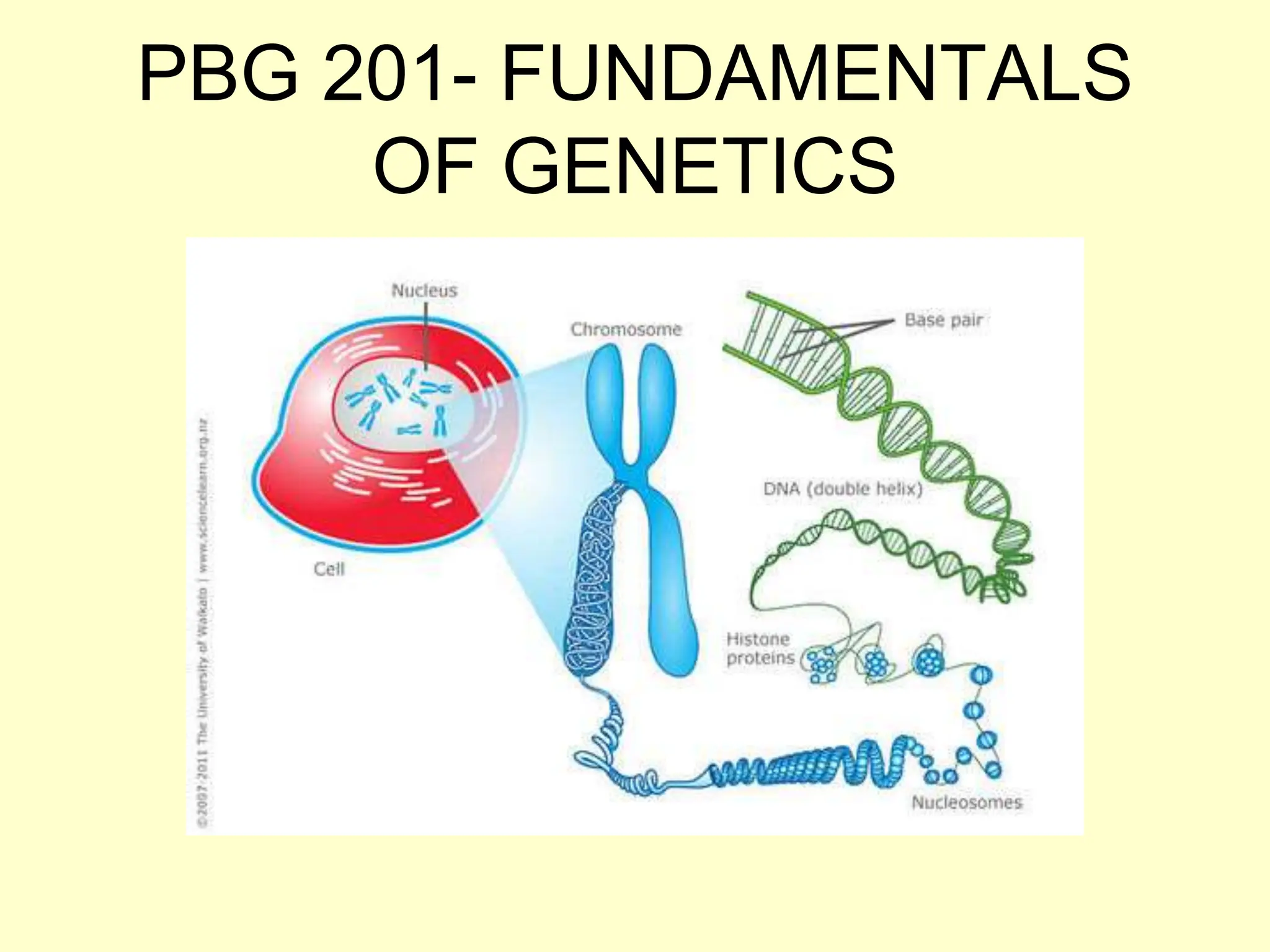
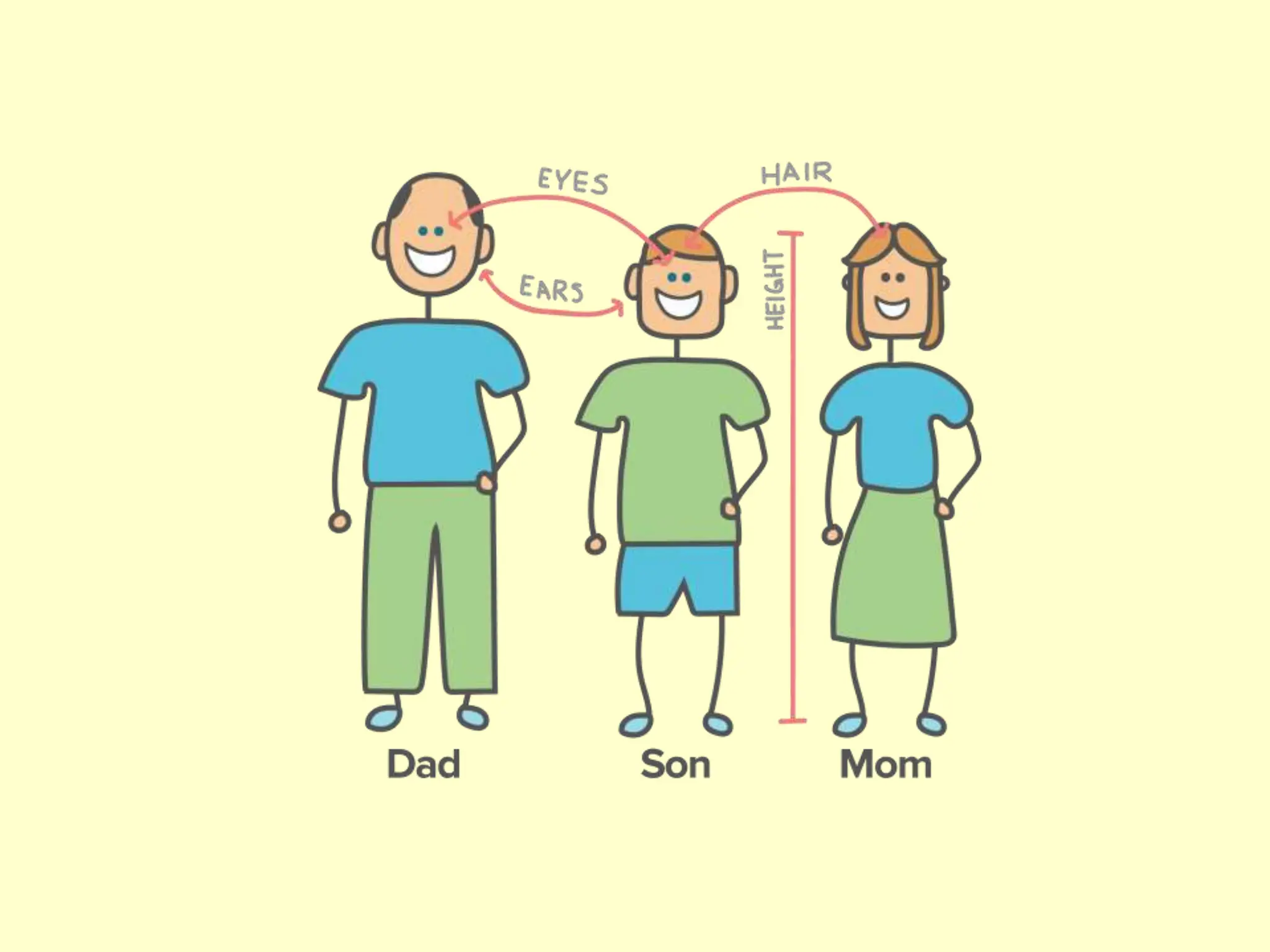
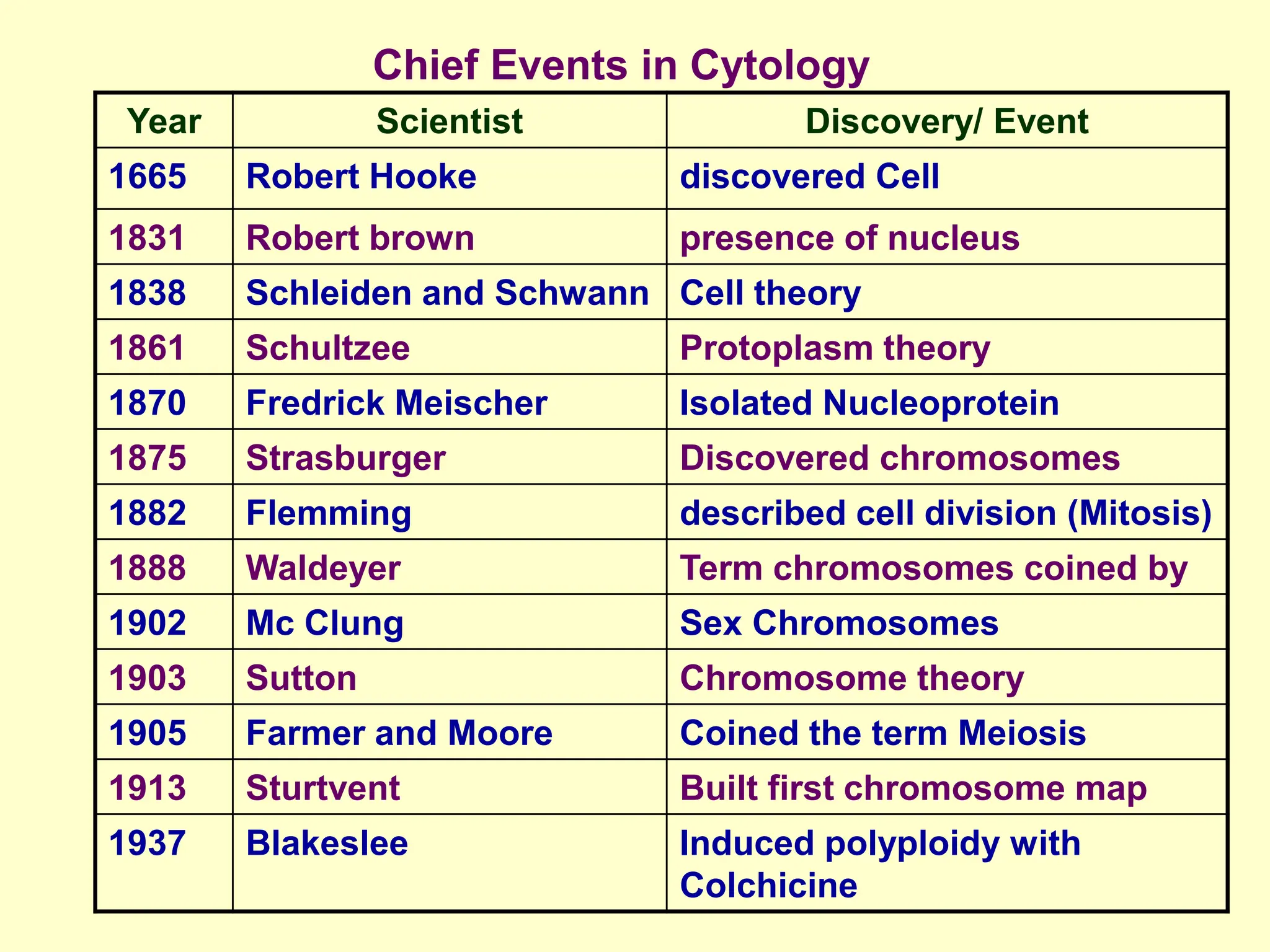
