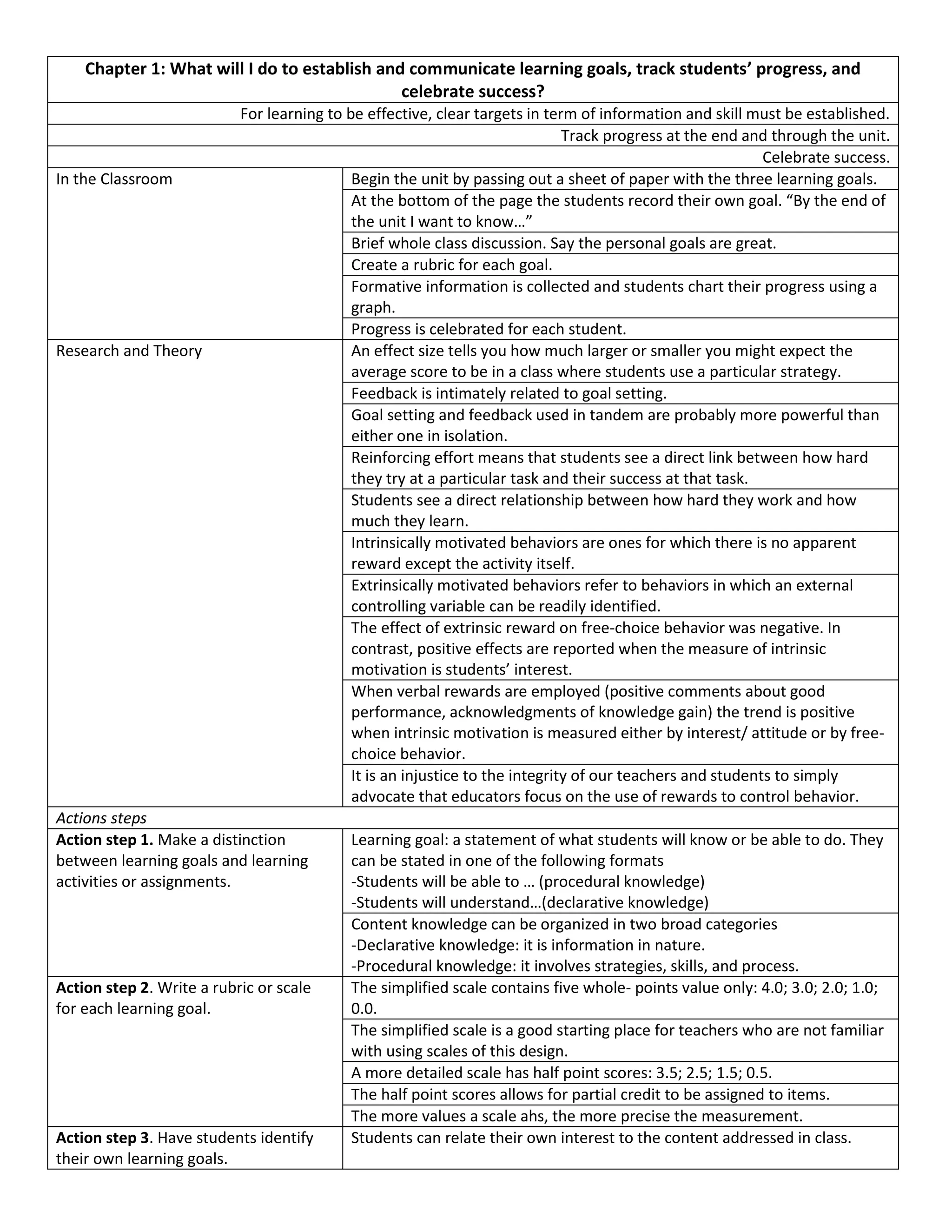
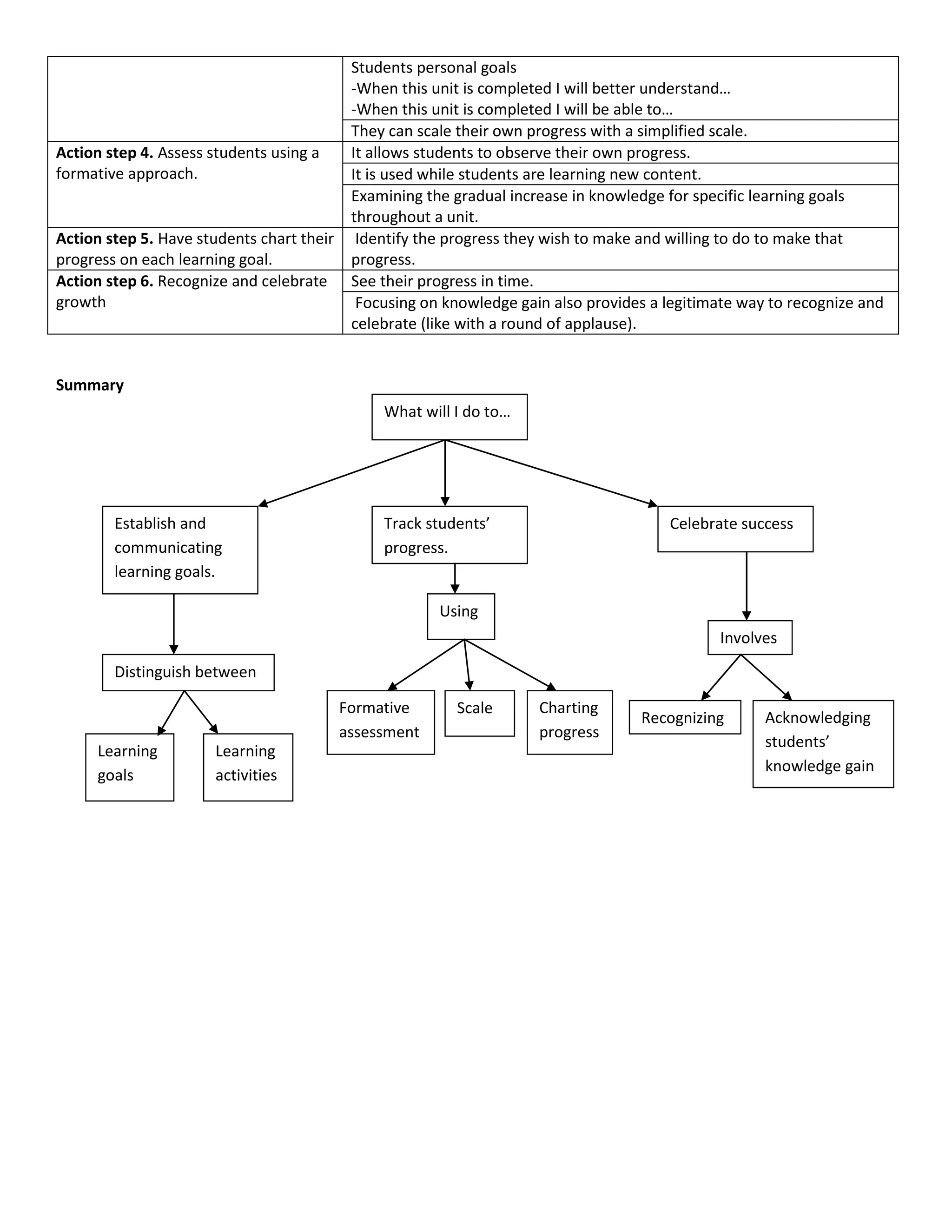
Establish and communicate learning goals using rubrics and scales. Track students' progress through formative assessment and having students chart their own progress. Celebrate success by recognizing and acknowledging students' knowledge gain and progress towards learning goals.