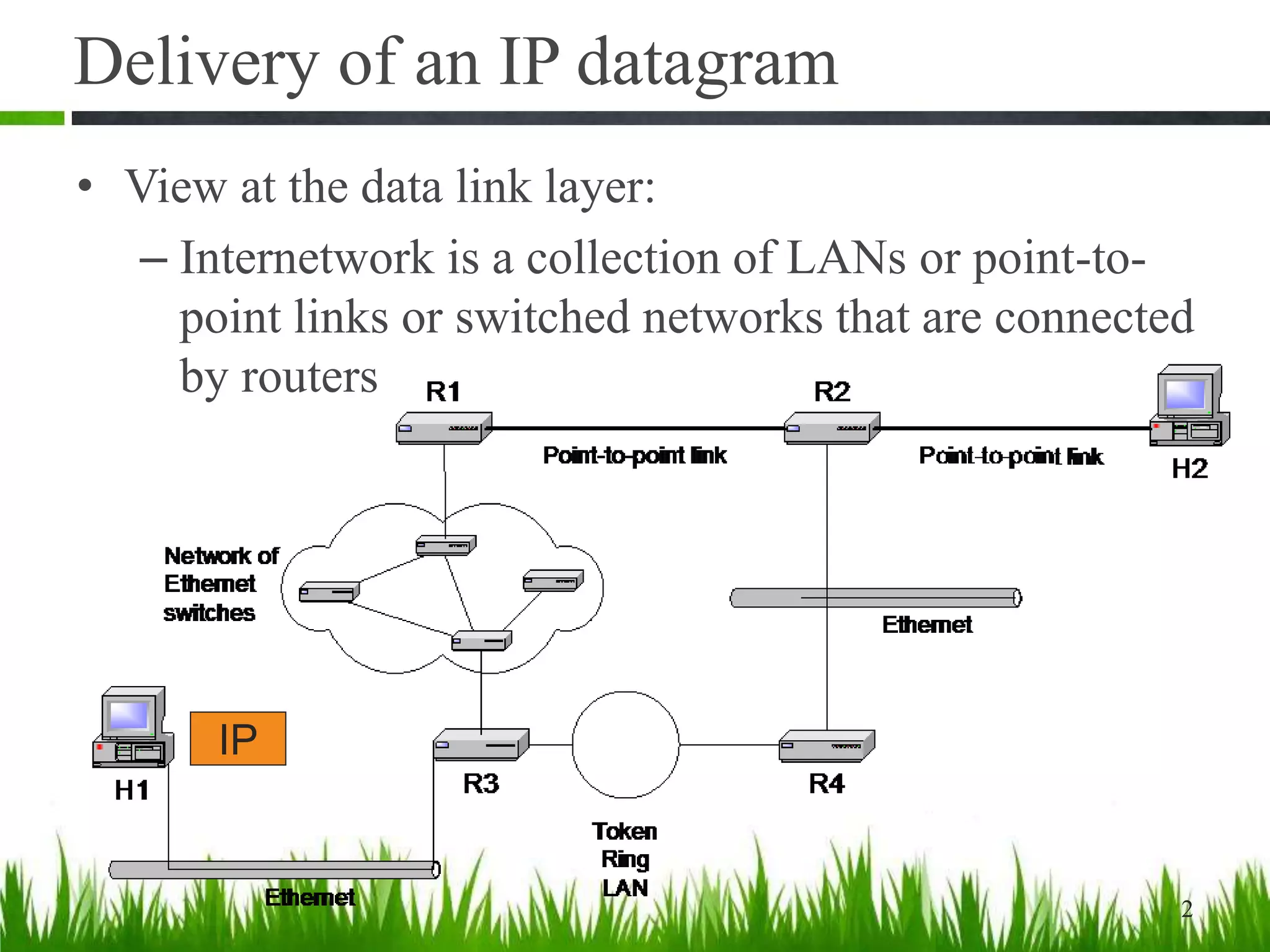
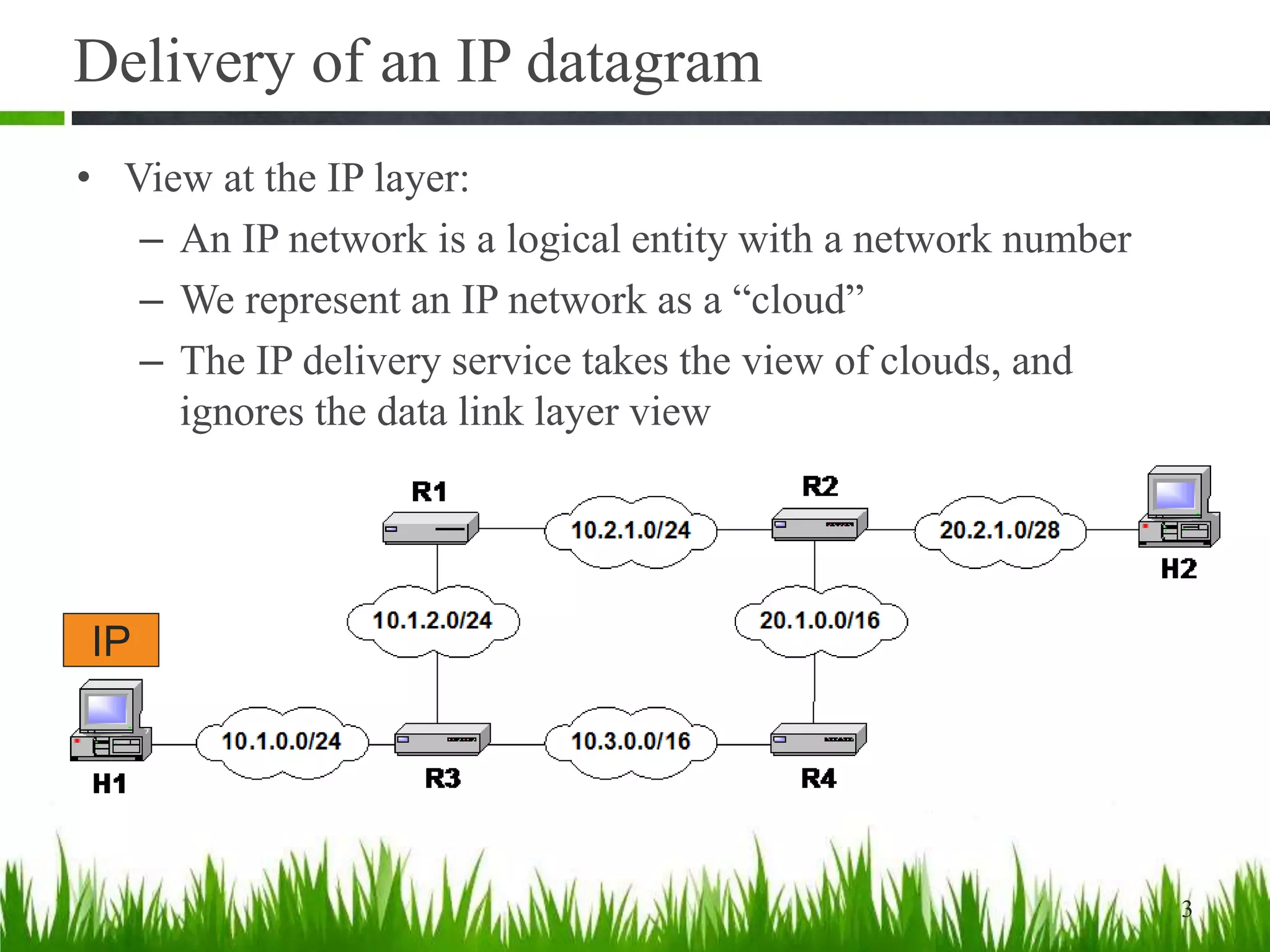
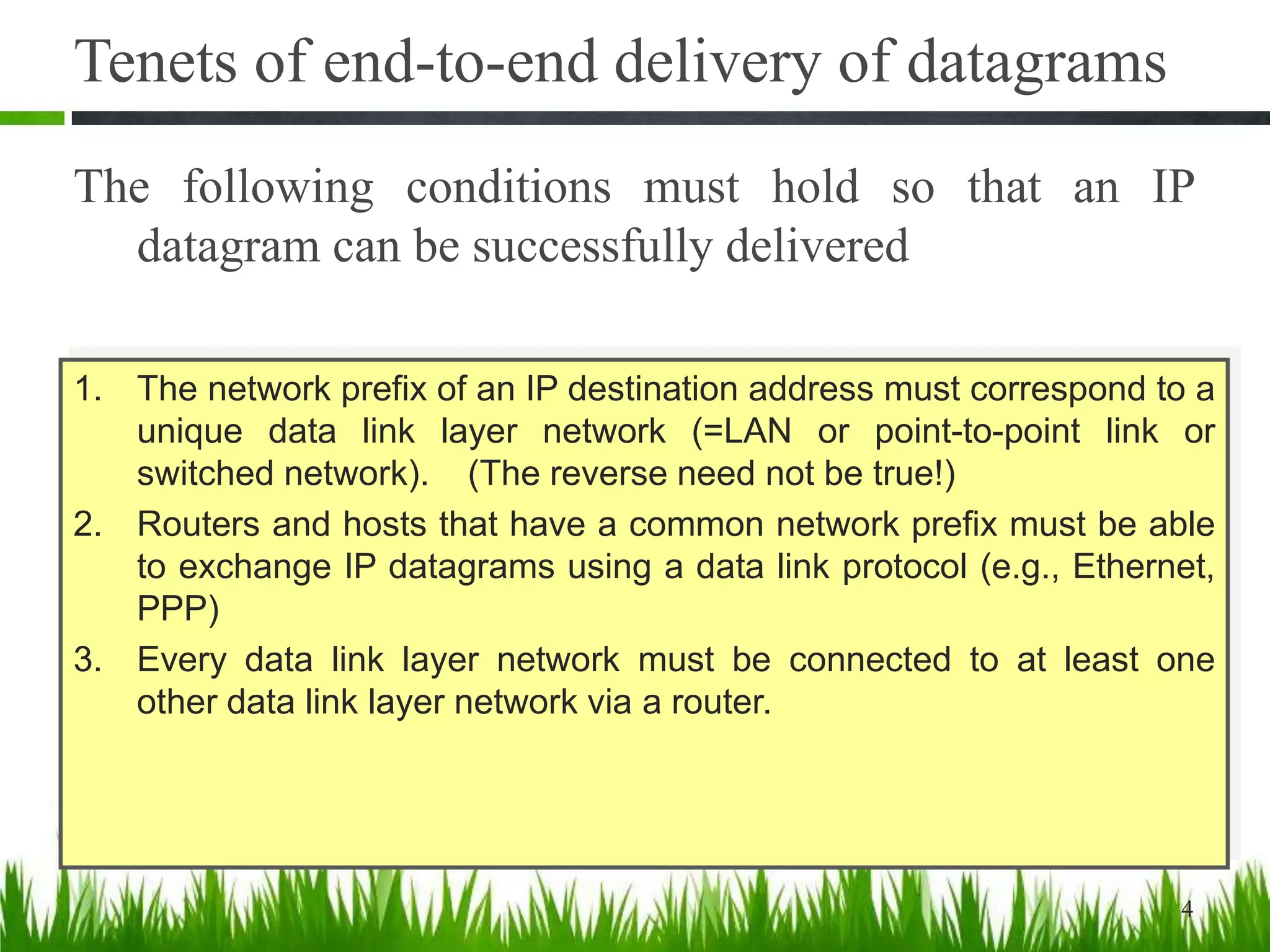
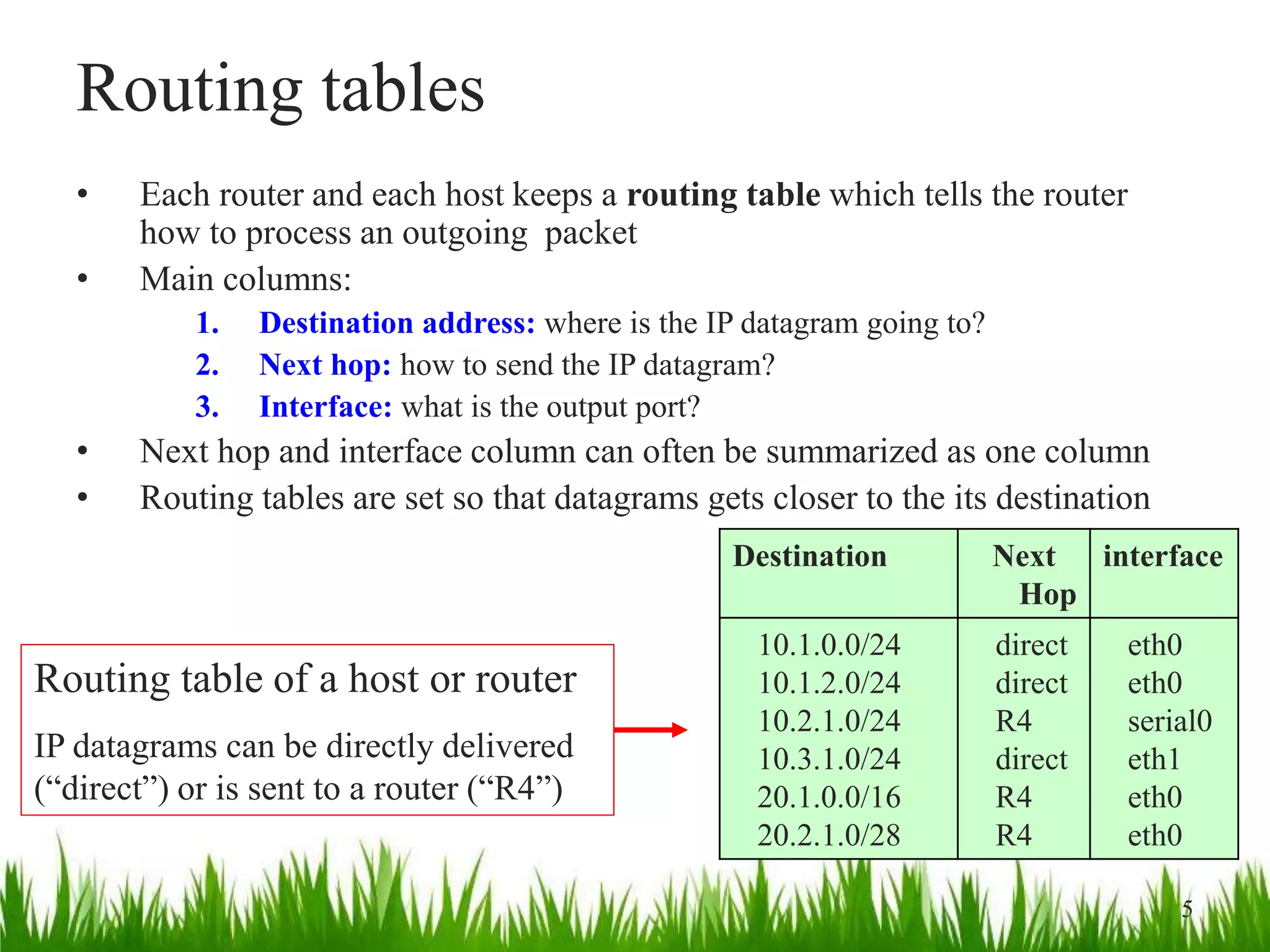
