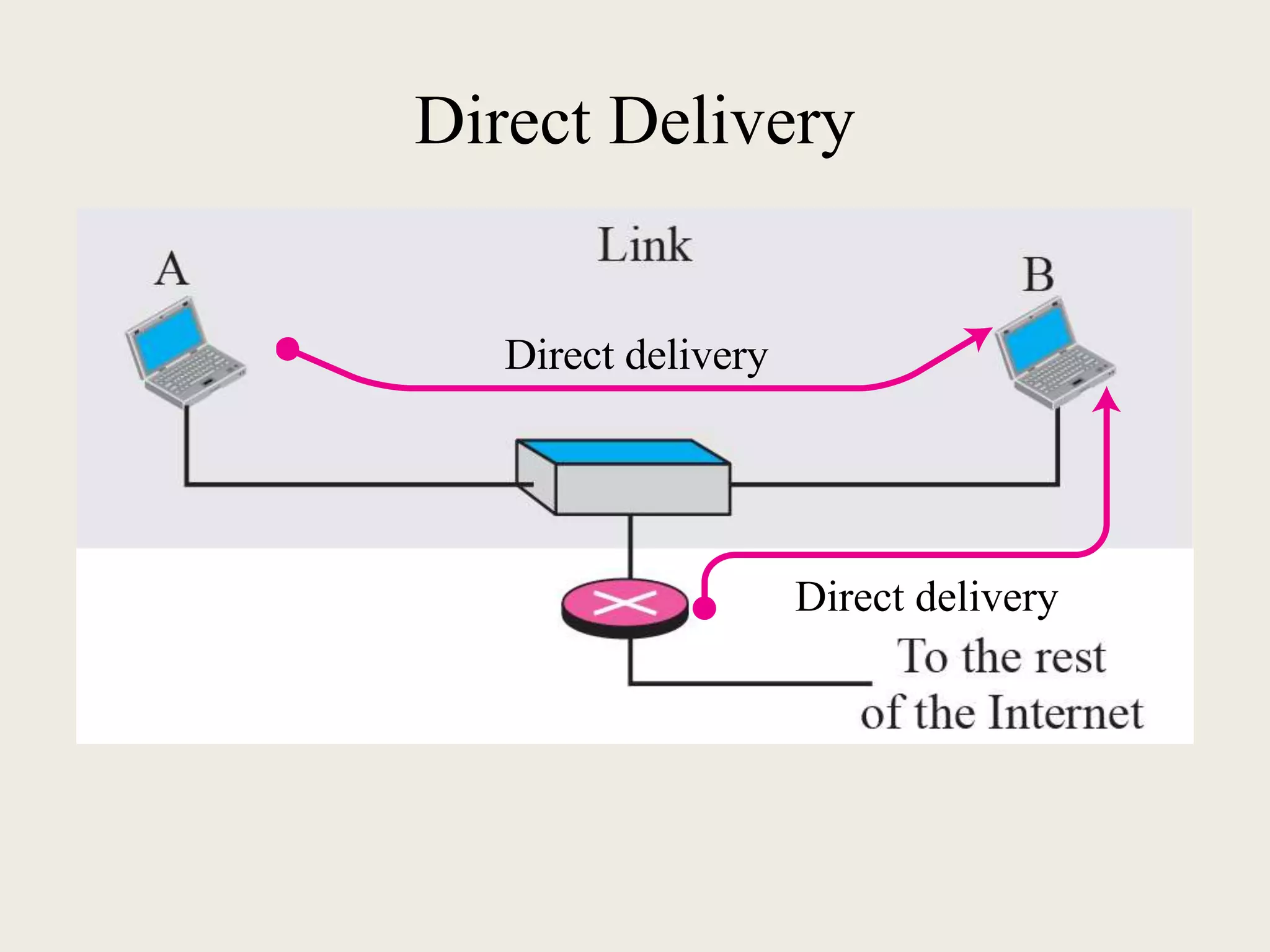
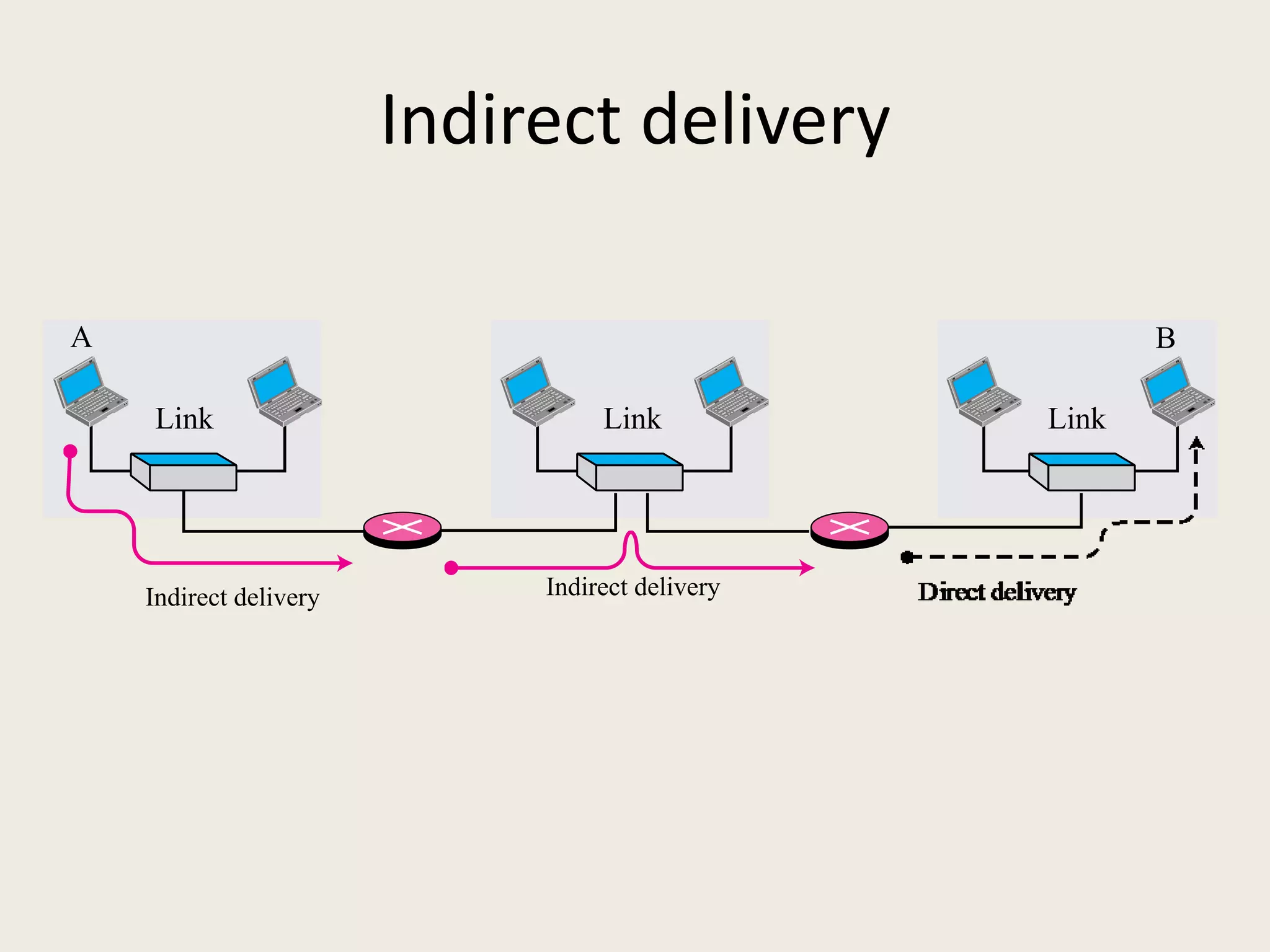
