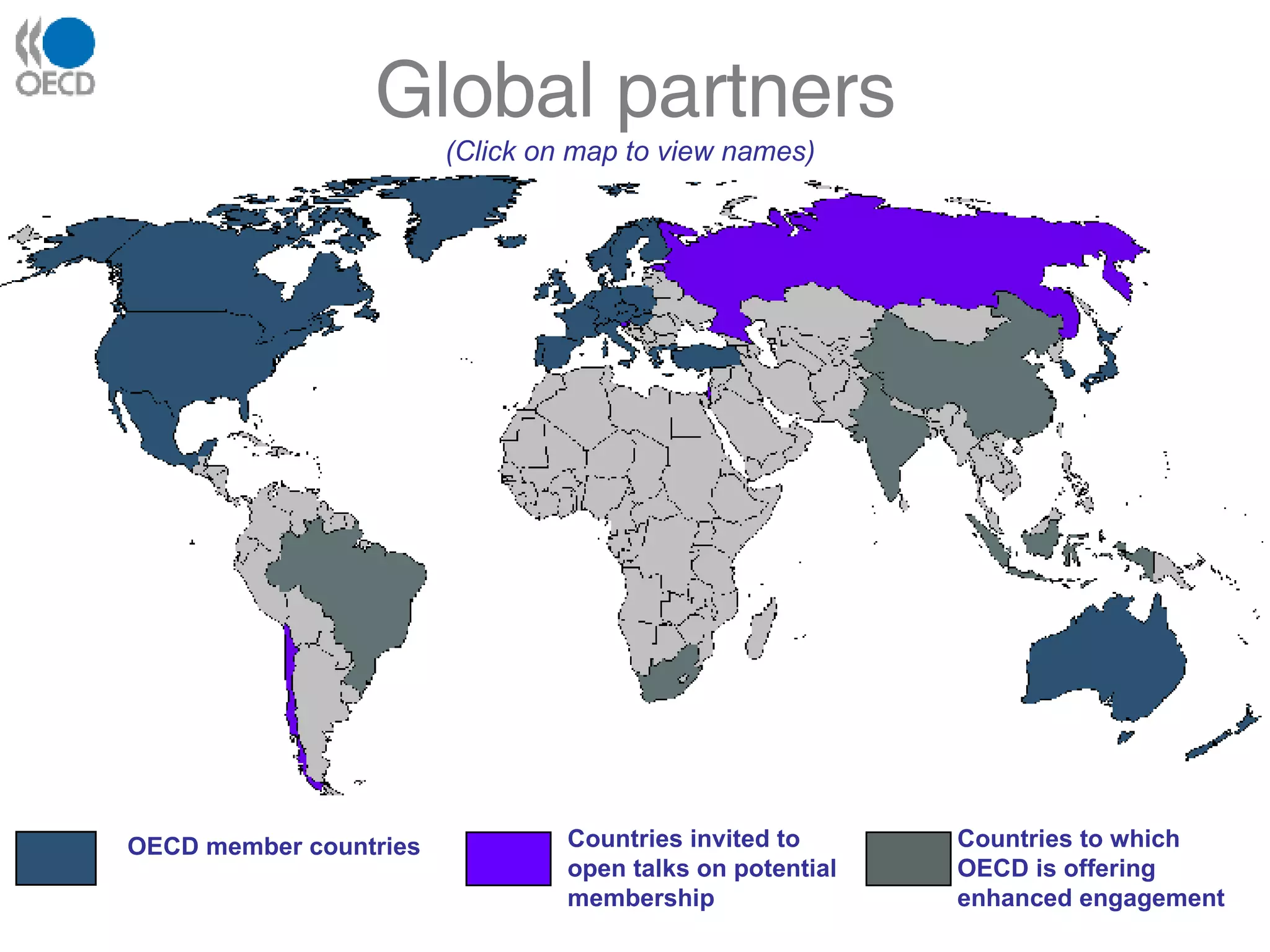
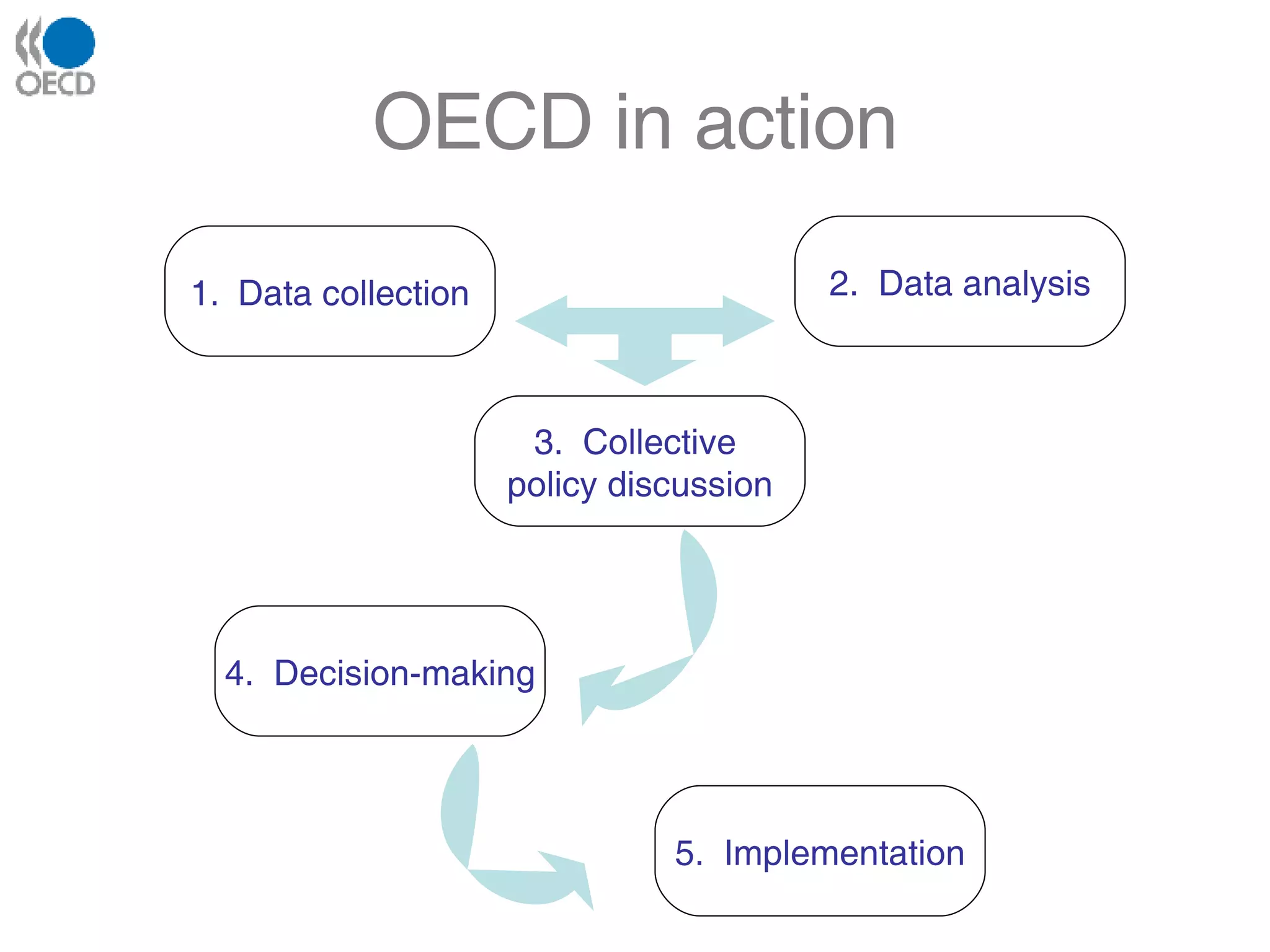
The OECD is an intergovernmental economic organization with 30 member countries that aims to stimulate economic progress and world trade. It provides statistics and analysis to compare policy experiences between countries. The OECD works with governments to find policies that improve economic and social well-being in areas like employment, education, innovation, and sustainable development. The organization is overseen by representatives from member countries and operates with the goals of supporting economic growth while also raising living standards.