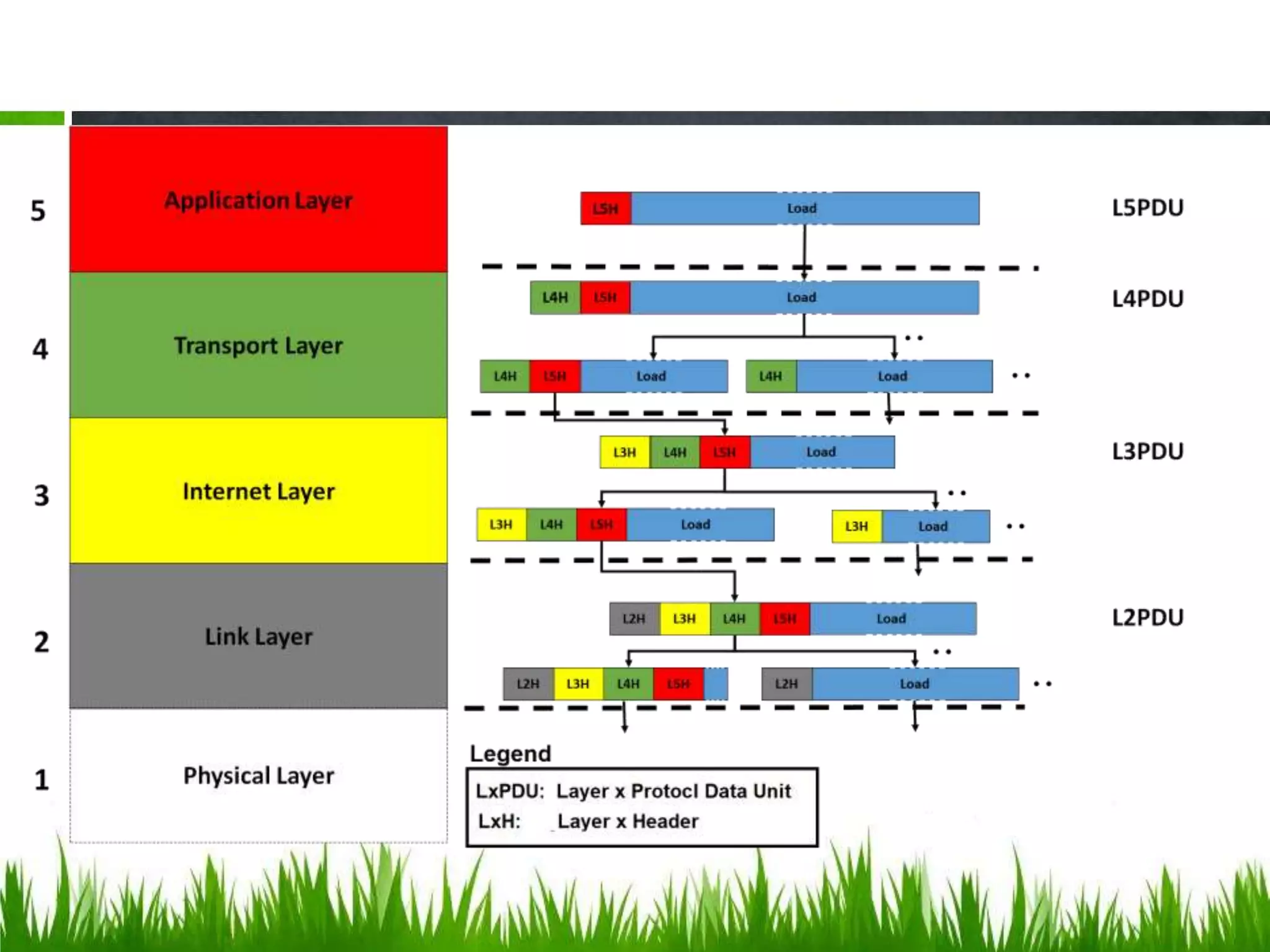
This document discusses IP forwarding and the delivery of IP datagrams. It covers:
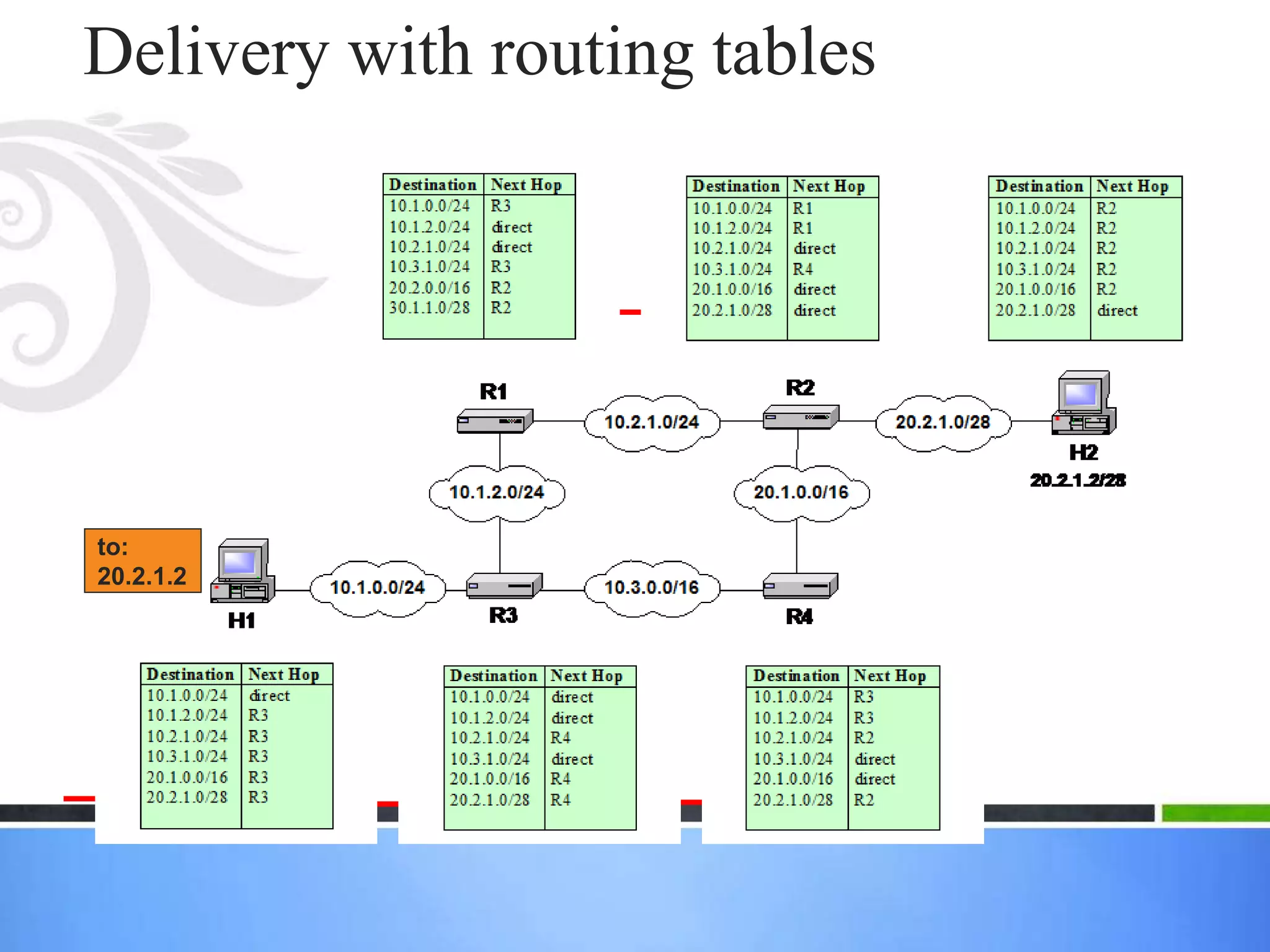
