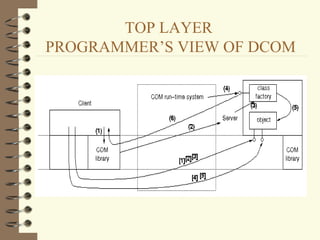
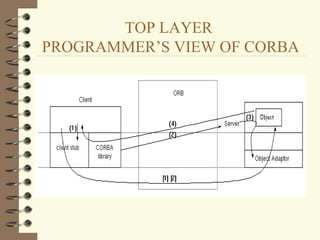
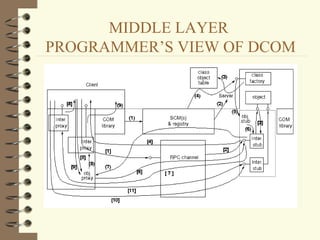
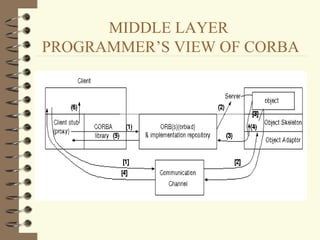
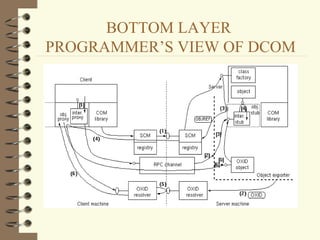
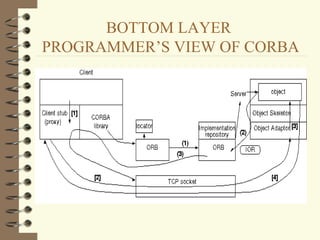
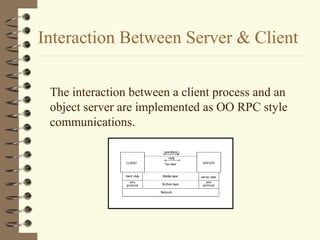
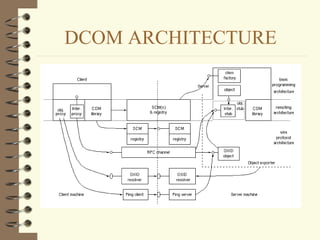
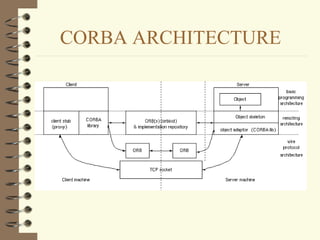
DCOM and CORBA are distributed object computing architectures that allow objects to communicate remotely. Both use a three-layer architecture - a top layer for programming interfaces, a middle remoting layer, and a bottom wire protocol layer. Key differences are that DCOM supports multiple interfaces per object while CORBA inherits all interfaces from a common base class, and DCOM's wire protocol is tied to RPC while CORBA's is not. Overall they provide similar distributed object capabilities with some differences in implementation details.









![DCOM IDL CORBA IDL
// definition of IGrid1 interface grid1
[ object, uuid(3CFDB283-CCC5-11D0-BA0B-00A0C90DF8BC), {
helpstring("IGrid1 Interface"), pointer_default(unique) long get(in short n, in short m);
] void set(in short n, in short m, in long
interface IGrid1 : IUnknown { value);
};
import "unknwn.idl";
interface grid2
HRESULT get([in] SHORT n, [in] SHORT m, [out] LONG *value);
{
HRESULT set([in] SHORT n, [in] SHORT m, [in] LONG value);
void reset(in long value);
}; };
// definition of IGrid2 interface grid: grid1, grid2
[ object, uuid(3CFDB284-CCC5-11D0-BA0B-00A0C90DF8BC),
helpstring("IGrid2 Interface"), pointer_default(unique)
]
interface IGrid2 : IUnknown {
import "unknwn.idl";
HRESULT reset([in] LONG value);
};
//uuid and definition of type library
[ uuid(3CFDB281-CCC5-11D0-BA0B-00A0C90DF8BC),
version(1.0), helpstring("grid 1.0 Type Library)
]
library GRIDLib
{
importlib("stdole32.tlb");
// definition of the component
[ uuid(3CFDB287-CCC5-11D0-BA0B-00A0C90DF8BC),
helpstring("Grid Class")
]
coclass CGri
{ [default] interface IGrid1;
interface IGrid2;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dcomvs-corba-130409103338-phpapp02/85/Dcom-vs-corba-14-320.jpg)