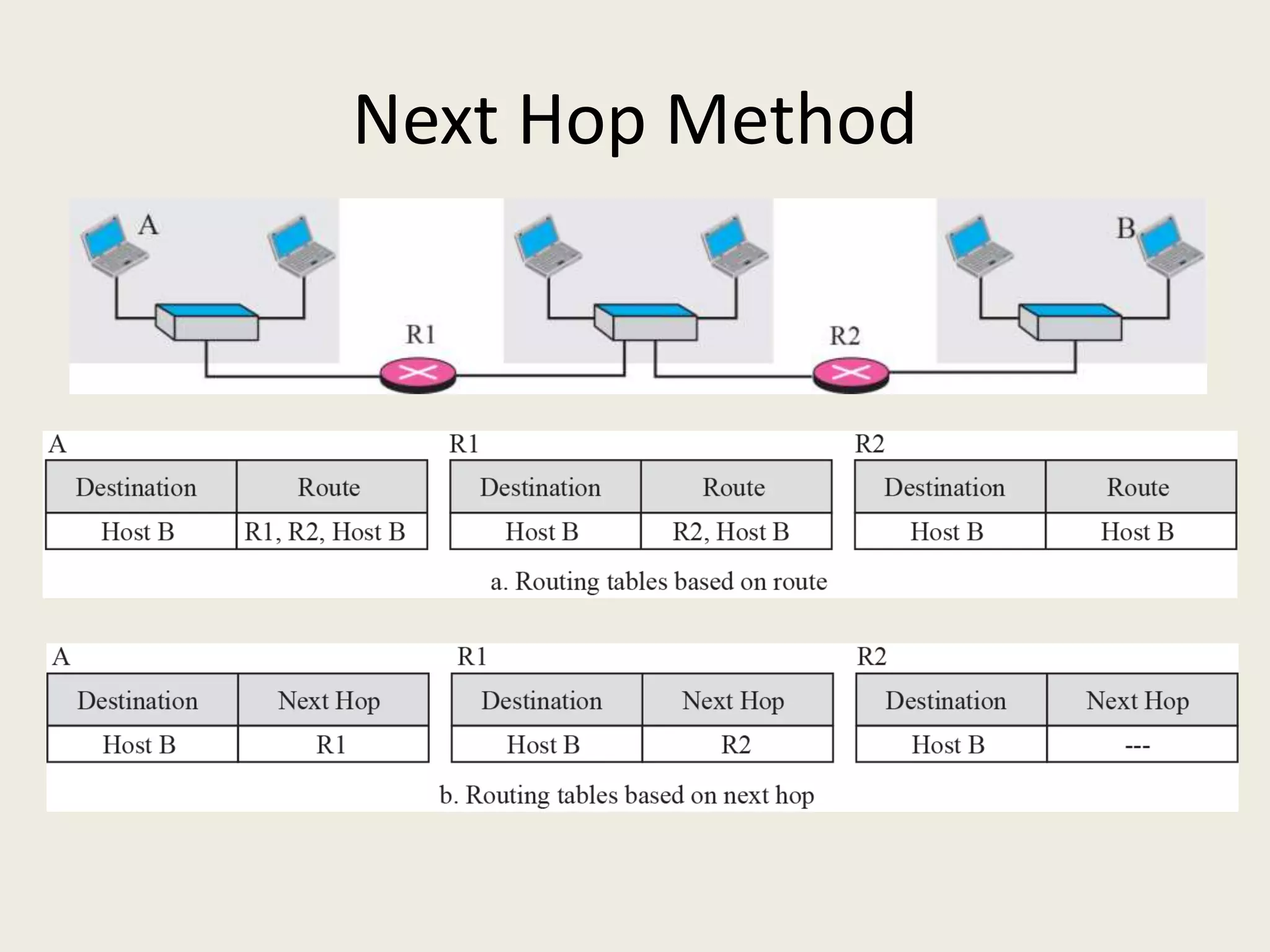
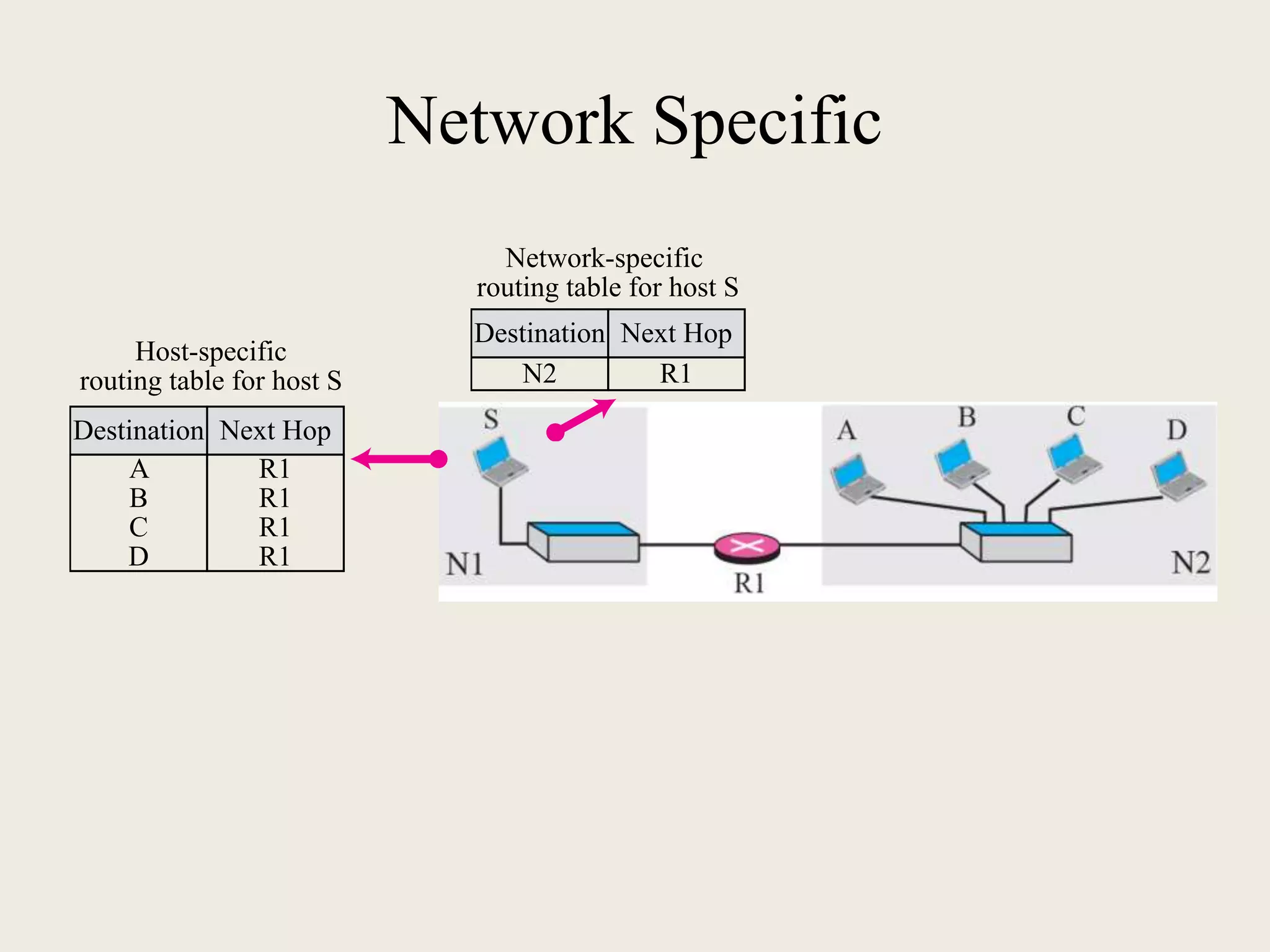
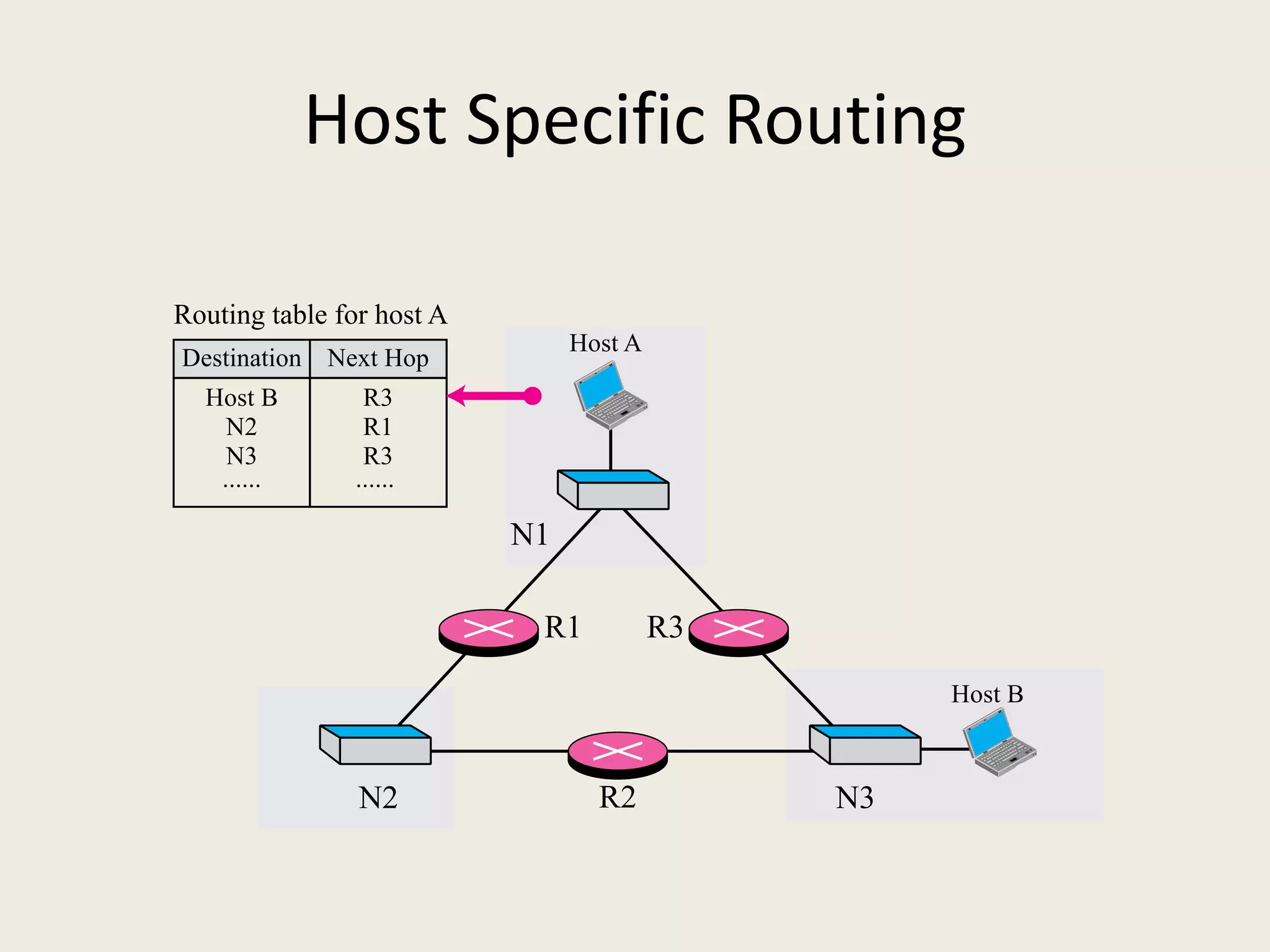