- IP networks are logical entities represented as "clouds" that ignore the underlying data link layers.
- For successful delivery, each data link network must connect to another via a router and network prefixes must correspond to unique data link networks.
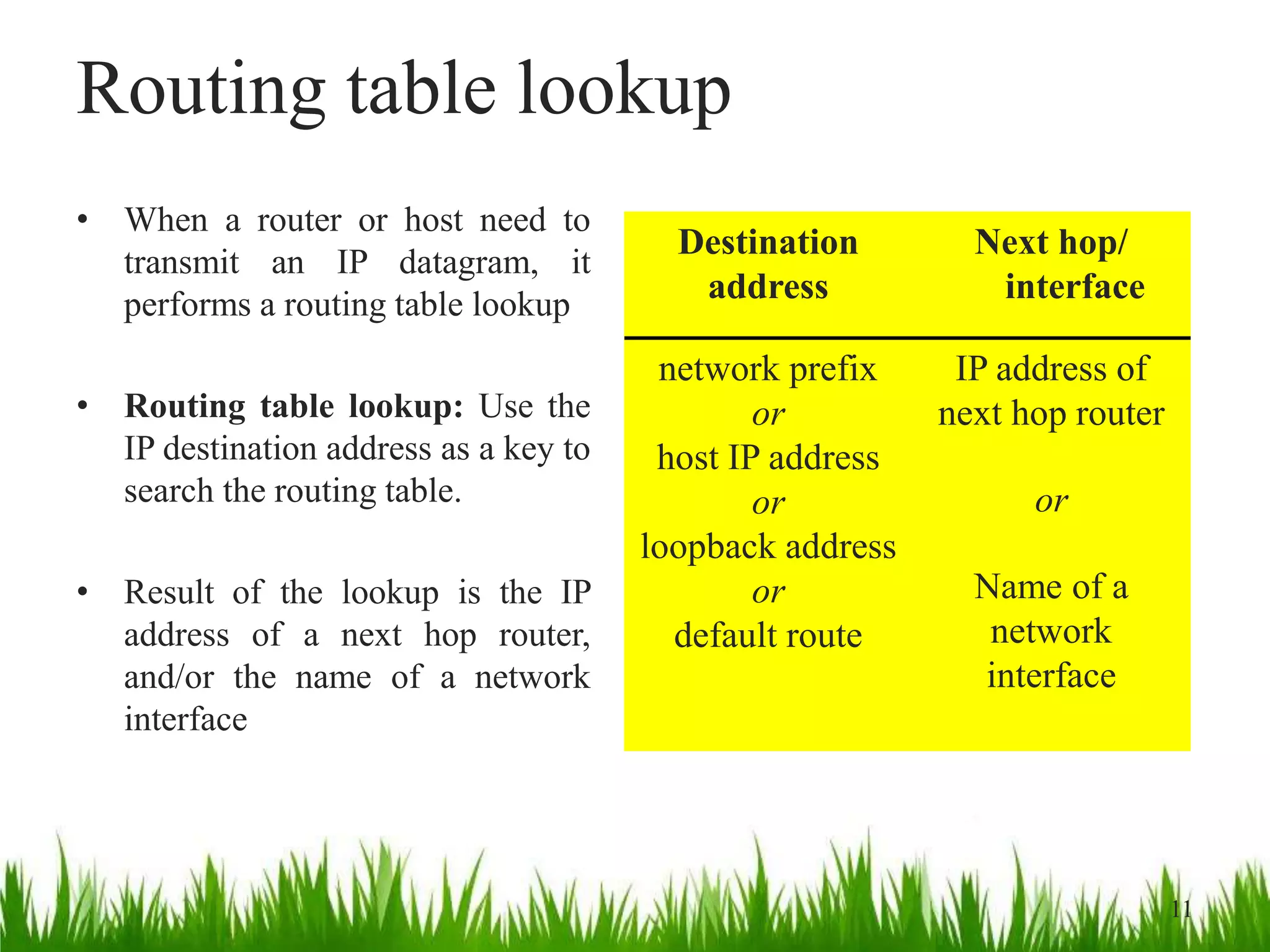
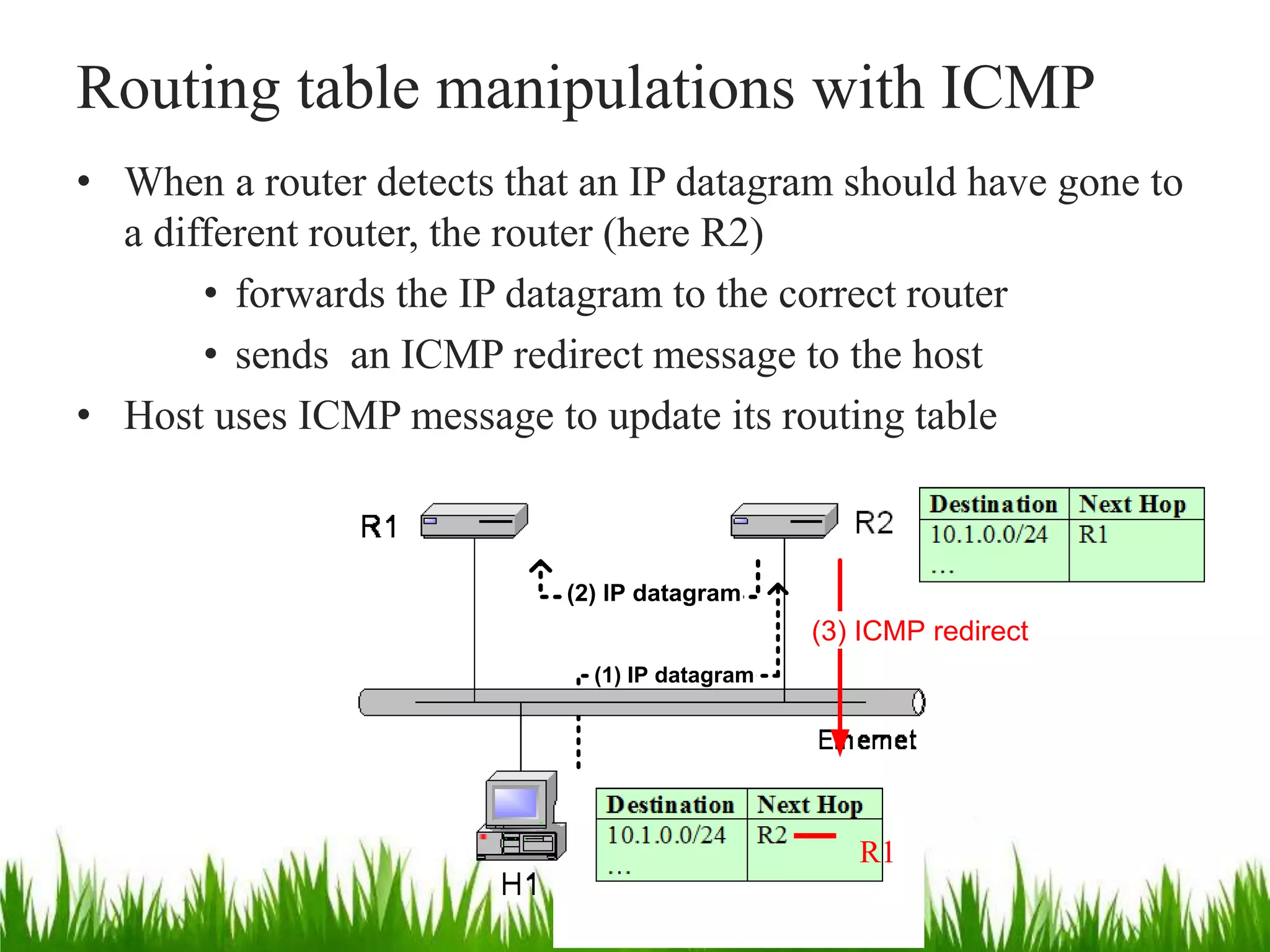
