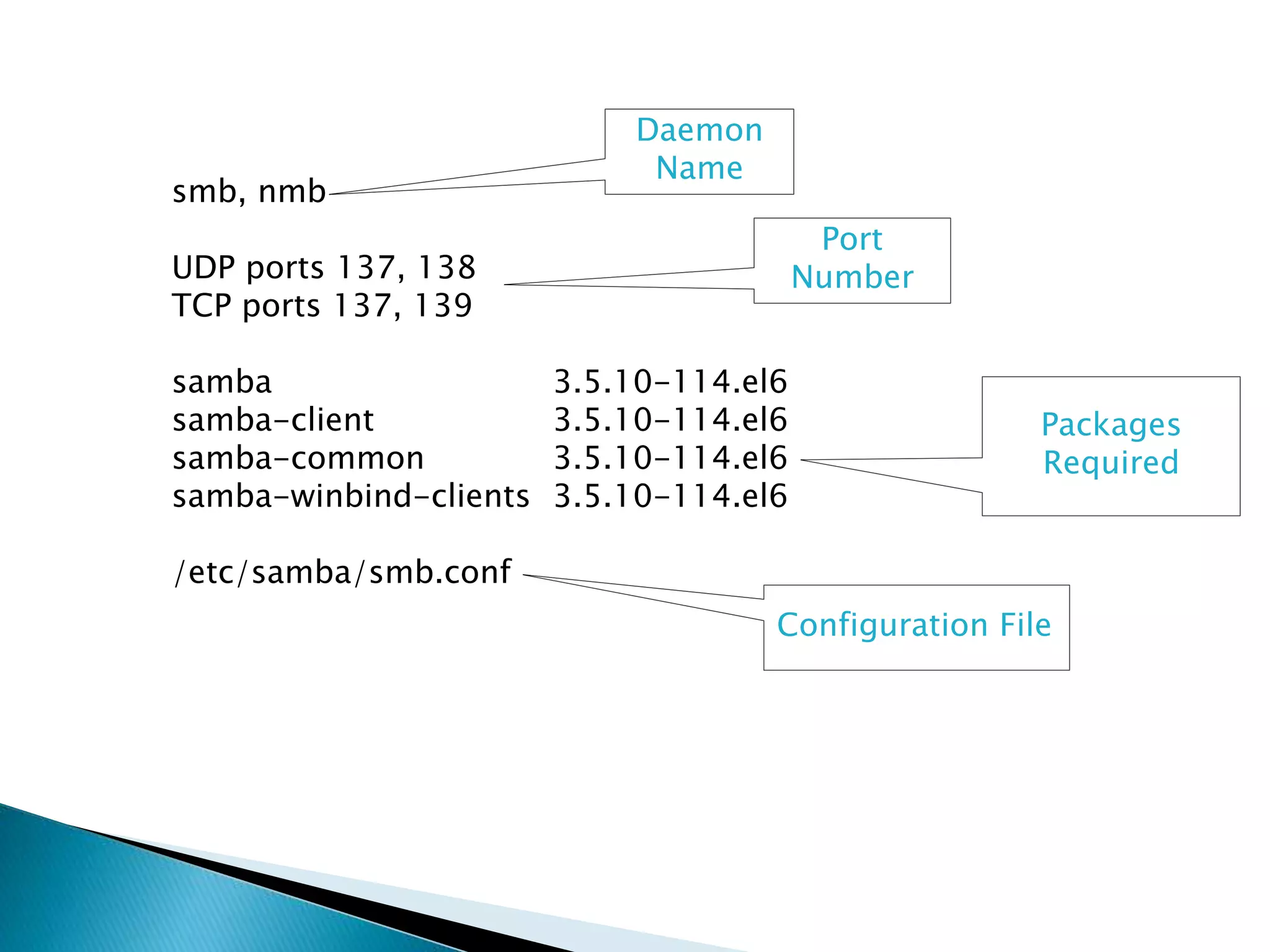
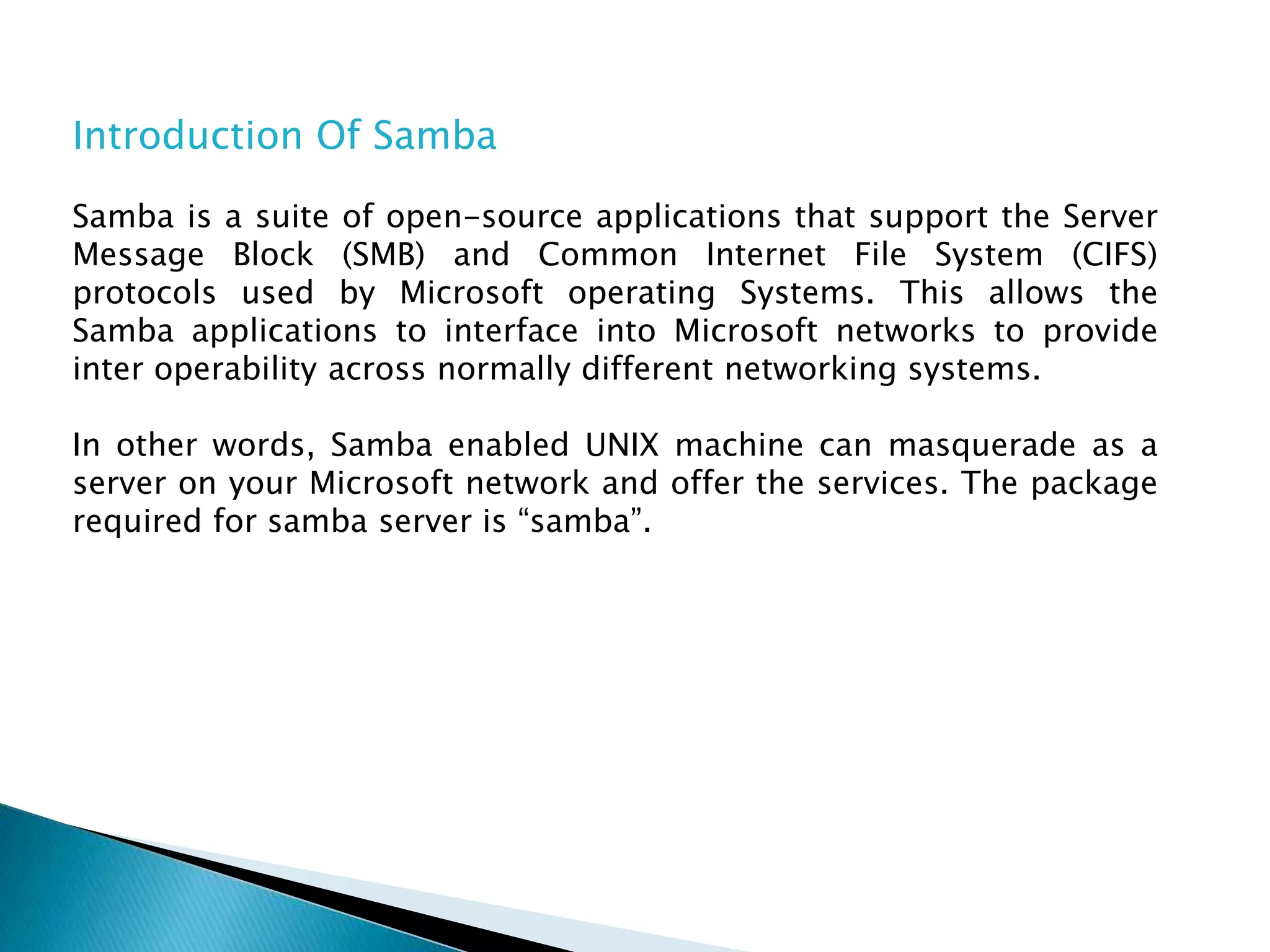
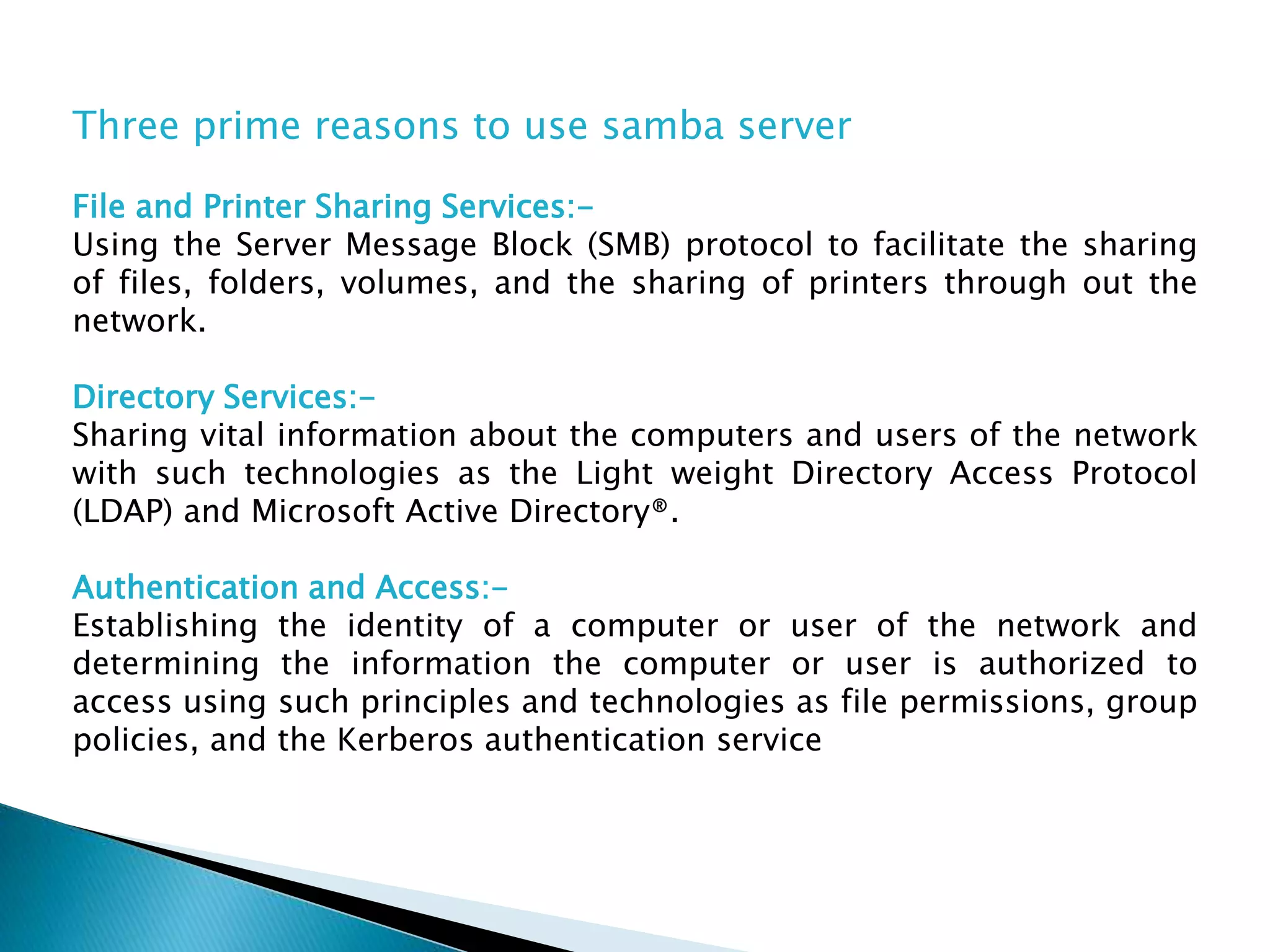
Samba allows UNIX machines to interface with Microsoft networks by supporting SMB and CIFS protocols. It provides file and printer sharing, directory services, and authentication/access control. Samba simulates a Windows domain server and works like a workgroup by default.