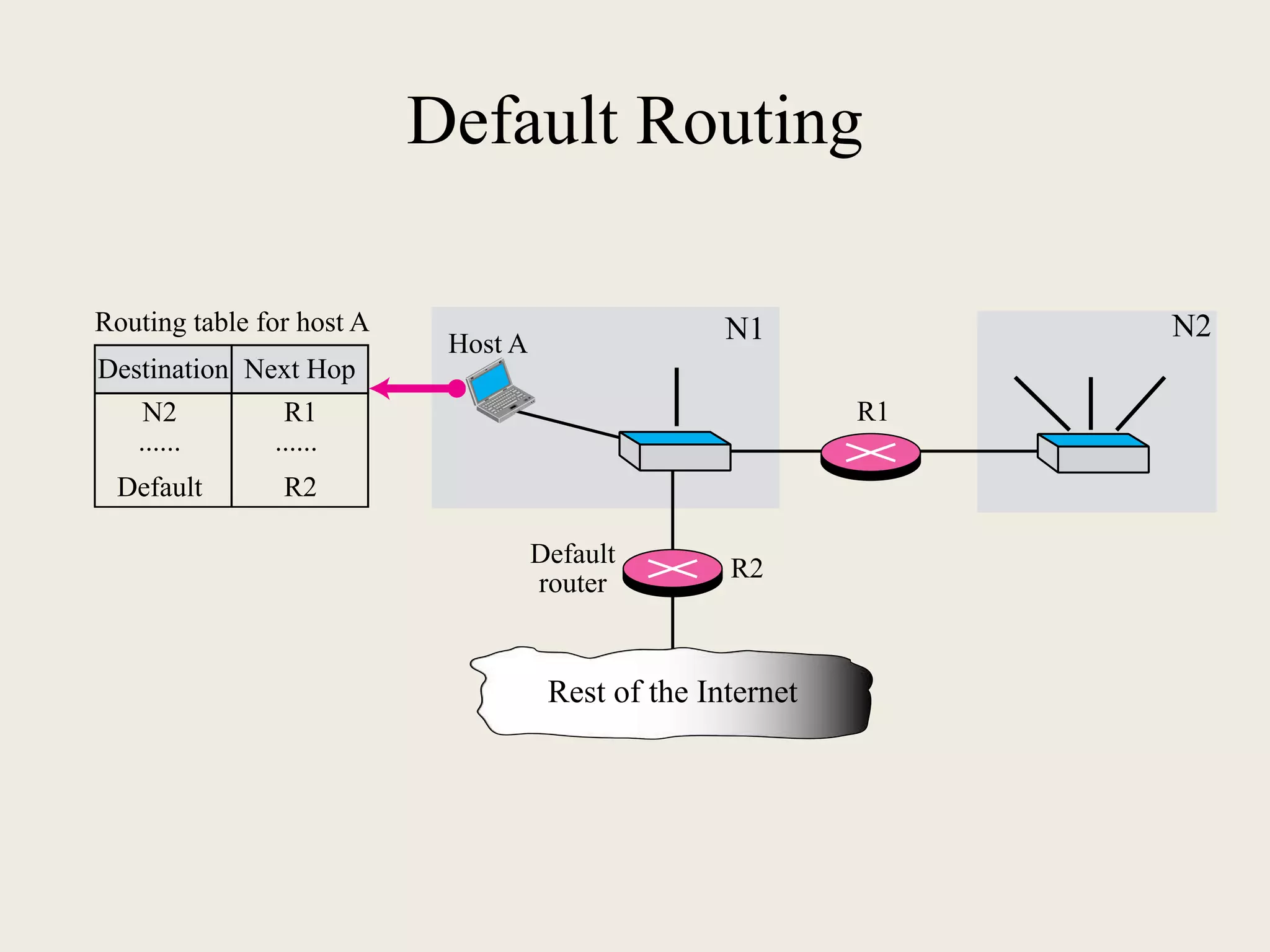
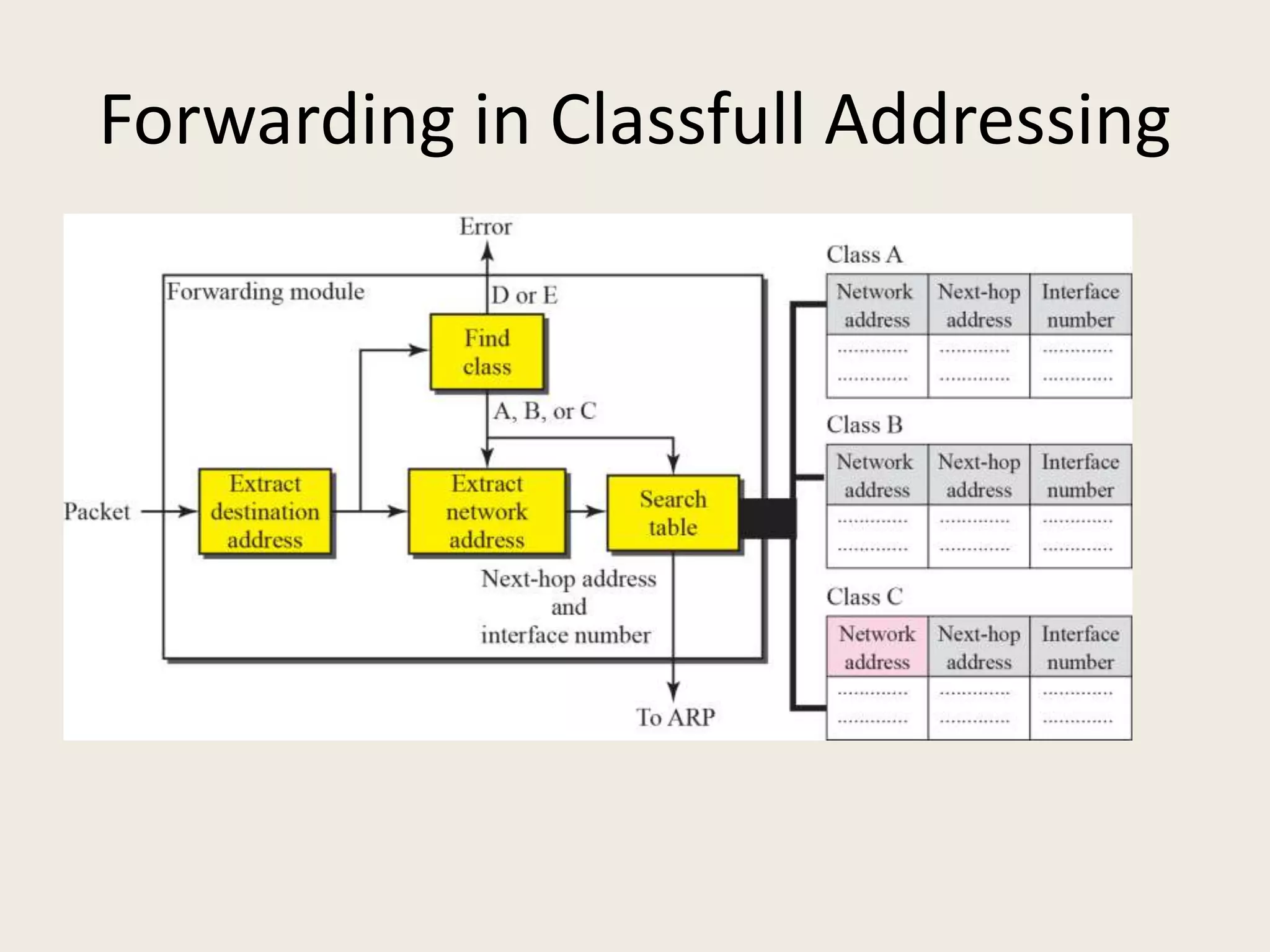