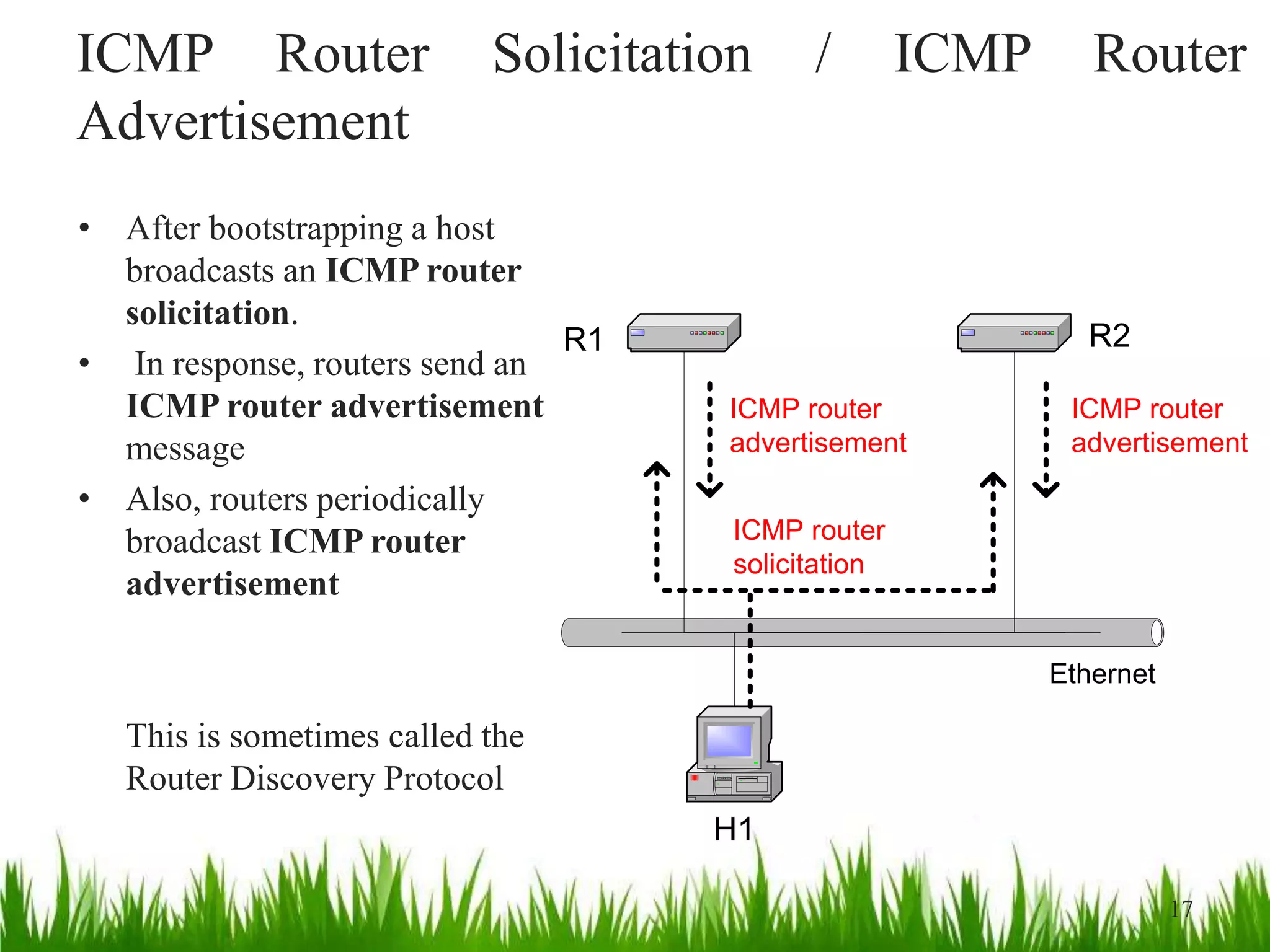
- Routers and hosts use routing tables to determine the next hop for outgoing datagrams based on destination address and interface.
