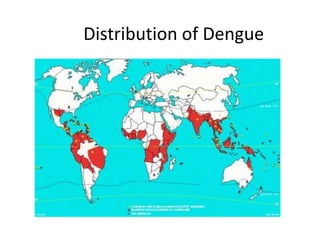
Viral pathogenesis is the process by which a viral infection leads to disease. It depends on factors from both the virus and host. Key viral factors include cell tropism, ability to cause cellular damage, and mechanism of replication. The host immune response largely determines the outcome, as it can clear the virus or become overactive and cause immunopathology. Some viruses like HIV can evade the immune system and establish chronic, persistent infections by infecting immune cells. This document provides examples of viral pathogenesis for various viruses like rubella, herpes, dengue, hepatitis B, and HIV.