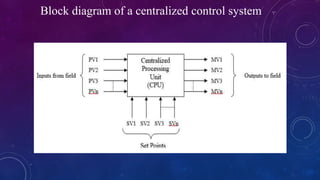
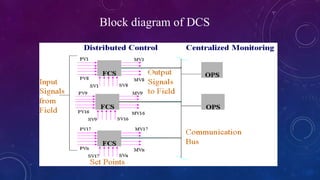
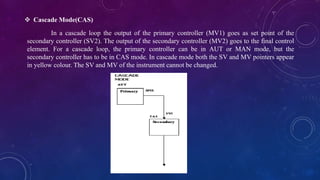
This document provides an overview of distributed control systems (DCS). It defines a DCS as a control system with distributed controllers located throughout the system to control subsystems, using proprietary communication protocols. The document describes the basic components of a DCS including field control stations, operator stations, and communication buses. It also outlines the different types of controller modes in a DCS.