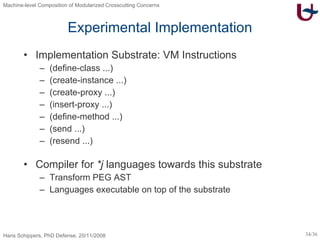
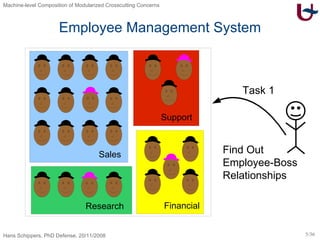
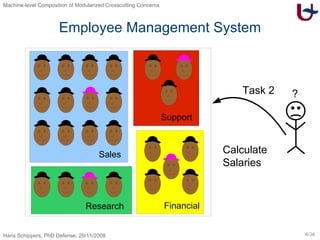
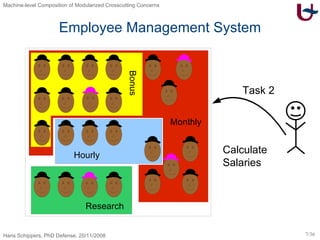
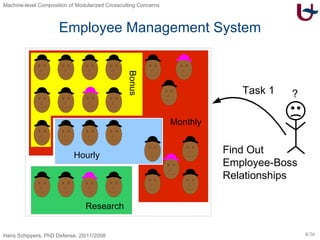
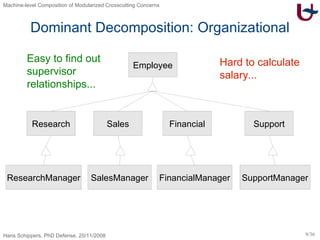
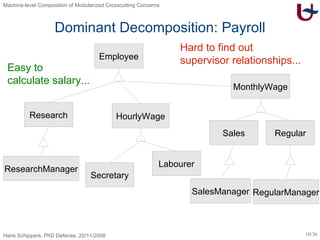
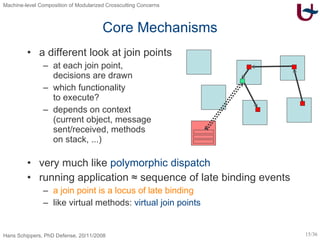
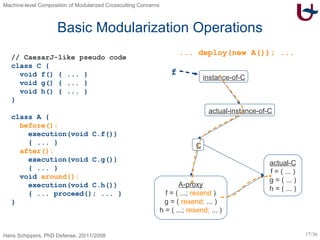
The document discusses different approaches to modularizing crosscutting concerns in software, including object-oriented programming (j), inter-type declarations (ij), aspect-oriented programming using pointcuts and advice (aj), and context-oriented programming (cj). It proposes a dedicated machine model based on objects and delegation as a core mechanism to support modularization at the machine level.



![State-of-the-Art: Weaving... Source Code Level [EAOP] Byte Code Level [AspectJ, Steamloom] ----- Application Level [EAOP, AspectJ] Machine Level [Steamloom]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presentationonly-123082080217-phpapp03/85/Machine-level-Composition-of-Modularized-Crosscutting-Concerns-13-320.jpg)

![A Dedicated Machine Model core concepts: objects and delegation [ECOOP 07] each application object, internally, consists of two a proxy (a mere placeholder ) and the actual object other application objects only directly see the proxy access to properties only via messages classes and instances classes are also represented by objects, also have a proxy instances reference the proxy only delegation ensures correct binding of self self object actual-object foo = ( ... ) bar = 23 delegate instance-of-C actual-instance-of-C v = 23 C actual-C m = ( ... ) m](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presentationonly-123082080217-phpapp03/85/Machine-level-Composition-of-Modularized-Crosscutting-Concerns-16-320.jpg)

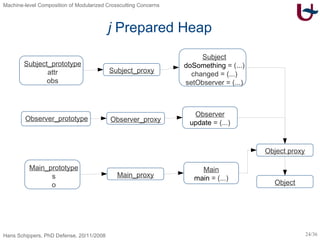
![j – Object-Oriented Programming [Skipper04] class Subject ext Object { Integer attr Observer obs void doSomething(Object x) { this.attr := 25 } void changed(Object x) { this.obs.update(this) } void setObserver(Observer x) { this.obs := x } } class Observer ext Object { void update(Subject x) { out.println(x.attr) } } class Main ext Object { Subject s Observer o void main(Main x) { x.s := new Subject; x.o := new Observer; x.s.setObserver(x.o); x.s.doSomething(null); x.s.changed(null) } }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presentationonly-123082080217-phpapp03/85/Machine-level-Composition-of-Modularized-Crosscutting-Concerns-23-320.jpg)
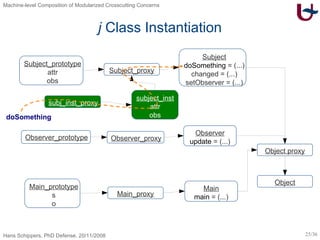
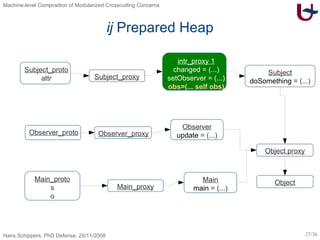
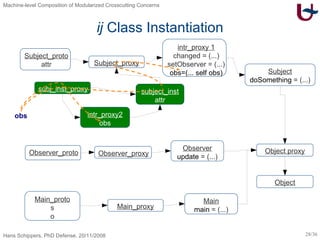
![ij – Inter-Type Declarations [Skipper04] class Observer ext Object { void update(Subject x) { out.println(x.attr) } Subject <-- Observer obs Subject <-- void changed(Object x) { this.obs.update(this) } Subject <-- void setObserver(Observer x) { this.obs := x } } class Subject ext Object { Integer attr void doSomething(Object x) { this.attr := 25 } } class Main ext Object { Subject s Observer o void main(Main x) { x.s := new Subject; x.o := new Observer; x.s.setObserver(x.o); x.s.doSomething(null); x.s.changed(null) } }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presentationonly-123082080217-phpapp03/85/Machine-level-Composition-of-Modularized-Crosscutting-Concerns-26-320.jpg)
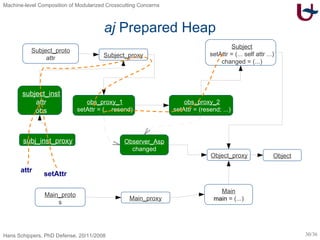
![aj – Pointcut and Advice AOP [Skipper04] class Subject ext Object { Integer attr void changed(Object x) { out.println(this.attr) } } aspect Observer { bool changed before set (Integer Subject.attr) { this.changed := v.neq(r.attr) } after set (Integer Subject.attr) { if (this.changed){ r.changed(null) } else { null } } } class Main ext Object { Subject s void main(Main x) { x.s := new Subject; x.s.attr := 25; } }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presentationonly-123082080217-phpapp03/85/Machine-level-Composition-of-Modularized-Crosscutting-Concerns-29-320.jpg)

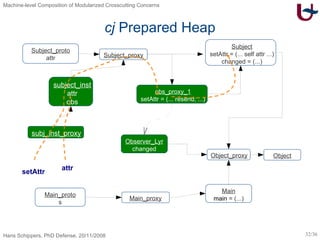
![Prototypical Implementation COLA Framework [Piumarta et al. ]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presentationonly-123082080217-phpapp03/85/Machine-level-Composition-of-Modularized-Crosscutting-Concerns-33-320.jpg)