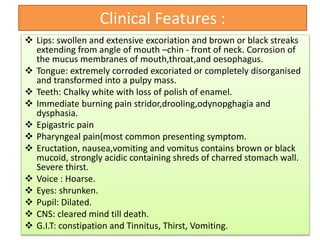
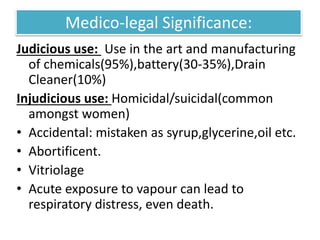
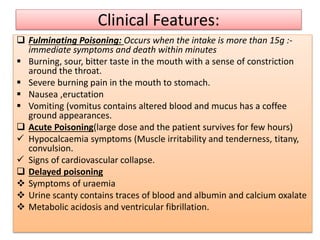
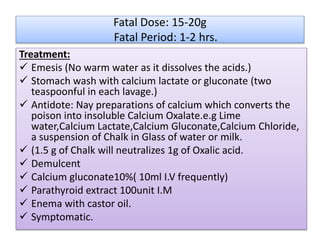
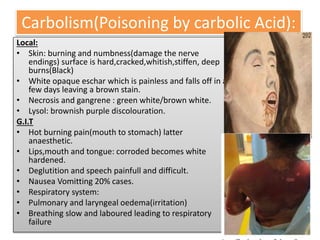
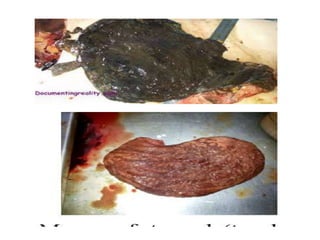
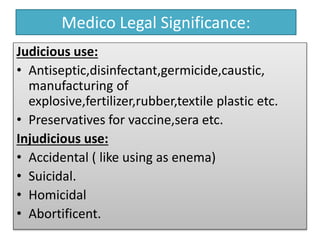
This document provides information on corrosive poisons including sulfuric acid, oxalic acid, phenol, and nitric acid. It describes their physical and chemical properties, mechanisms of action, clinical features of poisoning, treatment approaches, causes of death, and post-mortem appearances. It also discusses their judicious and injudicious uses and medicolegal significance. The document is intended to educate about these dangerous corrosive poisons through detailed descriptions and comparisons.