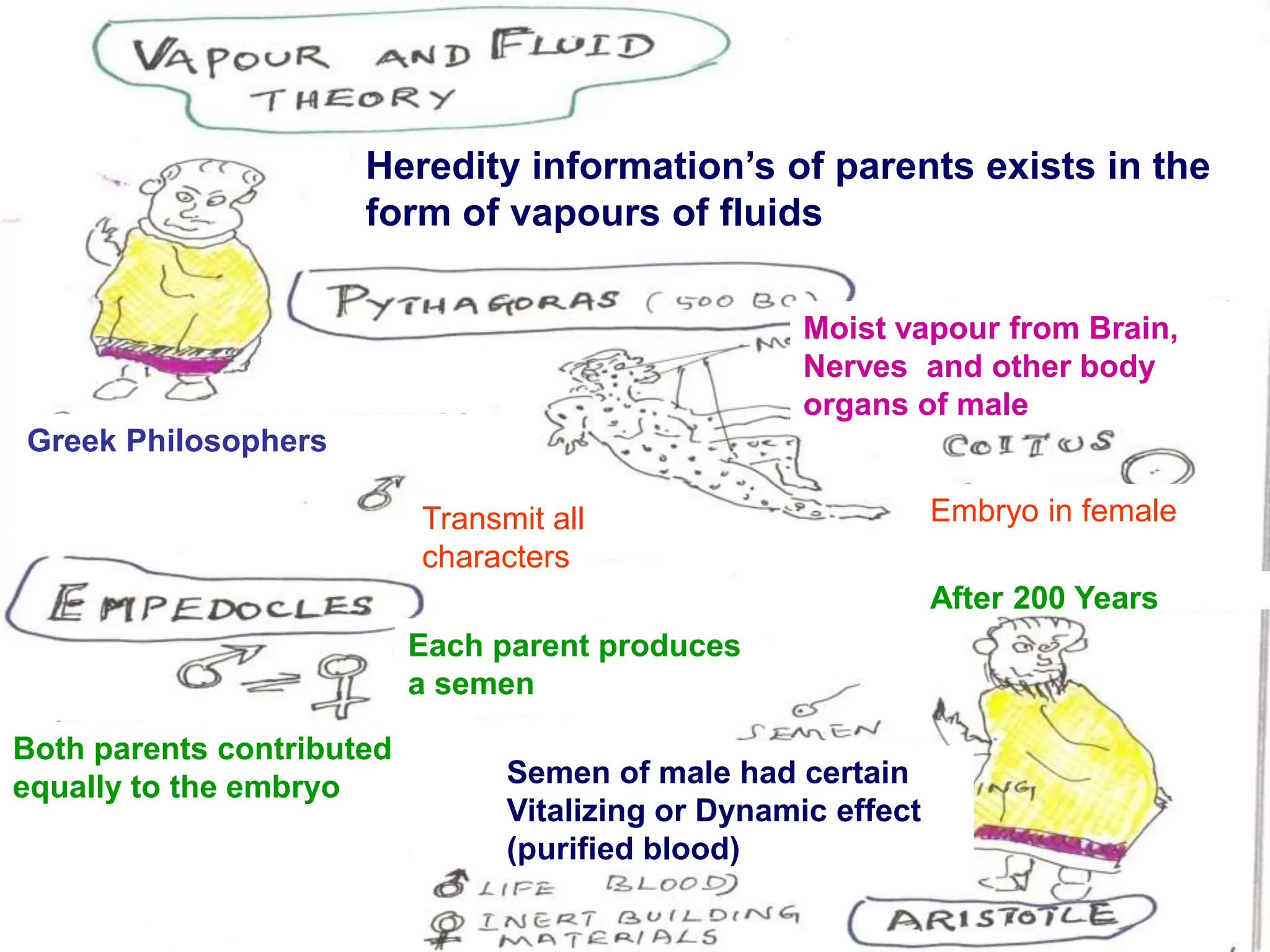
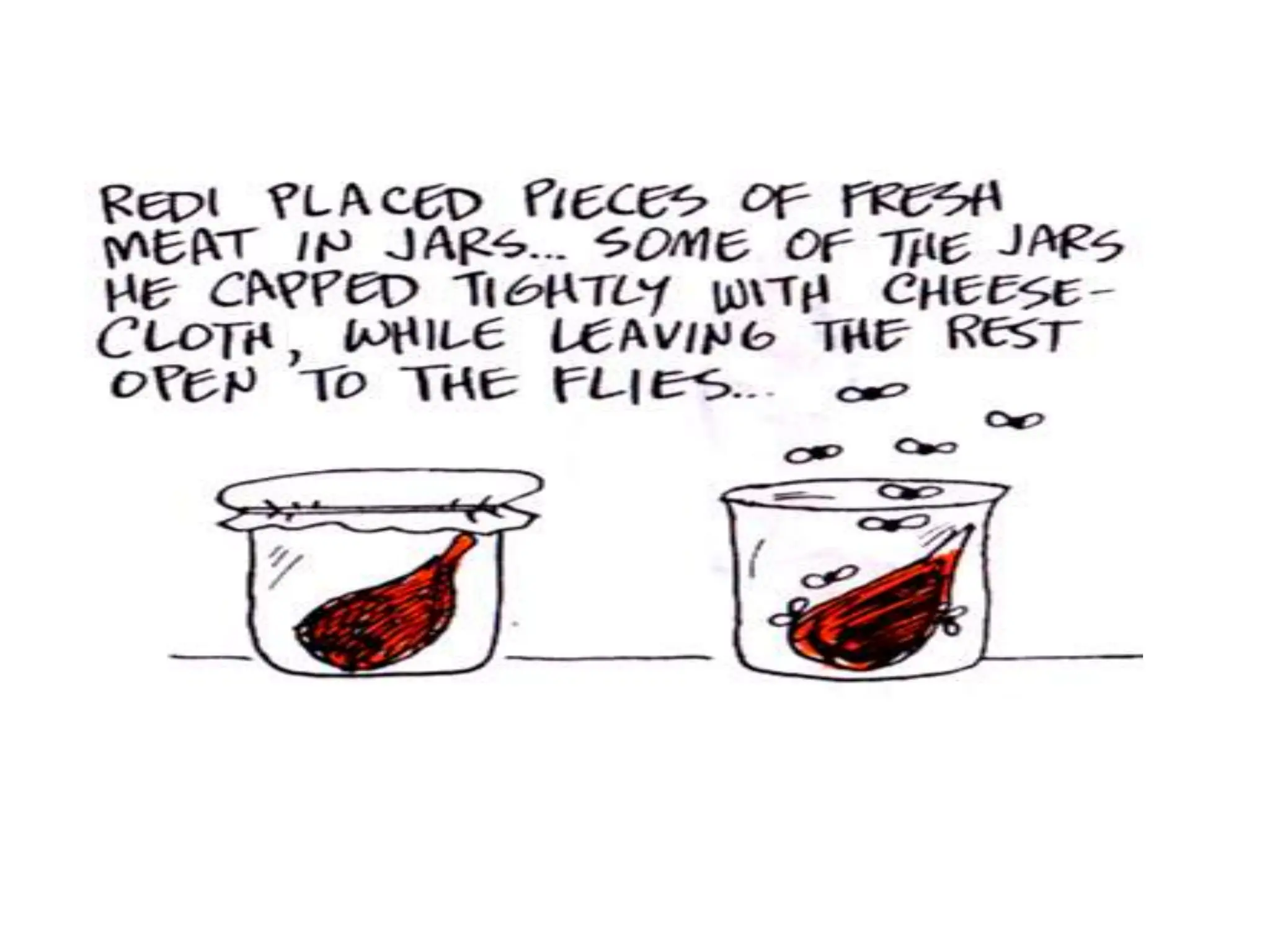
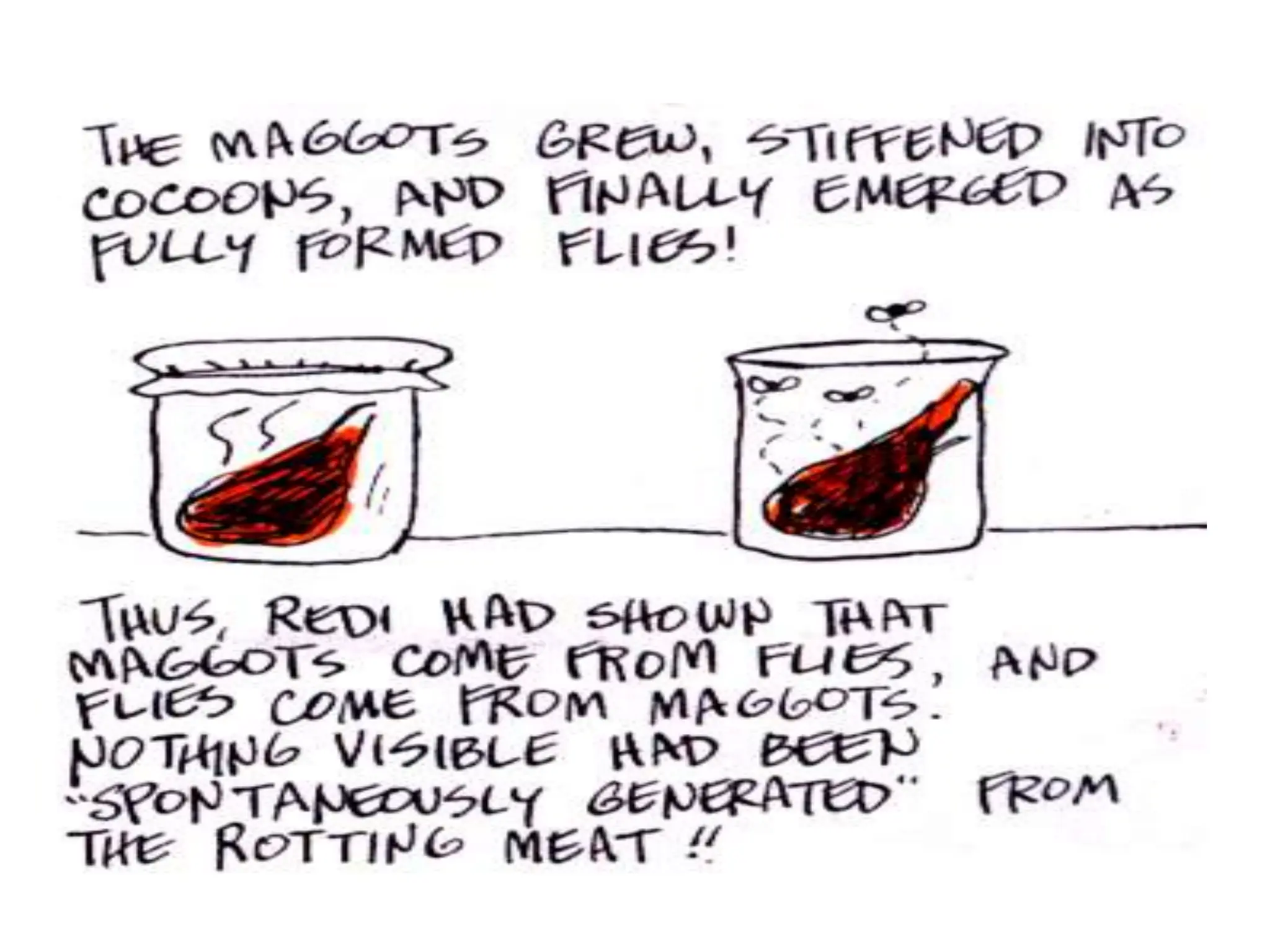
