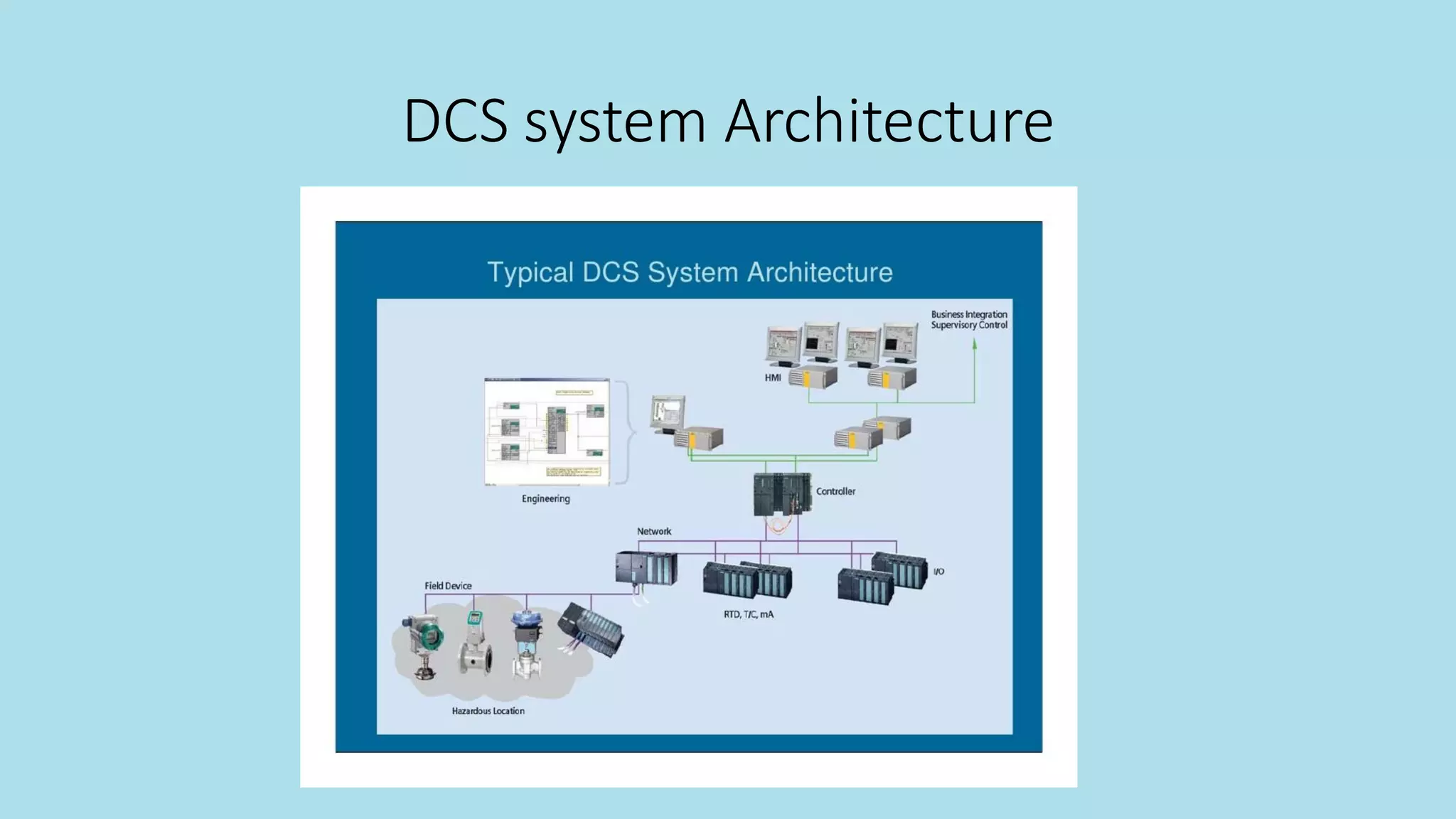
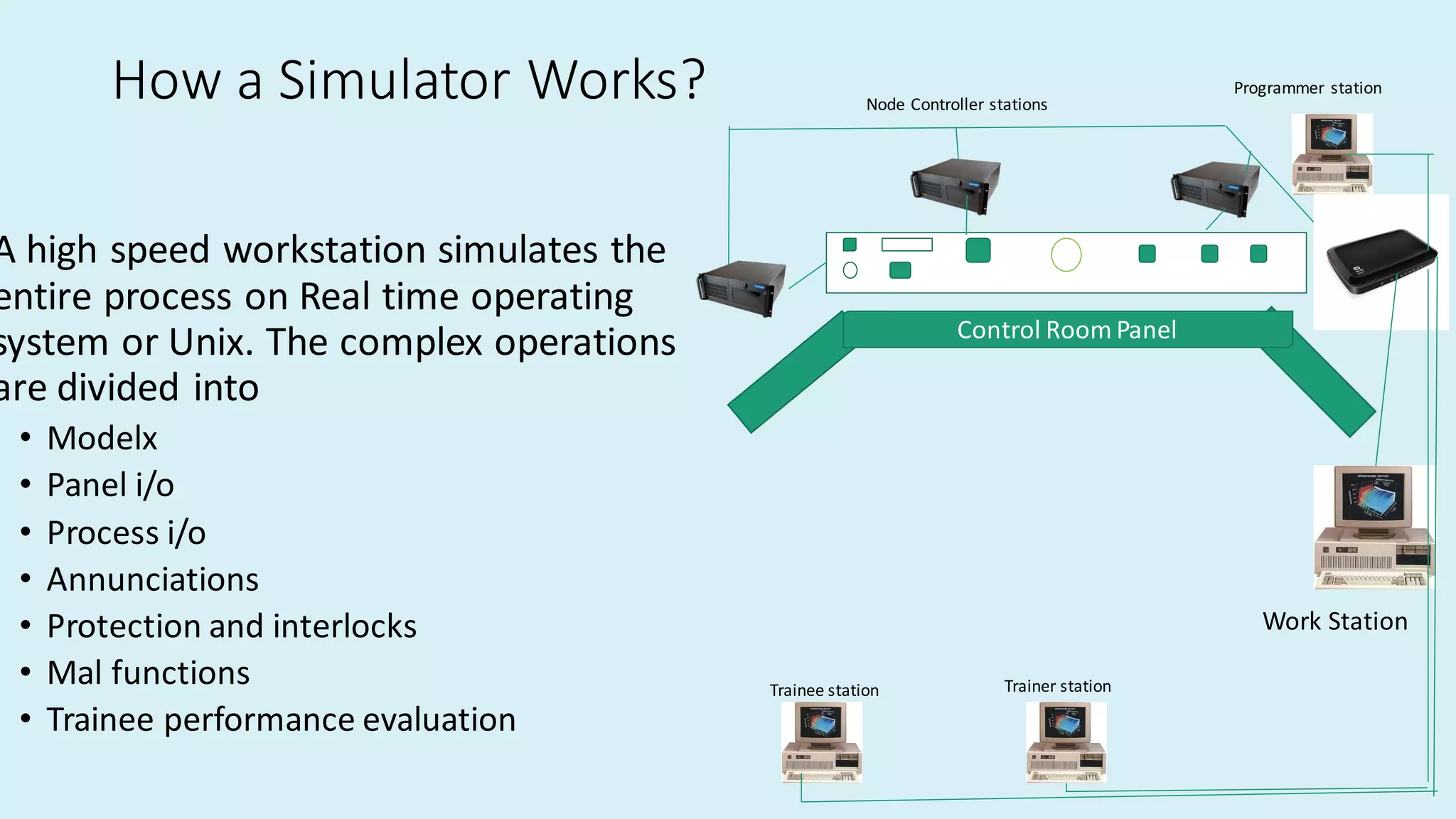
This document discusses intelligent instrumentation and power plant training simulators. It describes how instrumentation in power plants has advanced from pneumatic to digital controls using field bus technologies. Intelligent instruments now have self-check and control capabilities. Power plant simulators provide realistic replicas of control rooms to train operators. Simulators allow operators to practice responding to malfunctions and other scenarios in a risk-free environment. They provide advantages like backtracking, initializing conditions, and evaluating trainee performance. Overall, intelligent instruments and simulators have enhanced power plant monitoring, control, and training.