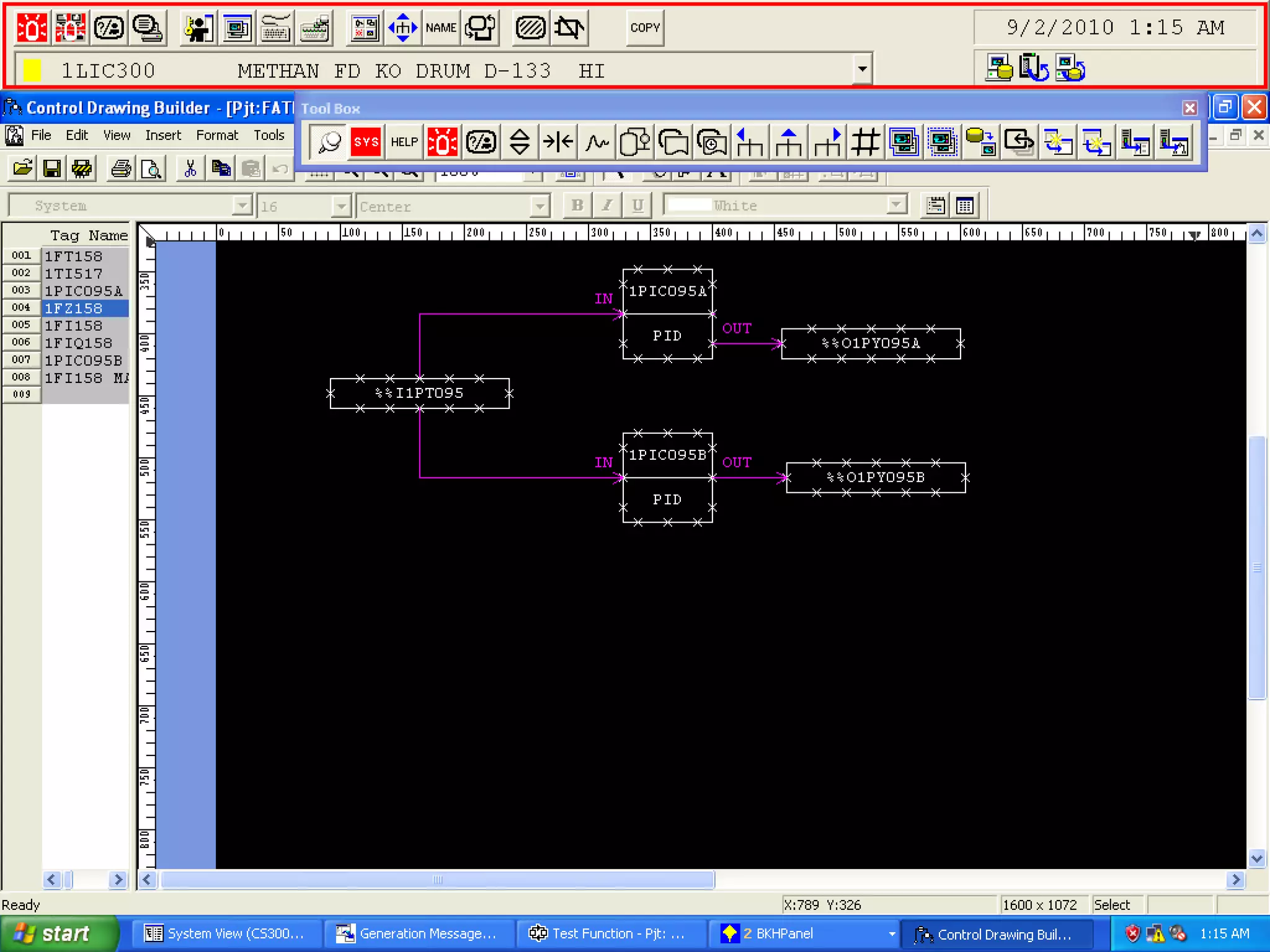
The document discusses control systems and their components. It provides information on distributed control systems (DCS), explaining that they are decentralized control systems with controller elements distributed throughout the system. It then describes the CENTUM CS 3000 system, including that it is Yokogawa's first DCS and its components like the Human Interface Station and Field Control Station. It also discusses communication components of DCS systems like Vnet/IP networks.