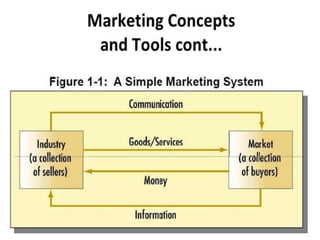
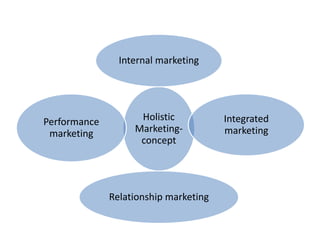
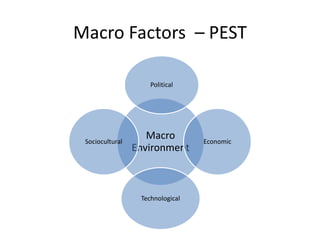
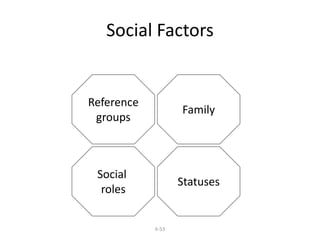
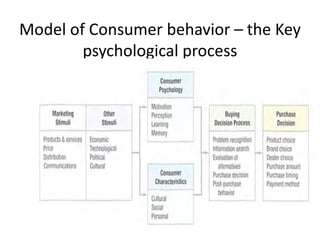
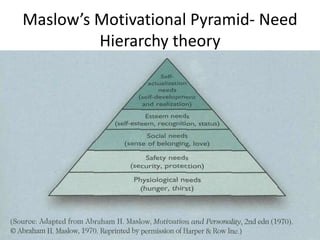
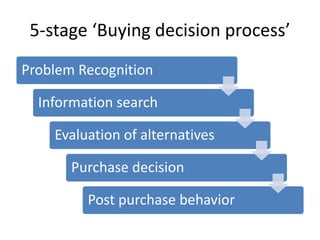
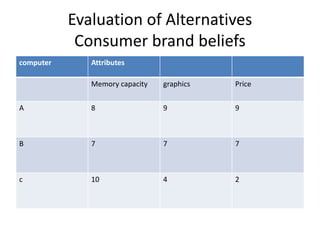
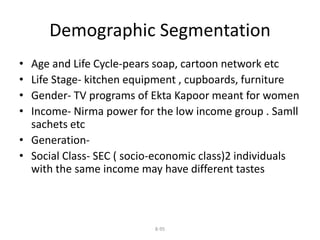
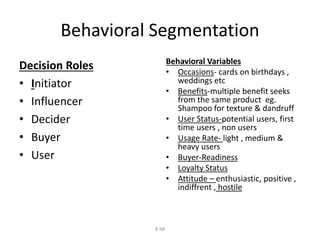
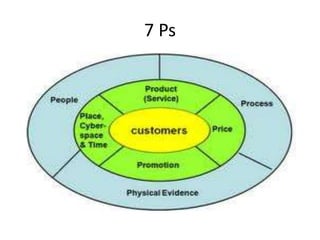
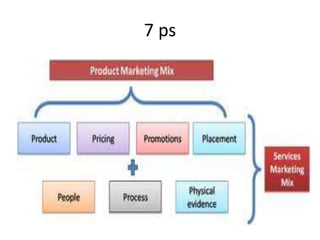
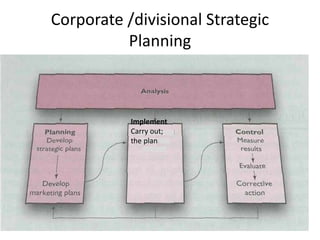
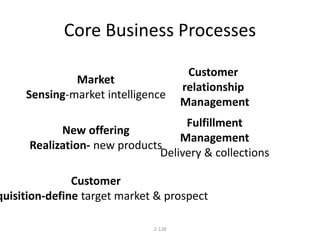
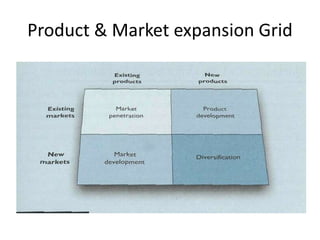
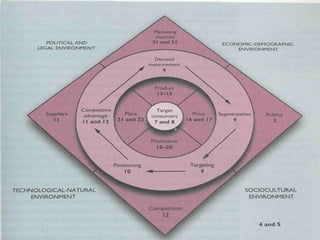
Marketing involves identifying customer needs and wants, developing products and services to meet them, and promoting and distributing those offerings. It is a process of creating value for customers to build profitable relationships. Effective marketing requires understanding factors like customer behavior, competitors, and the broader business environment. The goal is to choose target markets and grow customer base through superior customer value and satisfaction.



![What is Marketing ? ….
It is a process by which
-one identifies the needs and wants of the people.
-one determines and creates a product/service to meet the needs
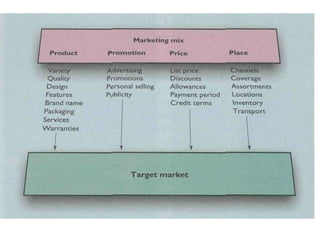
and wants. [PRODUCT]
-one determines a way of taking the product/service to the market
place. [PLACE]
-one determines the way of communicating the product to the
market place. [PROMOTIONS]
-one determines the value for the product.[PRICE].
-one determines the people, who have needs/ wants. [PEOPLE]
and then creating a transaction for exchanging the product for
a value.
and thus creating a satisfaction to the buyer's needs/wants.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/wadiamarketing1-141106004229-conversion-gate01/85/marketing-4-320.jpg)