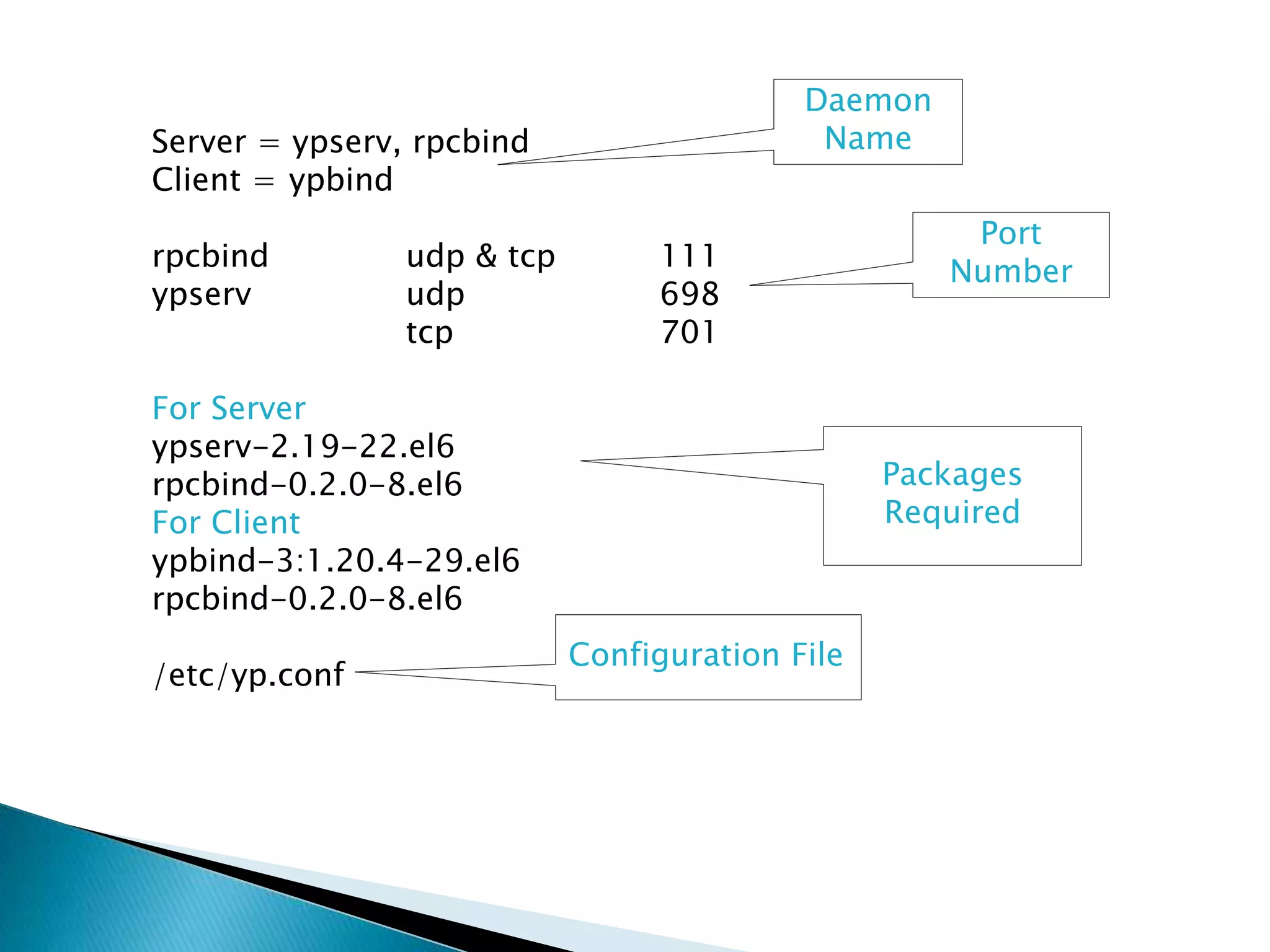
NIS enables centralized user authentication across networks by using a shared database. All systems can login with the same credentials and password changes are reflected everywhere. It was originally called Yellow Pages by Sun Microsystems.
DHCP automatically assigns IP addresses to devices on a network from a defined pool. It issues and manages IP addresses so they are not statically configured on each device.