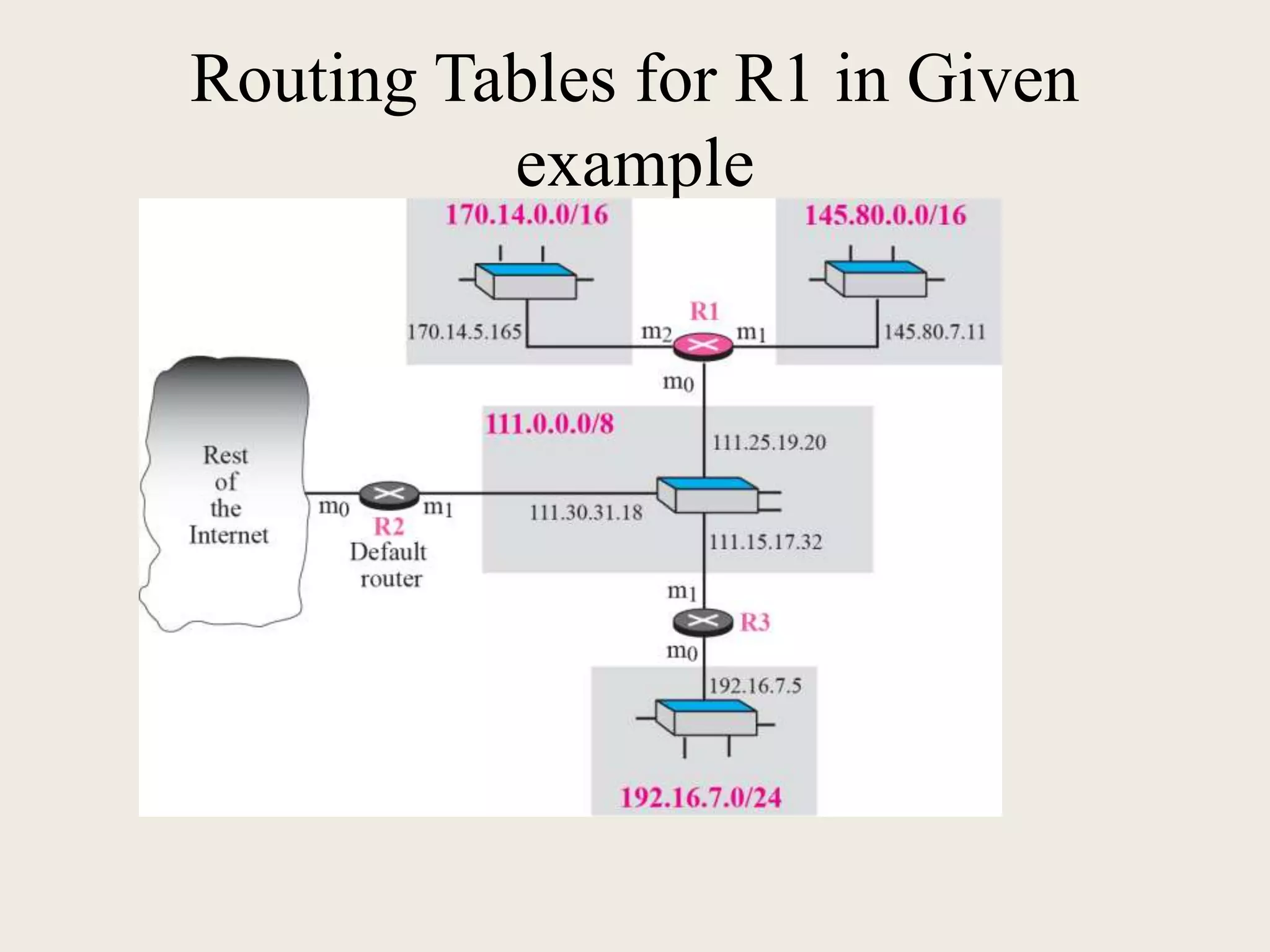
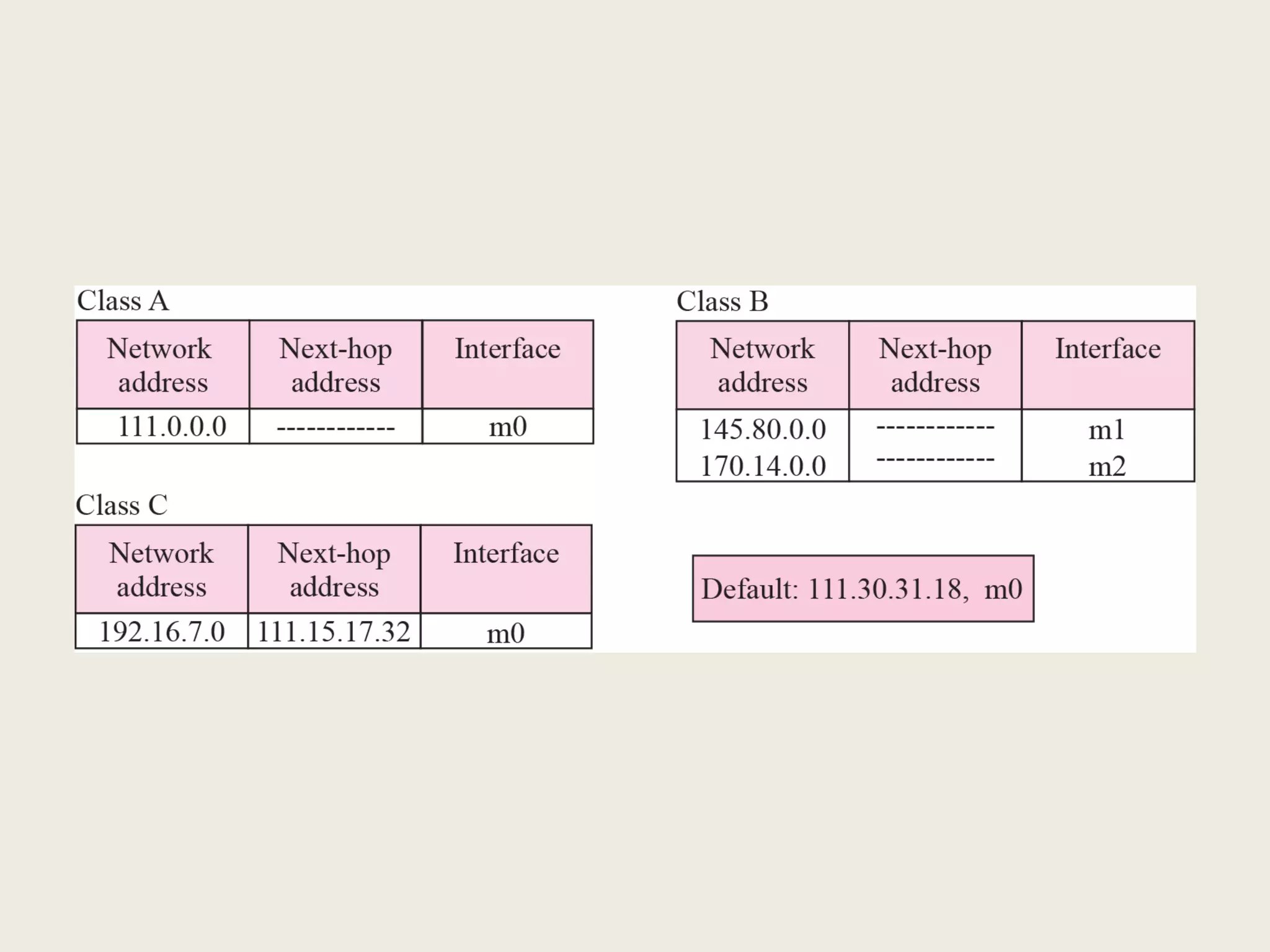
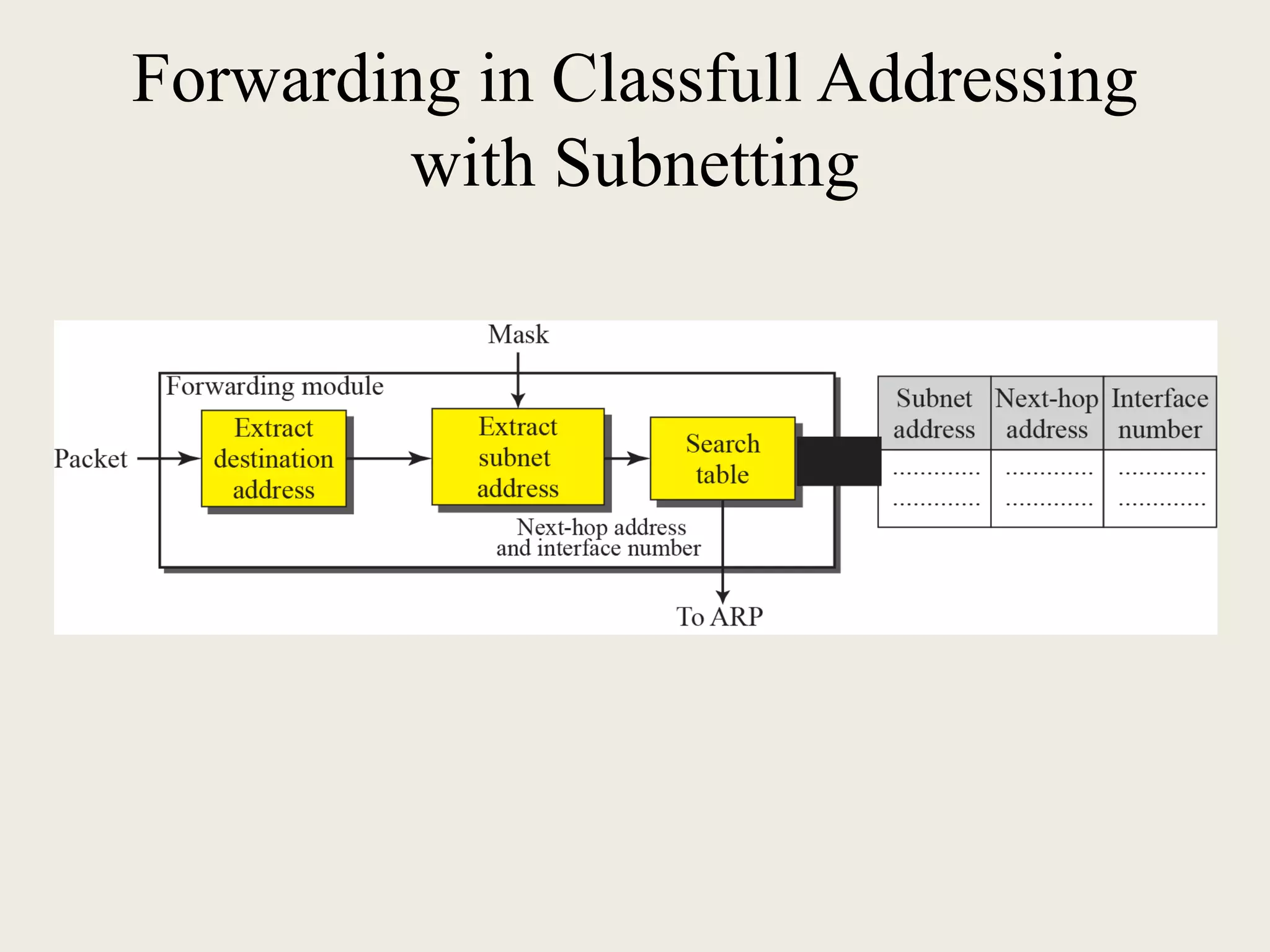
The document discusses the delivery and forwarding of IP packets, focusing on strategies of direct and indirect delivery. It highlights the role of forwarding to position packets towards their destination using routing tables based on destination addresses and labels. The example provided explains packet forwarding using classful addressing and subnetting within the context of a network routing table.