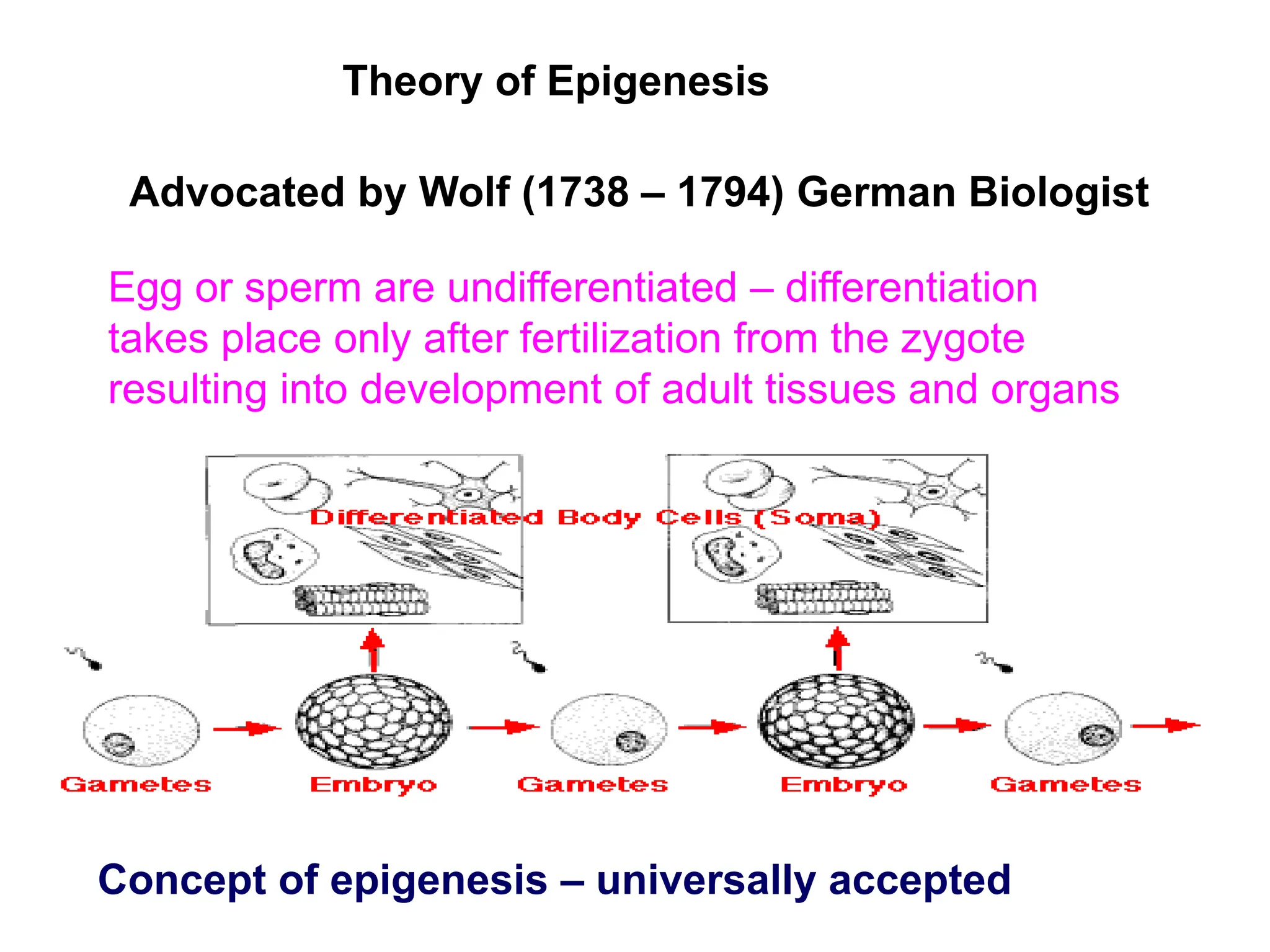
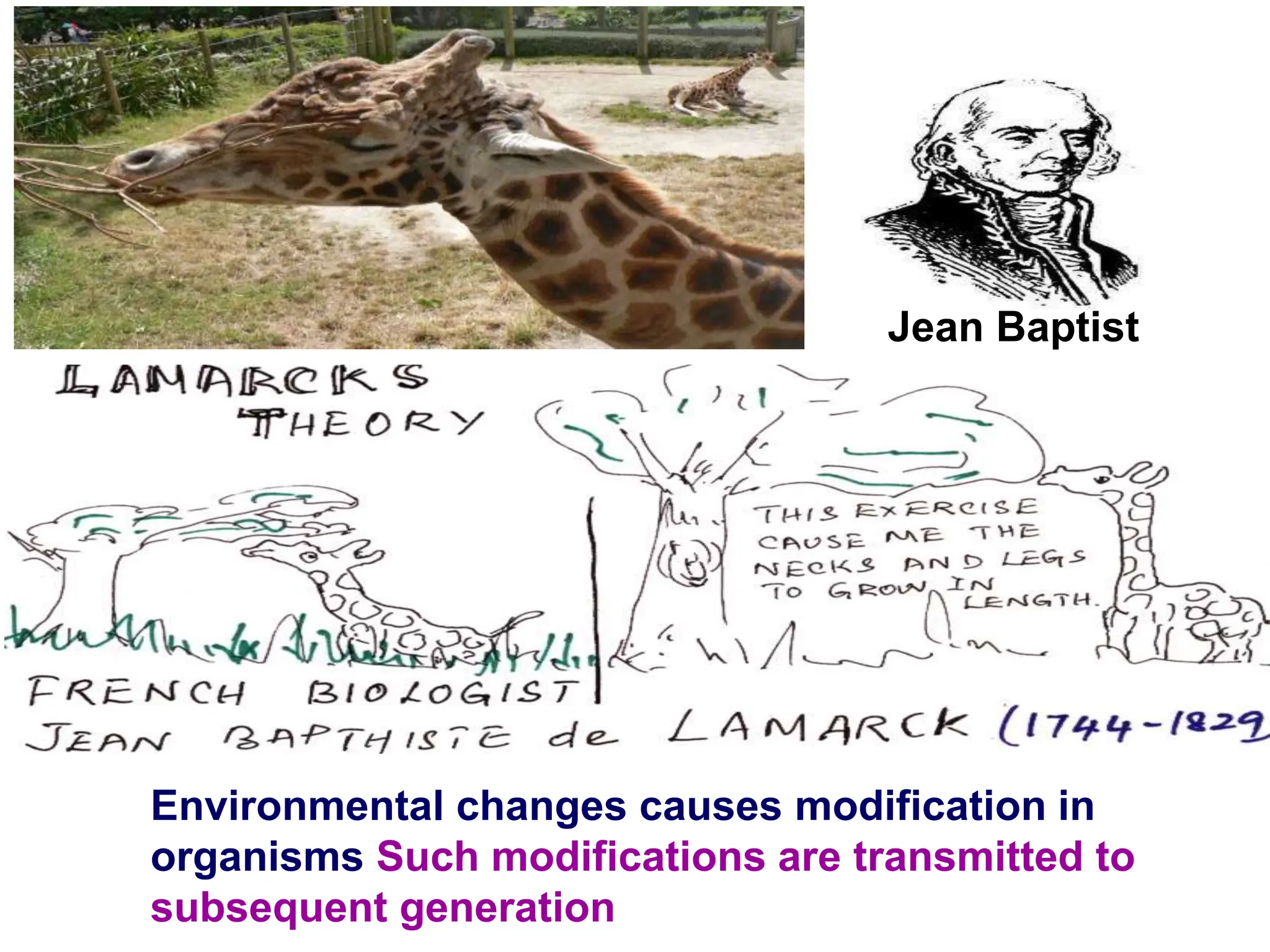
