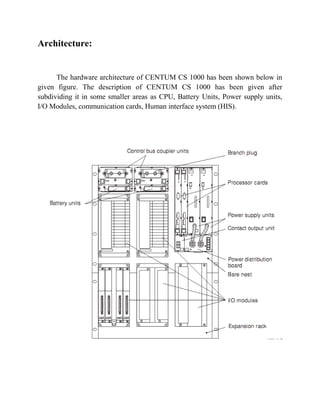
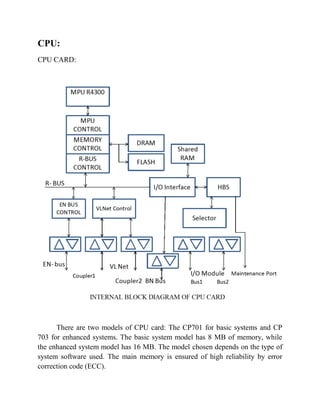
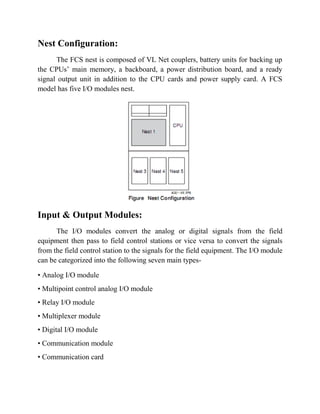
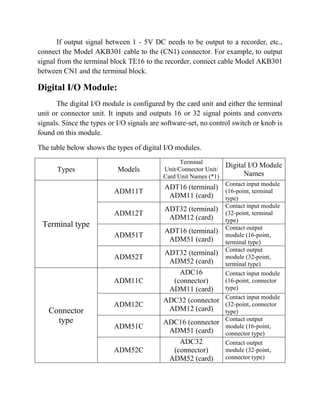
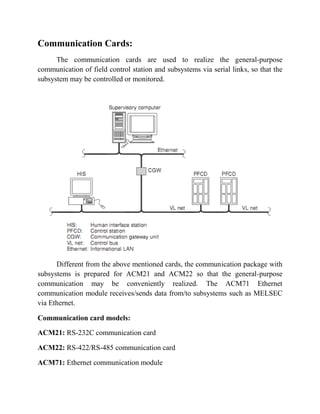
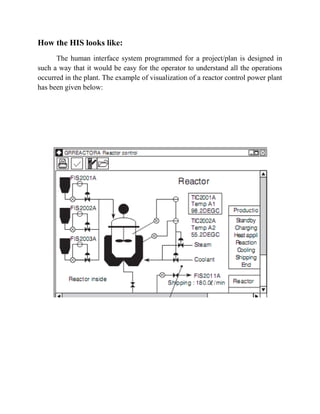
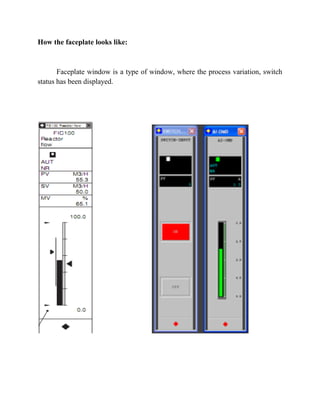
The document describes a distributed control system (DCS) used to control manufacturing processes. A DCS uses distributed controllers connected by a network for communication and monitoring. It typically uses custom processors as controllers and proprietary protocols for communication. Key components include input/output modules, a central processor, communication cards and a human interface system for monitoring and operation. DCS systems are applied to control continuous or batch processes in various industries like power generation, environmental systems and traffic control.