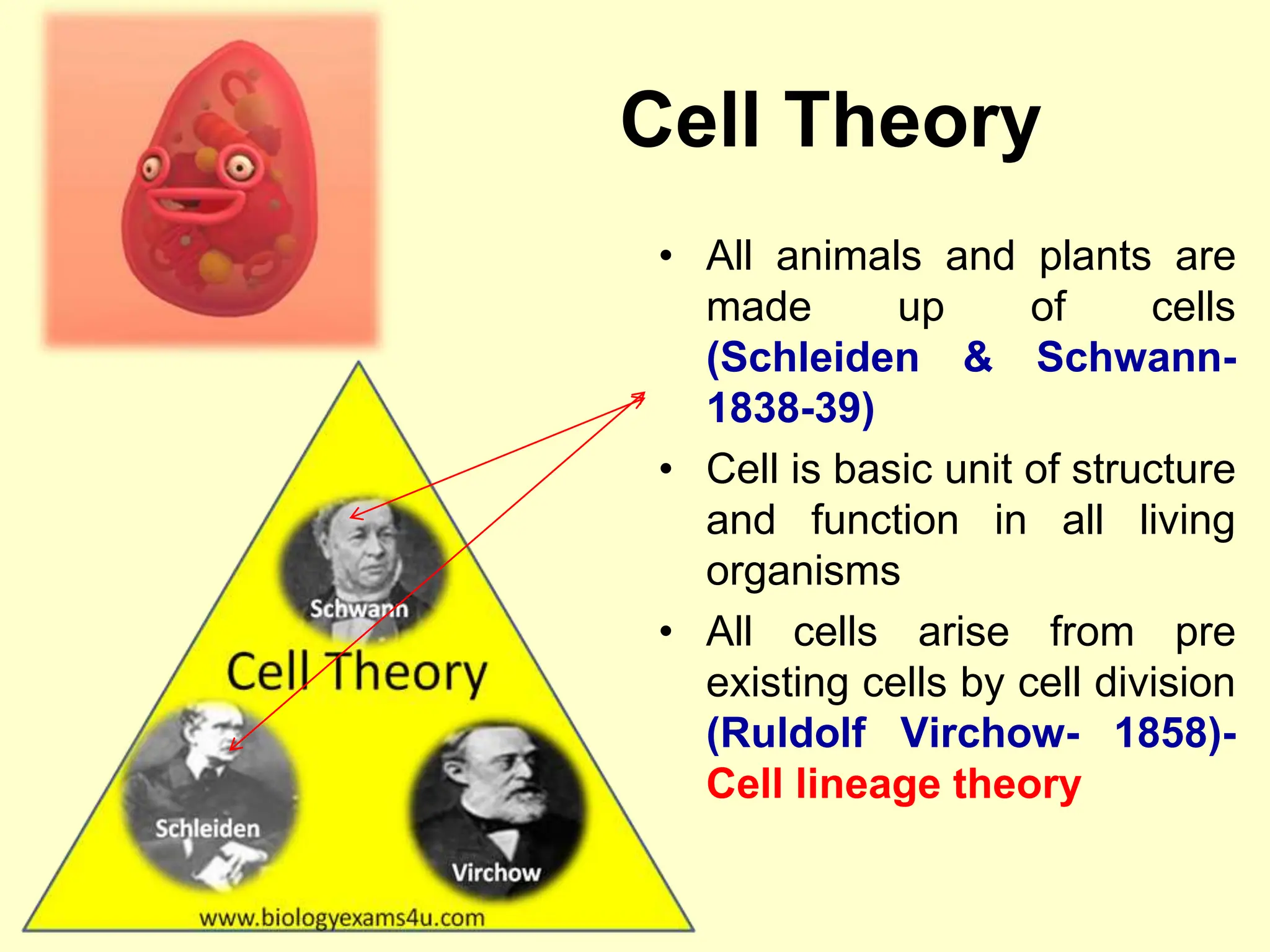
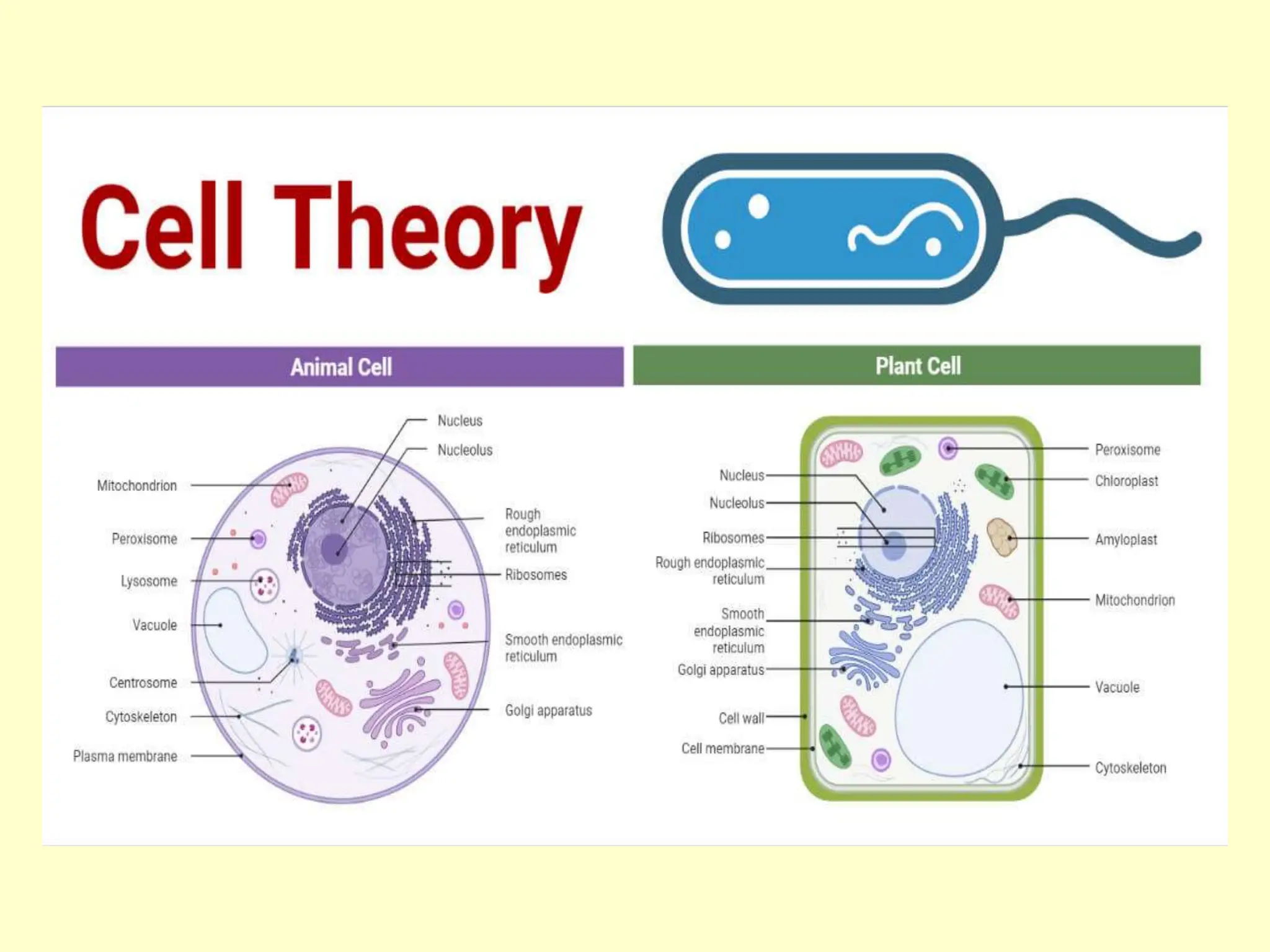
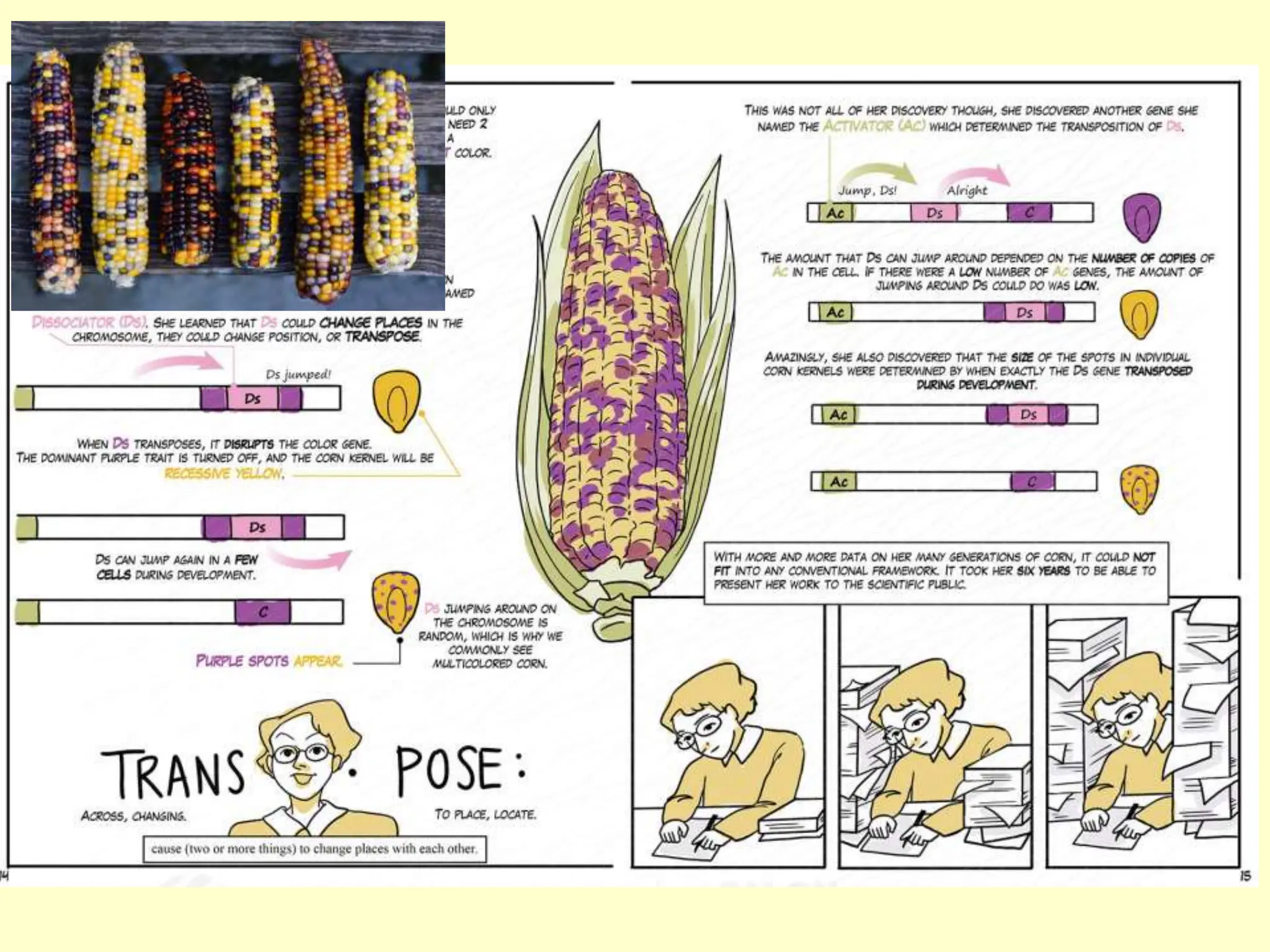
The document provides an overview of fundamental concepts in genetics, including heredity, inheritance, and the history of significant scientific discoveries in genetics and cytogenetics. Key figures like Gregor Mendel, who established the laws of inheritance, and later researchers such as Watson and Crick, who elucidated the structure of DNA, are highlighted. It discusses the evolution of genetic science from basic hereditary principles to advanced genomic studies, underscoring the contributions of various scientists over time.