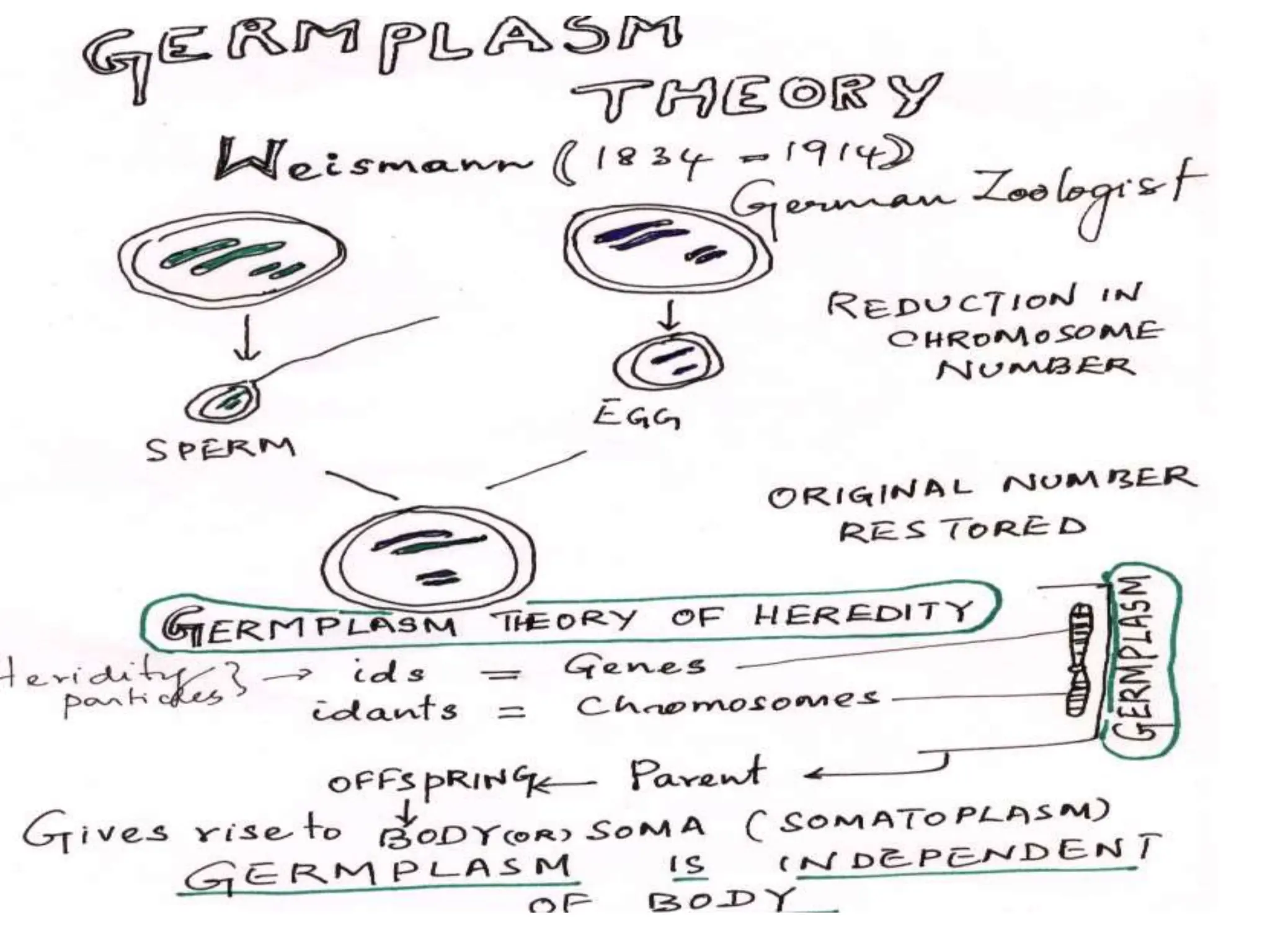
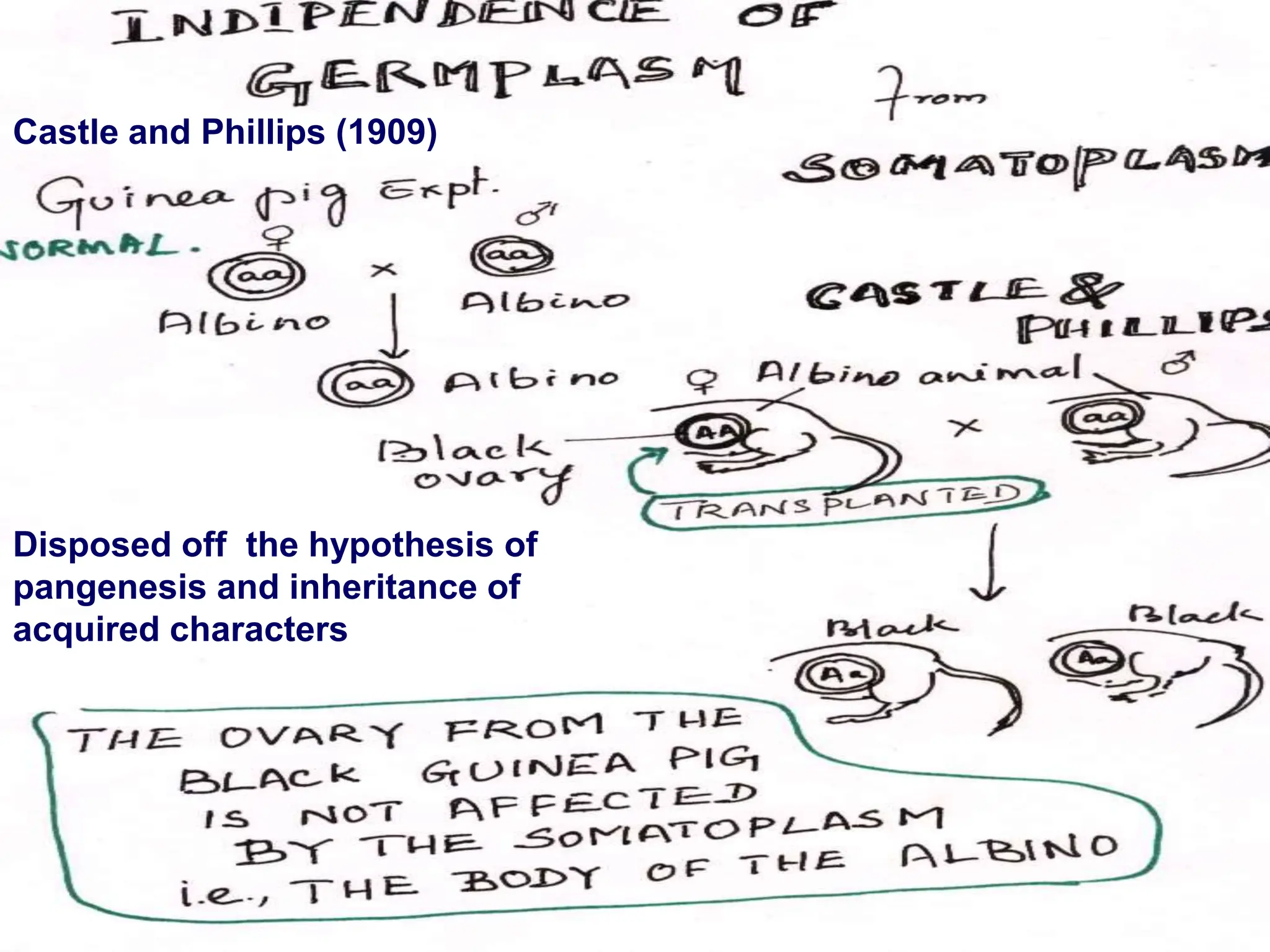
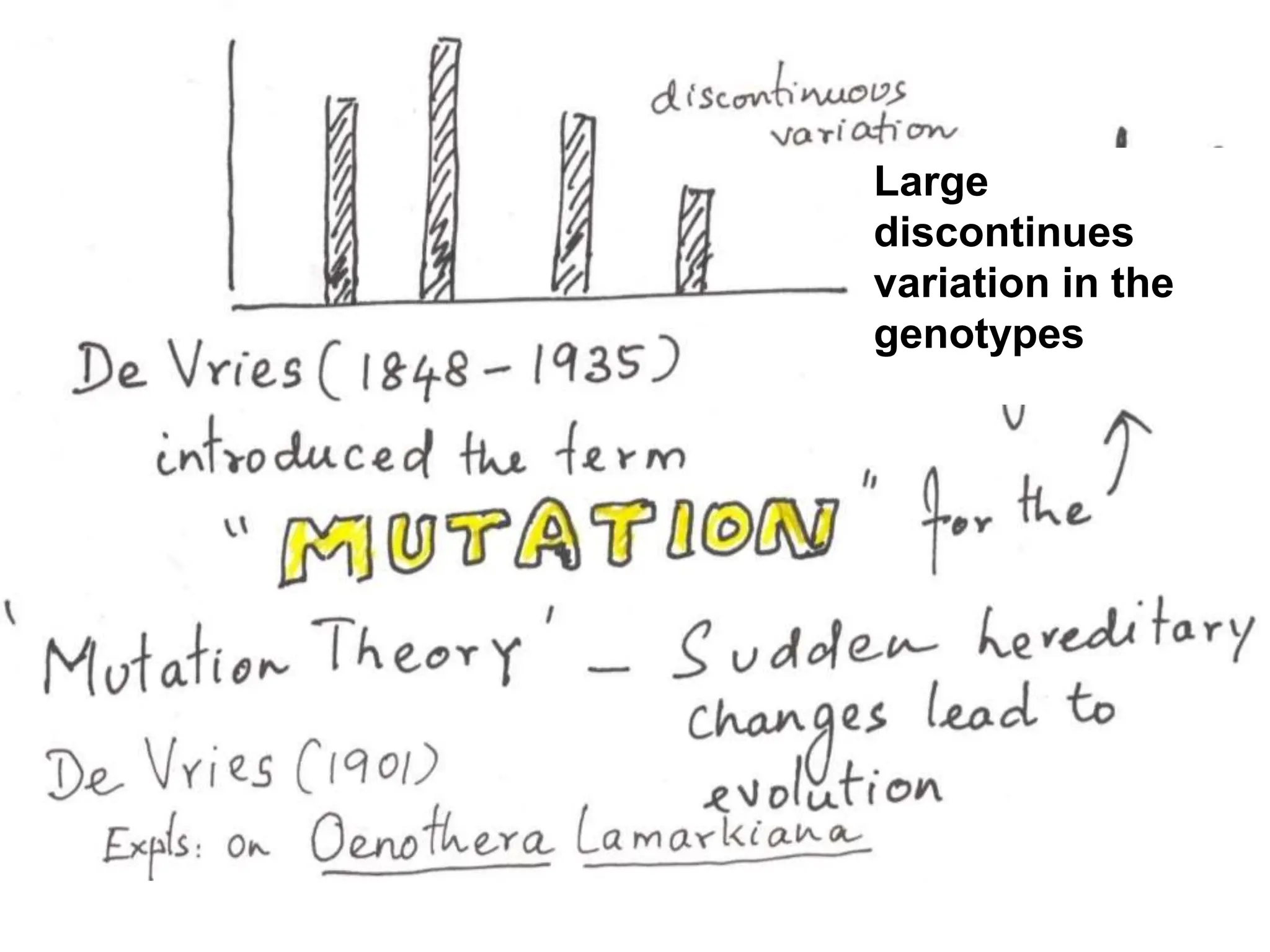
The document discusses pre-Mendelian theories of heredity, including vapour and fluid theory, magnetic power theory, preformation theory, Lamarck's theory, Darwin's theory, germplasm theory, and mutation theory. It highlights milestones in plant reproduction, such as the description of sexual reproduction by Camerarius and the creation of the first artificial hybrid by Thomas Fairchild. Weismann's germplasm theory emphasized that only germplasm, not somatoplasm, transmits hereditary information across generations.