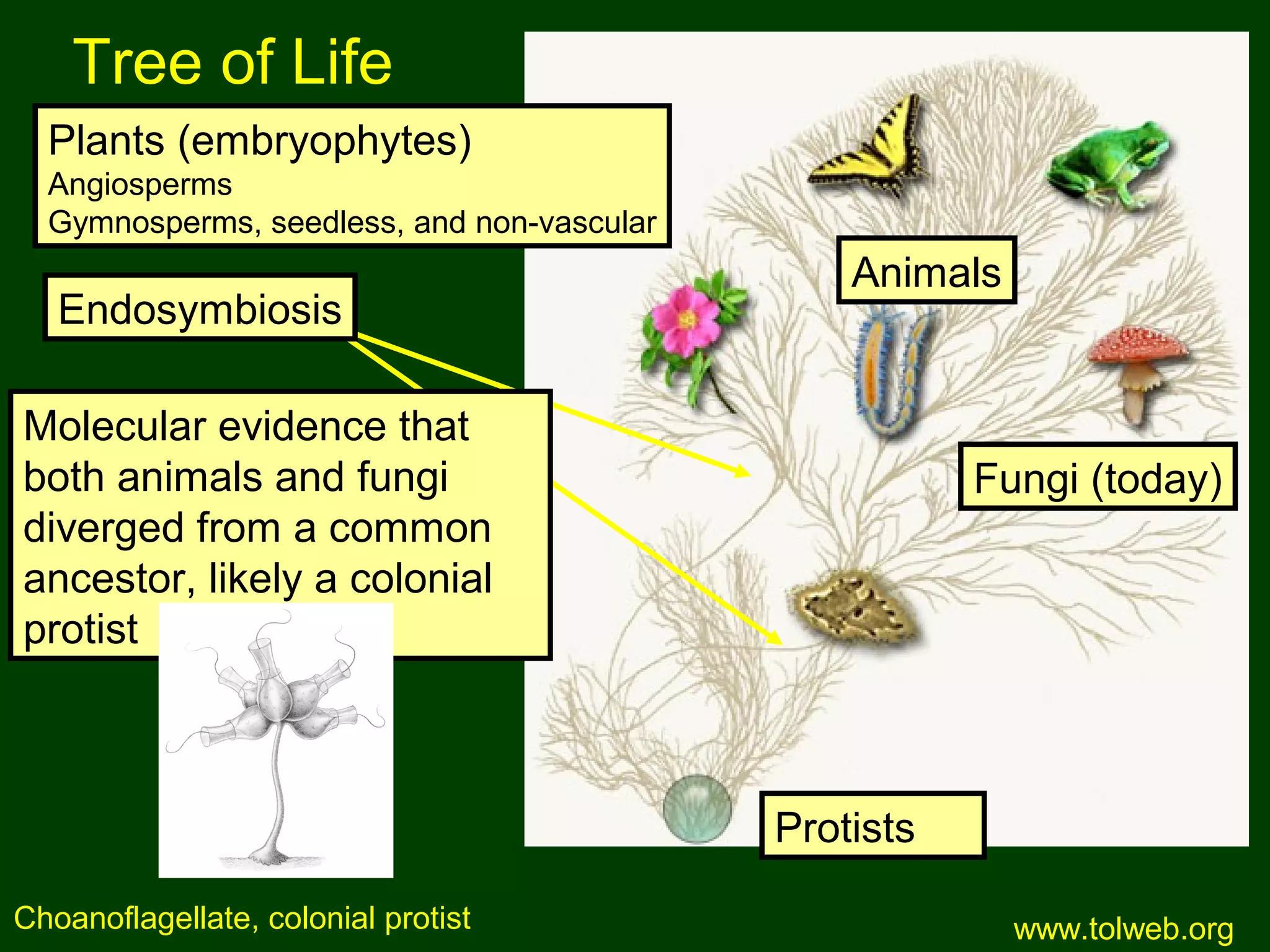
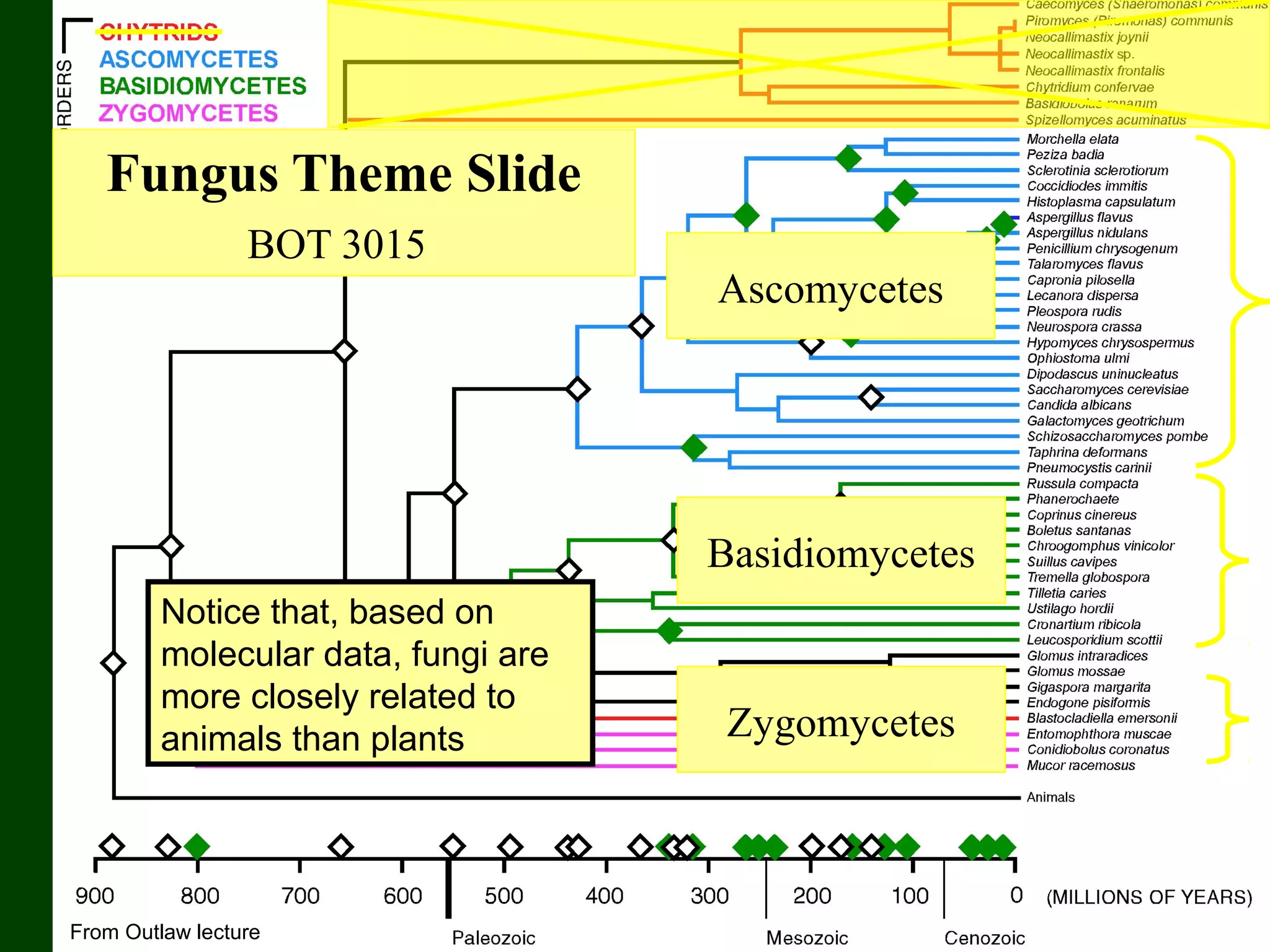
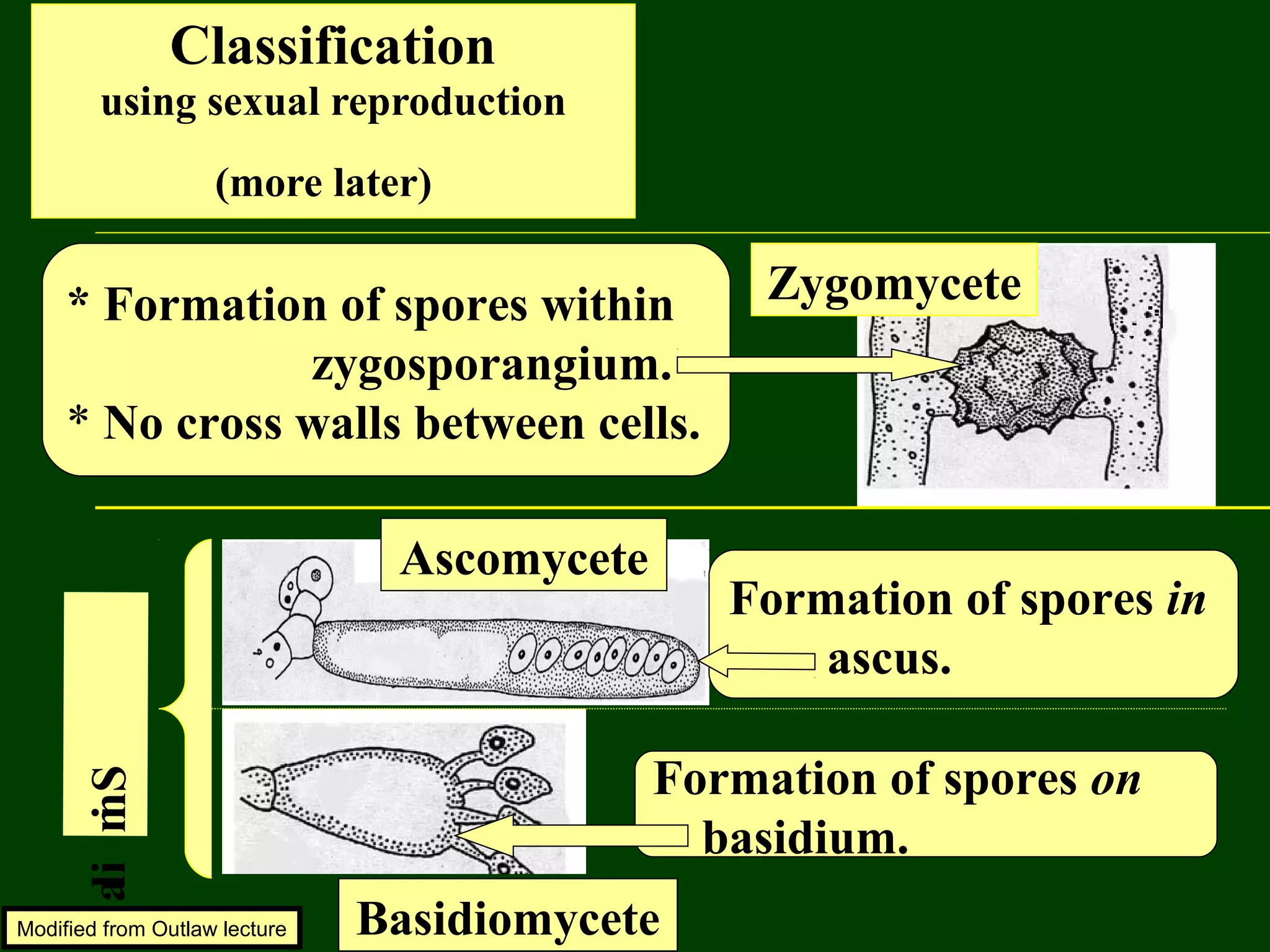
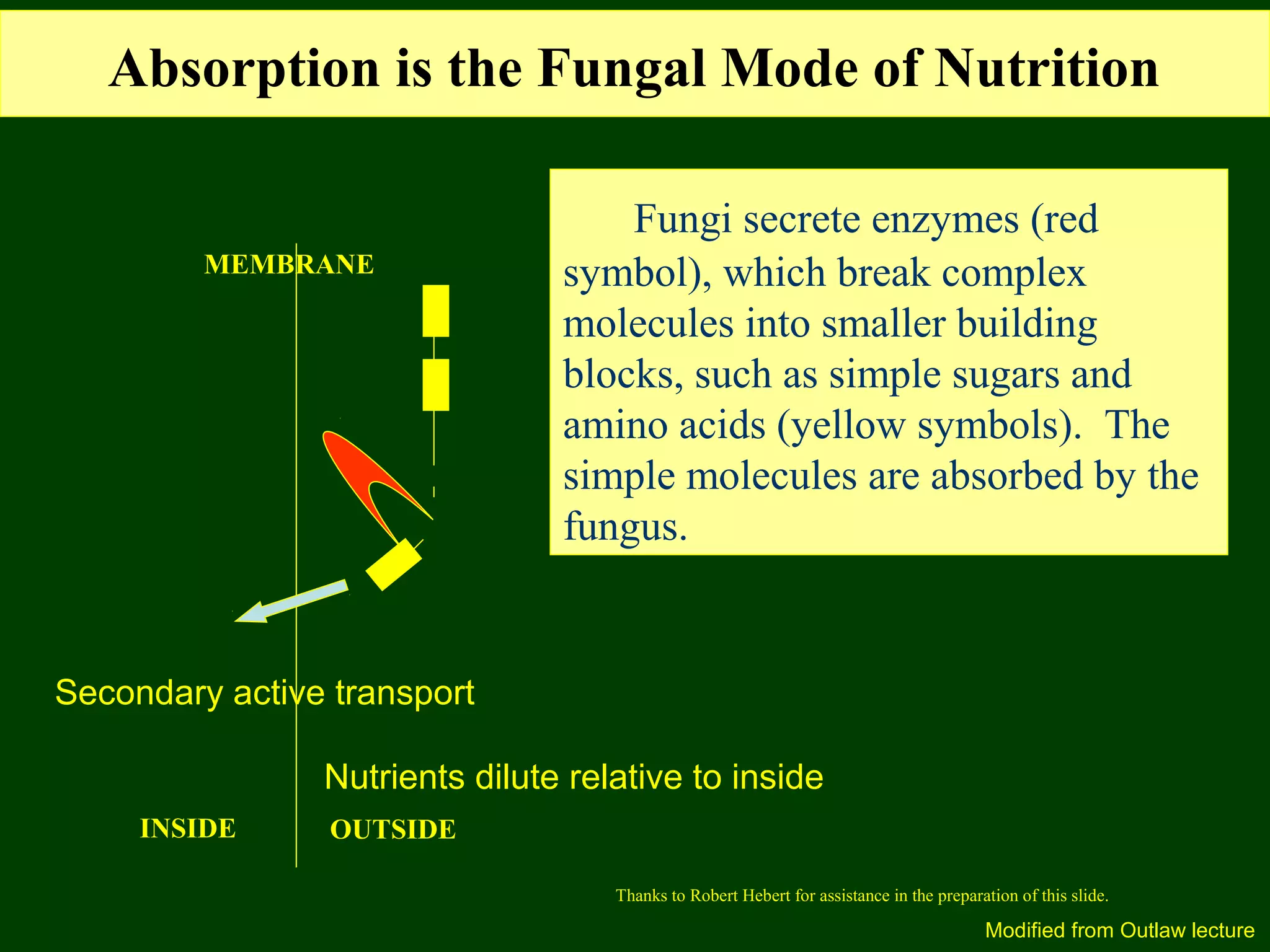