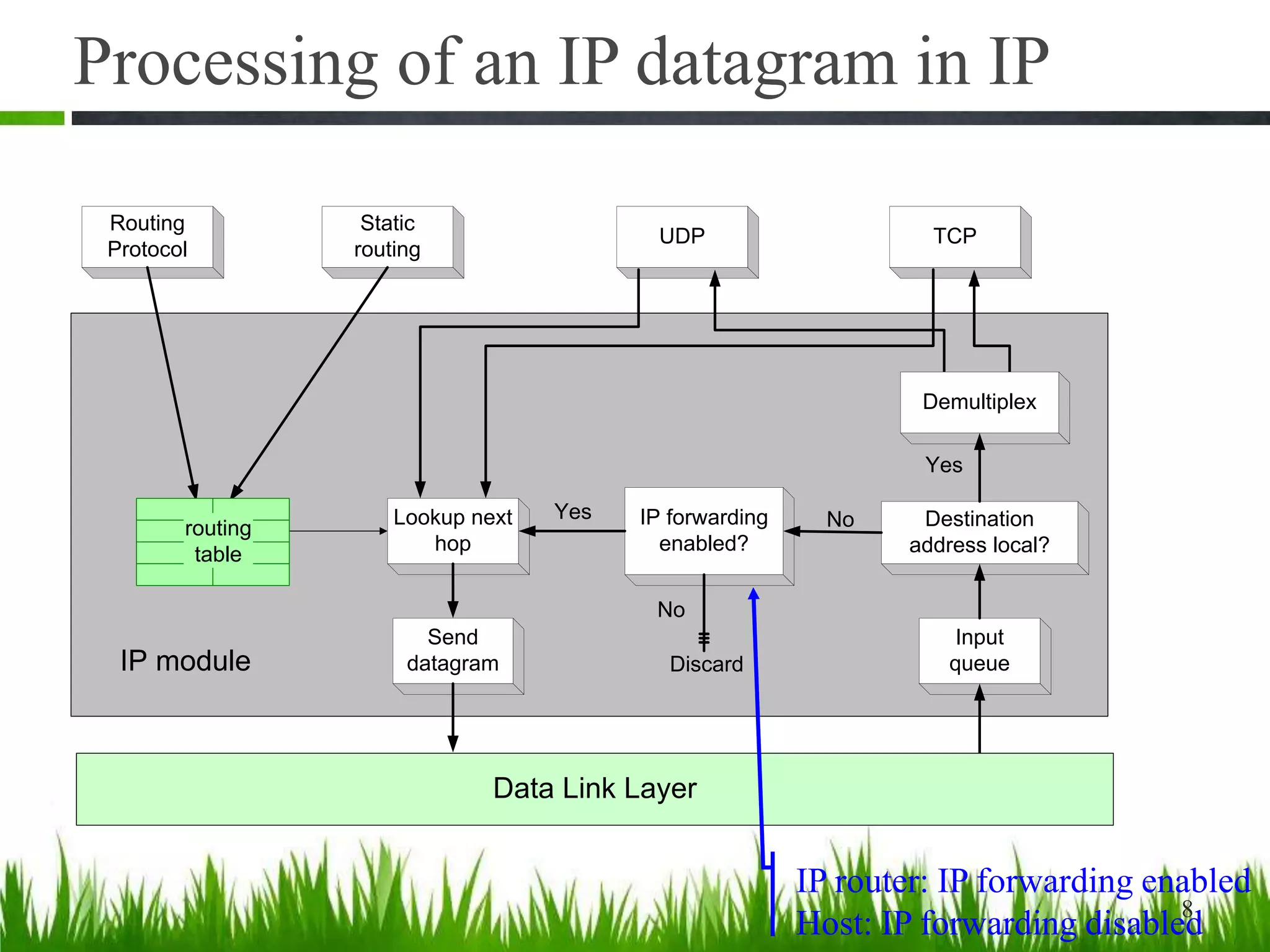
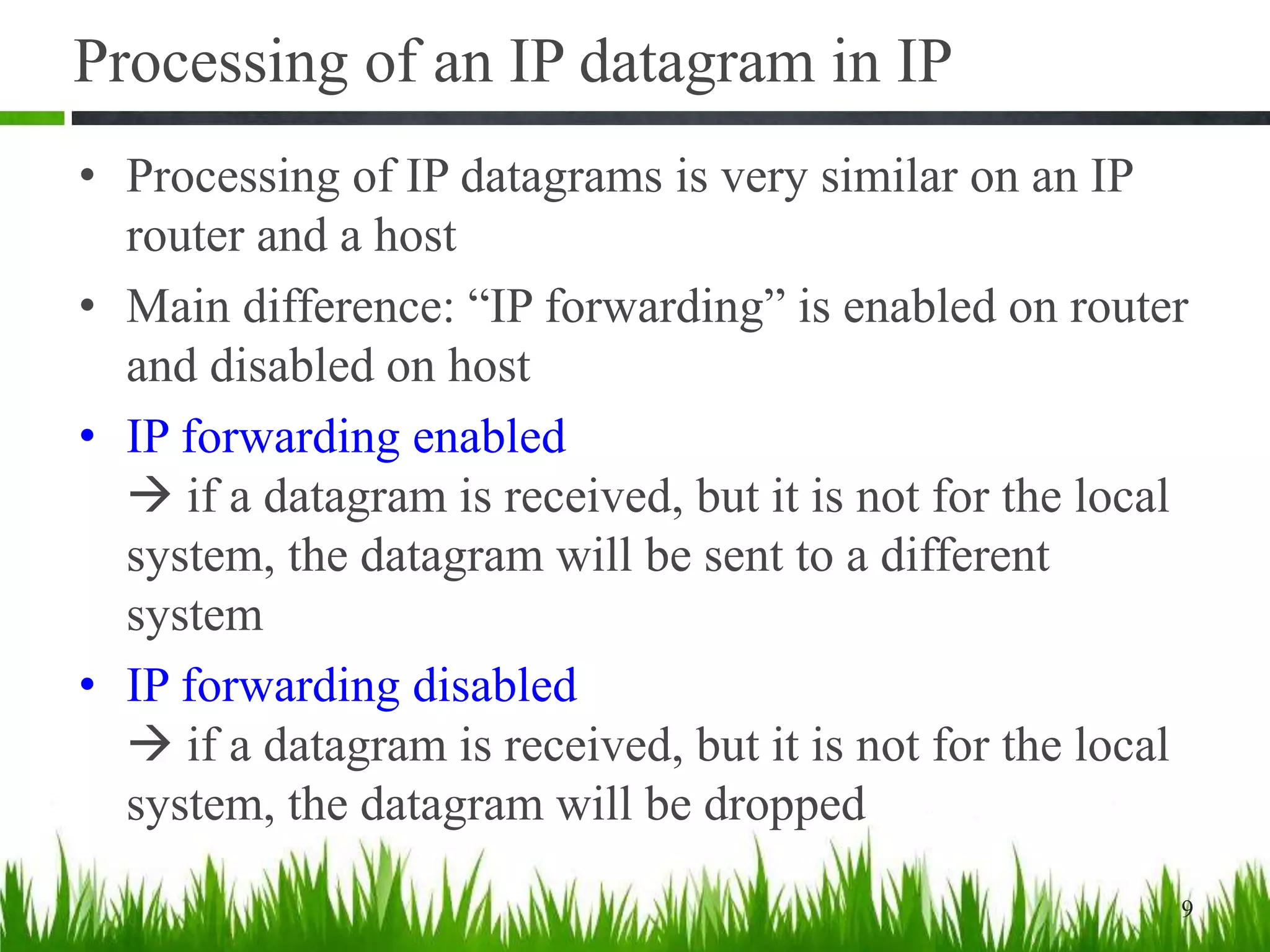
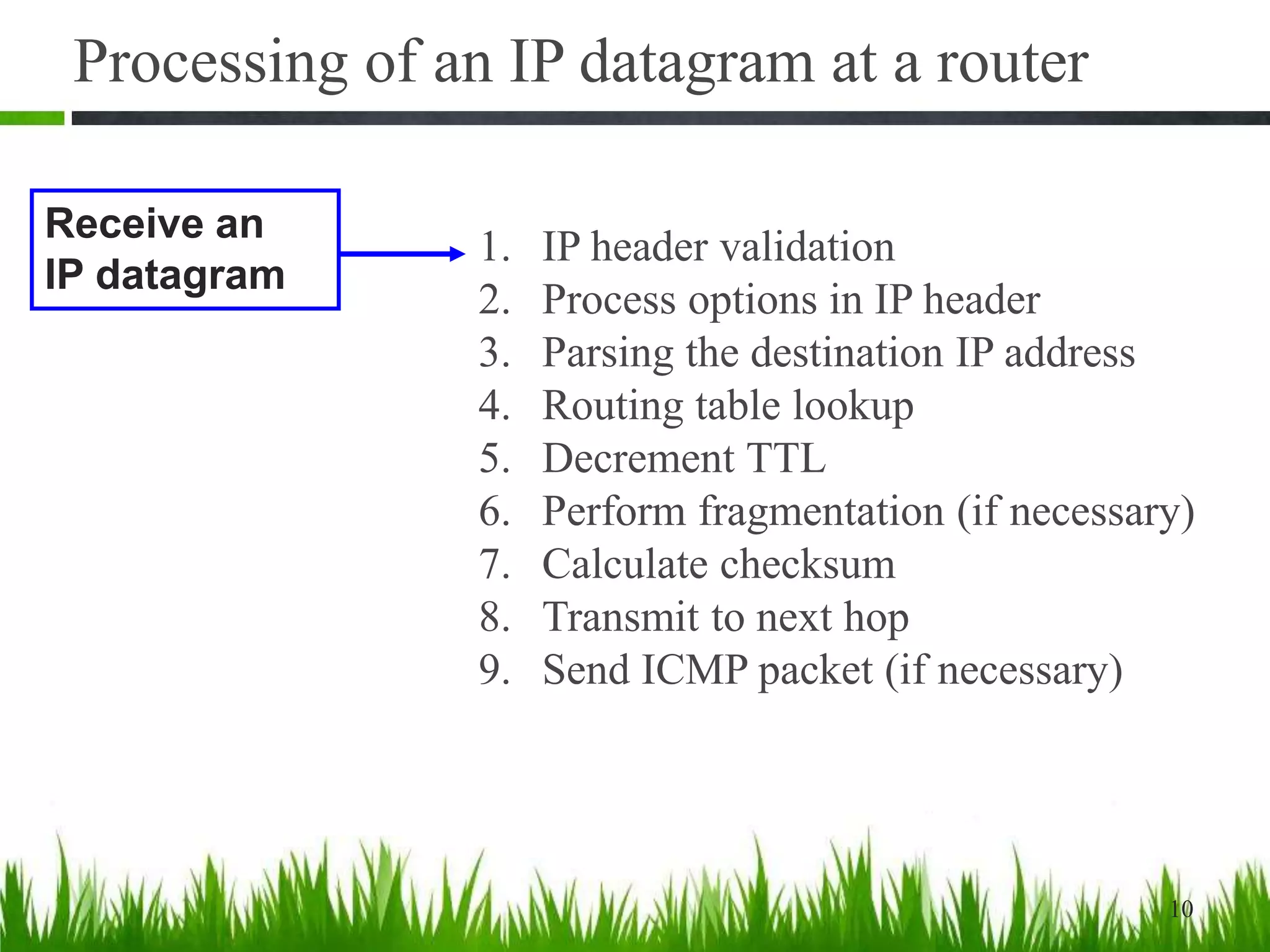
- IP forwarding processes incoming datagrams, looking them up in routing tables to determine the outgoing interface. It is enabled on routers and disabled on hosts.
