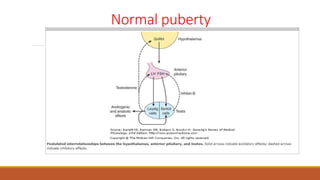
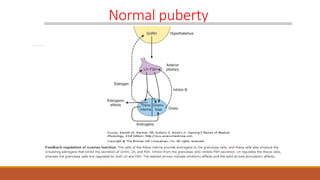
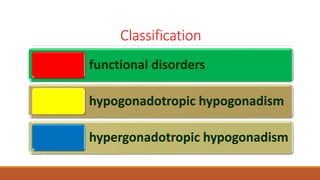
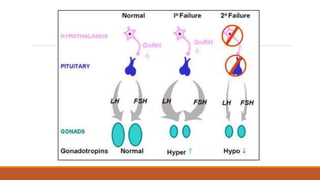
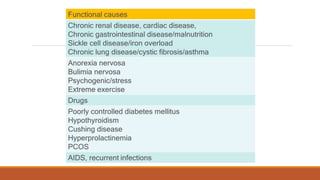
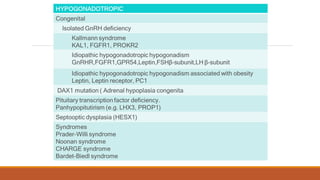
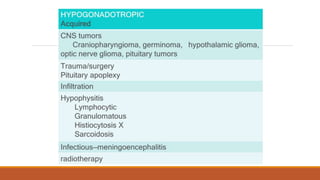
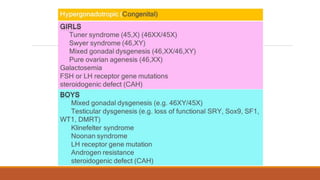
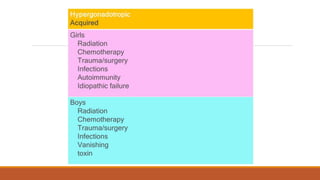
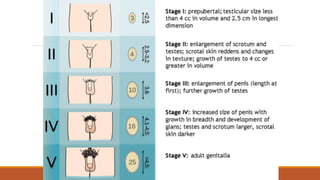
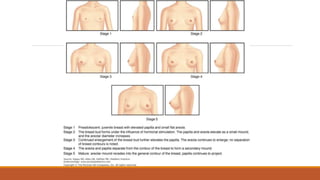
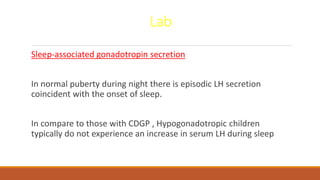
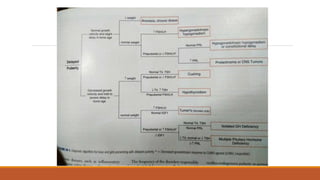
This document provides information on delayed puberty, including its definition, causes, evaluation, and treatment. Delayed puberty can be functional, due to hypogonadotropic hypogonadism, or hypergonadotropic hypogonadism. The most common cause is constitutional delay of growth and puberty. Evaluation involves medical history, physical exam, lab tests like LH, FSH and bone age. Treatment depends on the underlying cause, but aims to induce normal pubertal development and growth. For constitutional delay, watchful waiting is often recommended, while permanent hypogonadism requires hormone therapy like testosterone to initiate puberty.