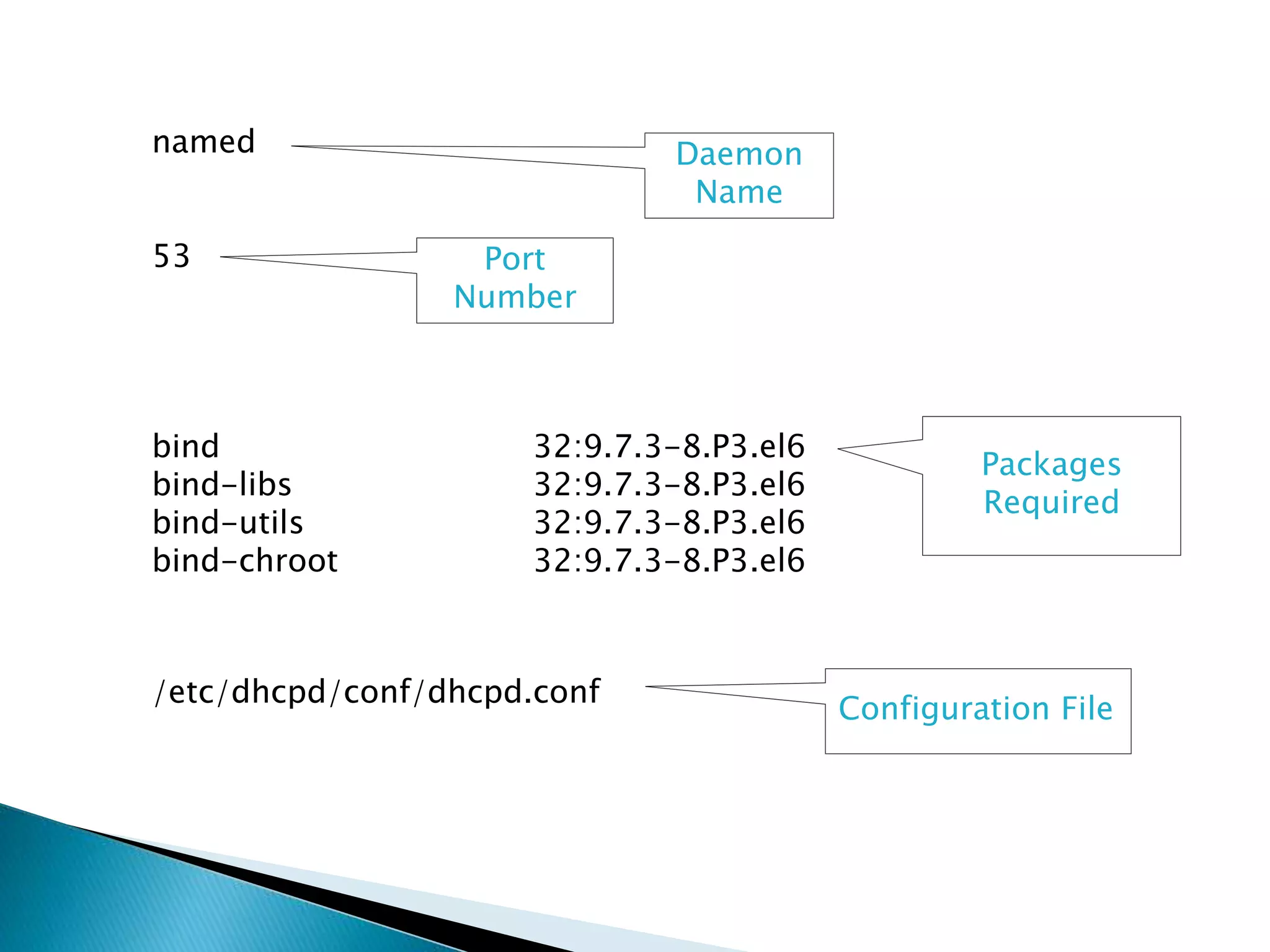
DNS translates human-friendly domain names to IP addresses so computers can communicate. If