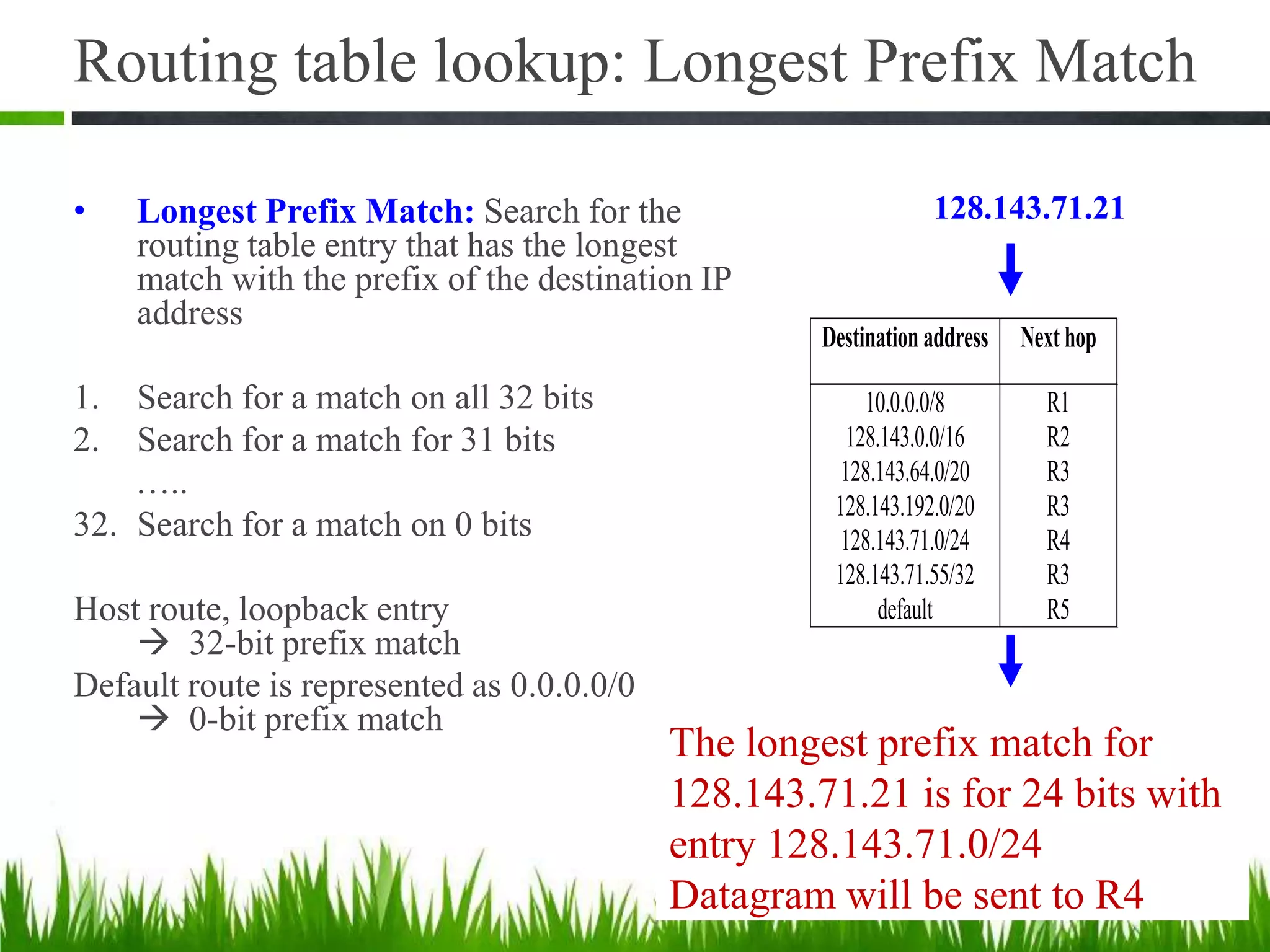
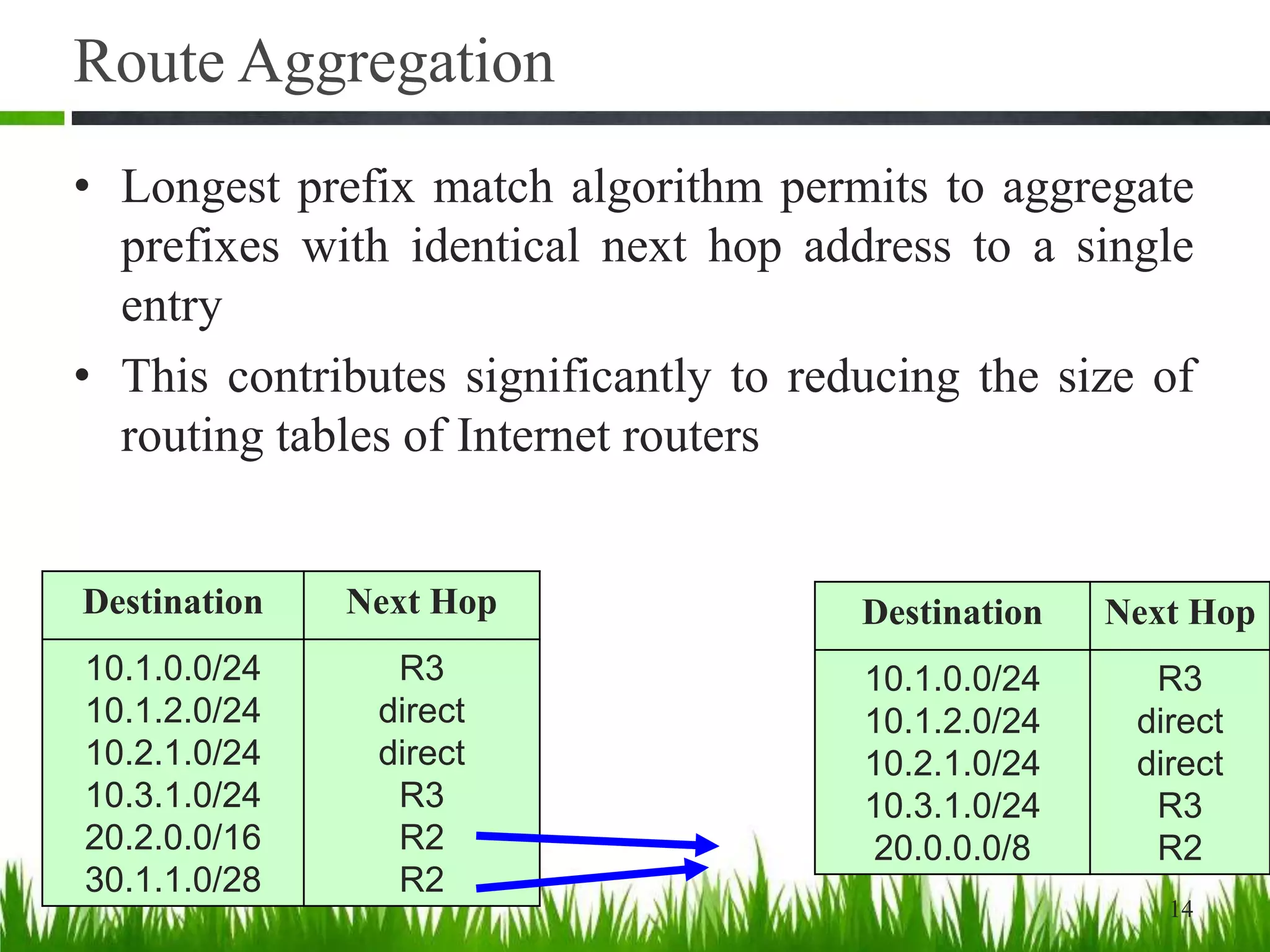
- The longest prefix match is used for routing table lookups to determine the most specific match. Route aggregation reduces routing table