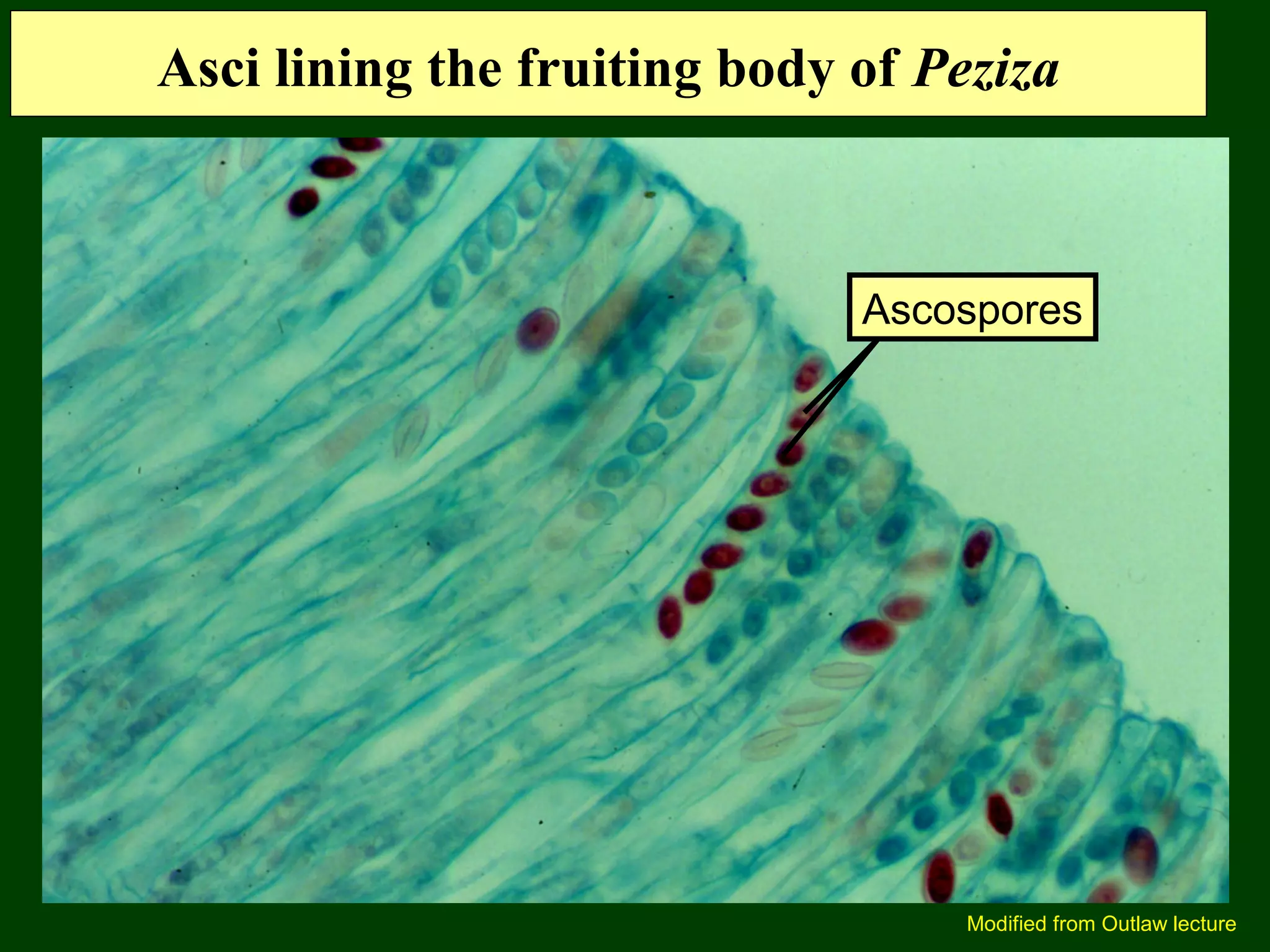
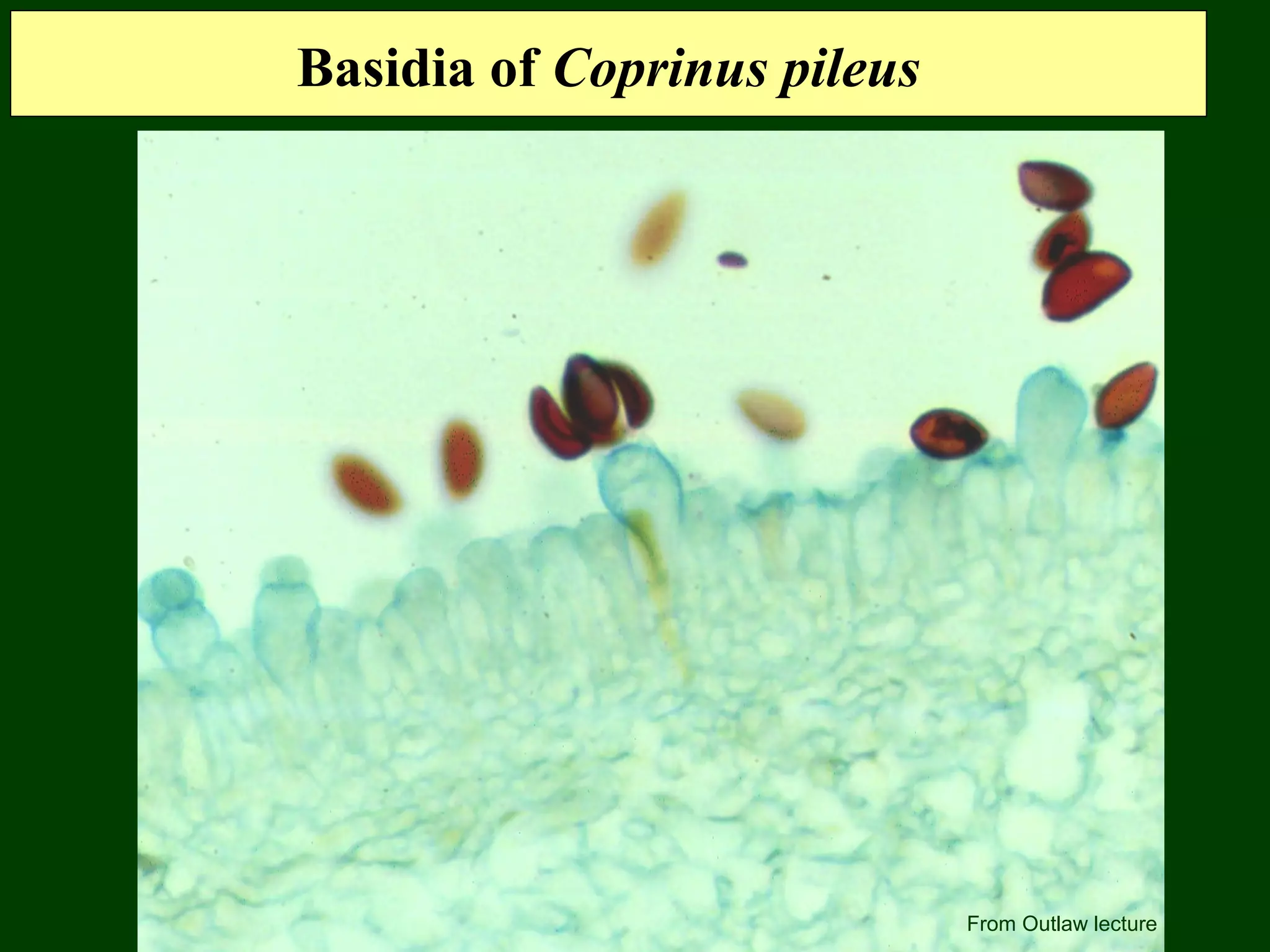
This document provides an overview of fungi, including their phylogenetic placement, importance, characteristics, and classification. It discusses that fungi diverged from a common ancestor with animals, likely a colonial protist. Key characteristics of fungi include eukaryotic cells with chitin cell walls, absorption of nutrients, secretion of digestive enzymes, filamentous hyphae, and both sexual and asexual reproduction via spores. The major phyla of fungi - Zygomycota, Ascomycota, and Basidiomycota - are described in terms of their life cycles, sexual spore structures, and examples. Common mushrooms, molds, and parasitic fungi are highlighted.