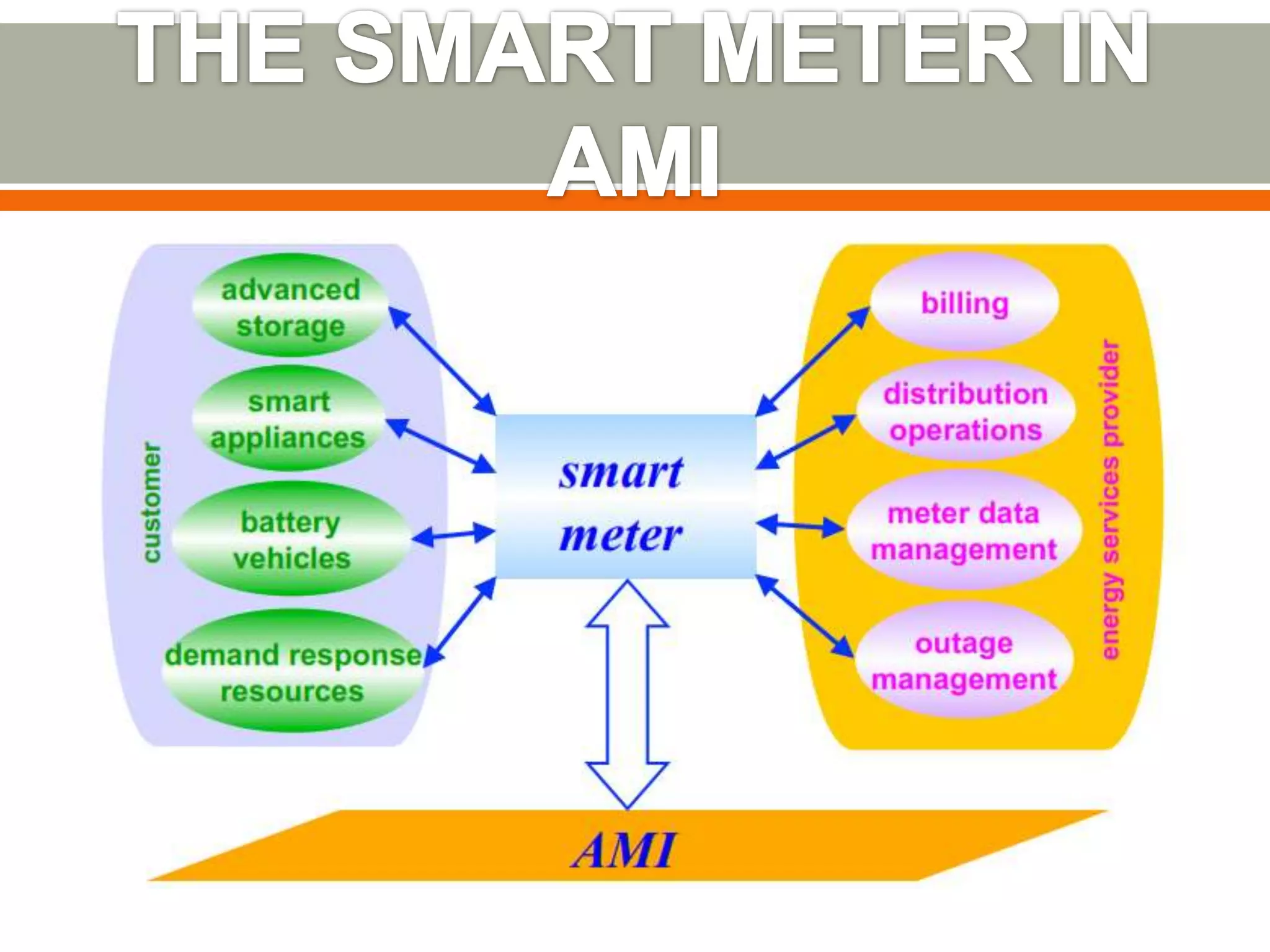
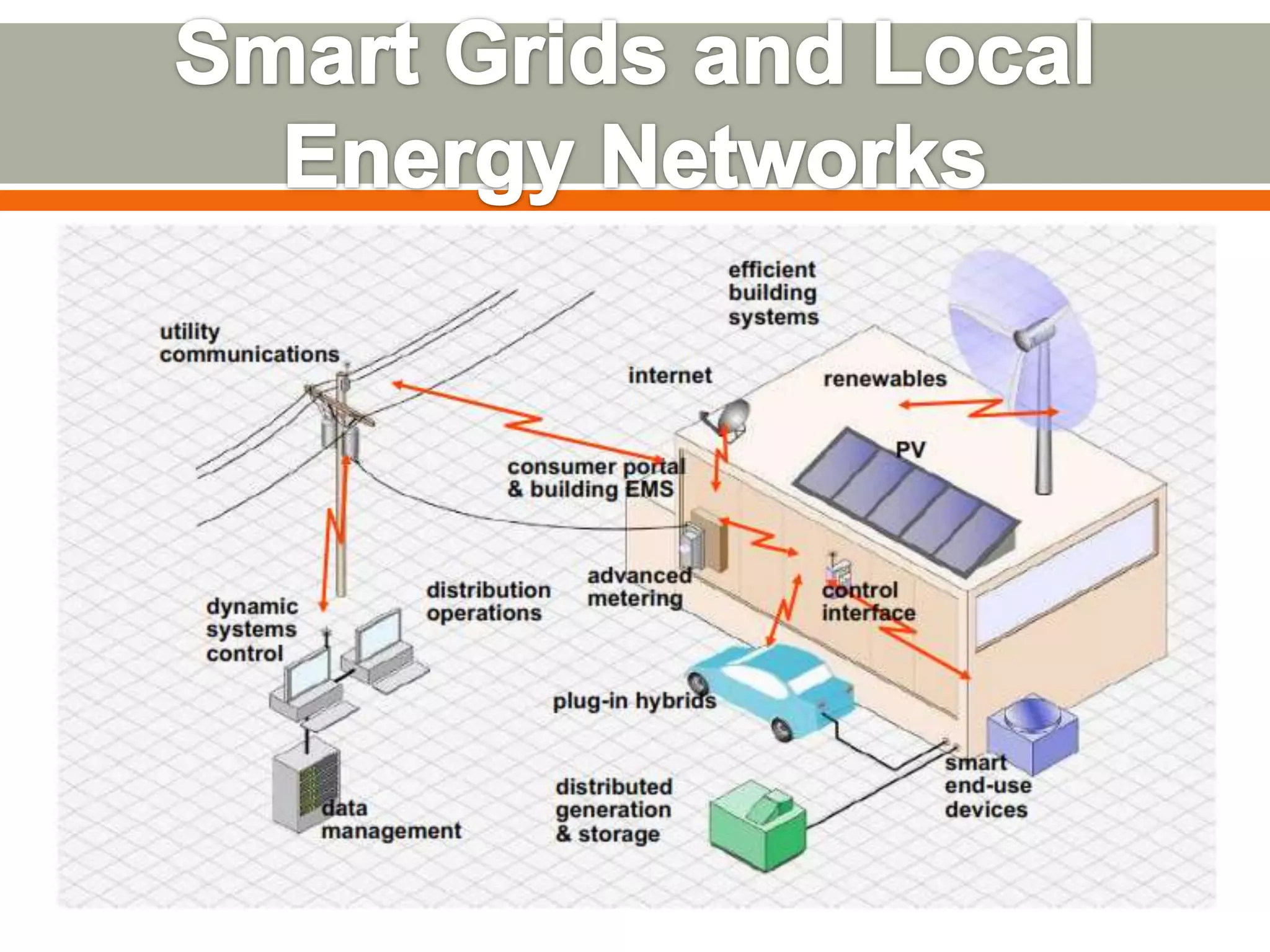
This document discusses smart grids and the role of advanced metering infrastructure in India. It notes that India has one of the weakest electrical grids in the world with high transmission losses. A smart grid uses communication and information technologies to better manage electricity distribution and demand. Advanced metering infrastructure is a key component, allowing two-way communication between utilities and customers to provide energy usage data and enable demand response programs. This can help improve grid reliability and efficiency while empowering consumers.