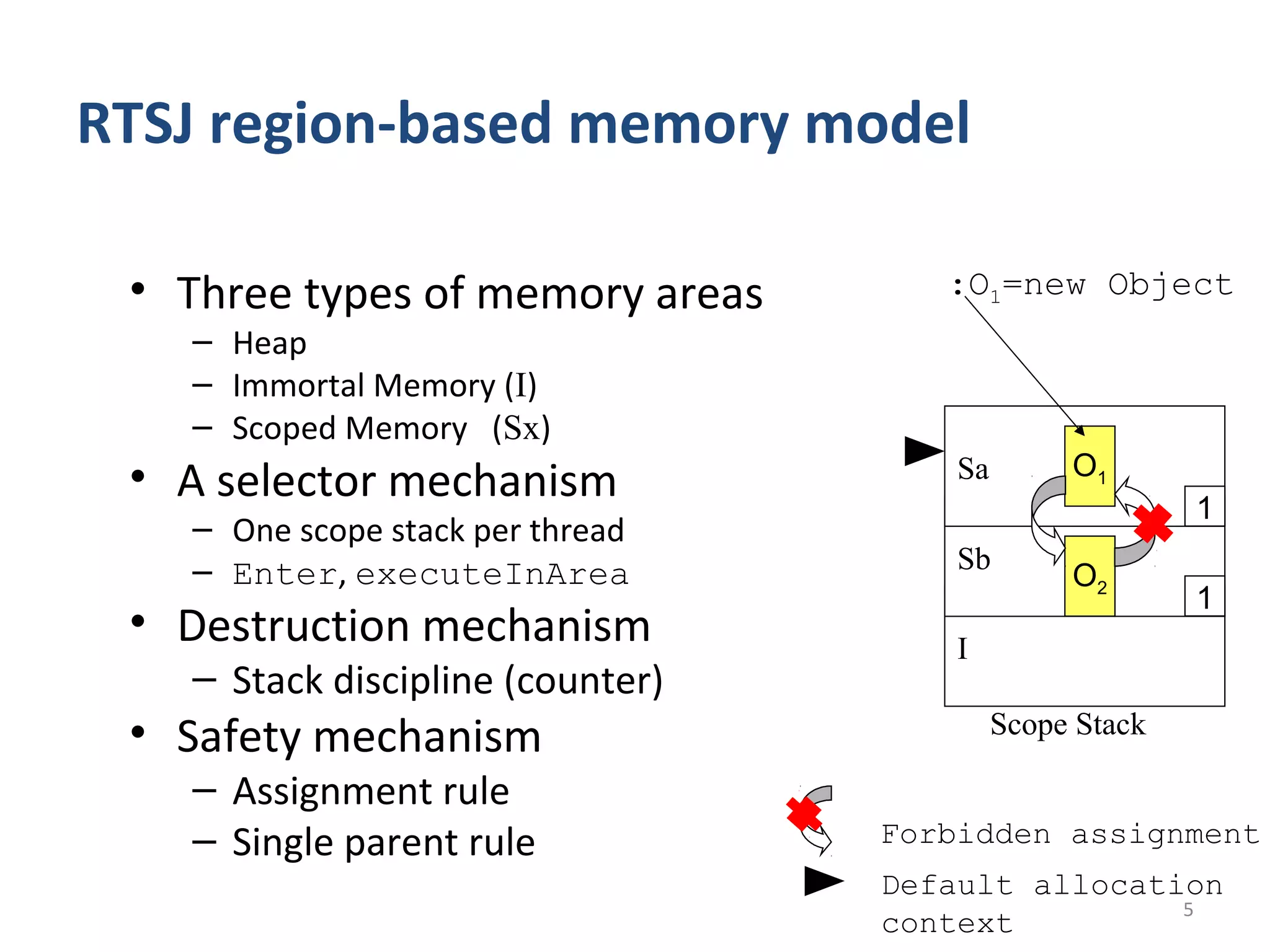
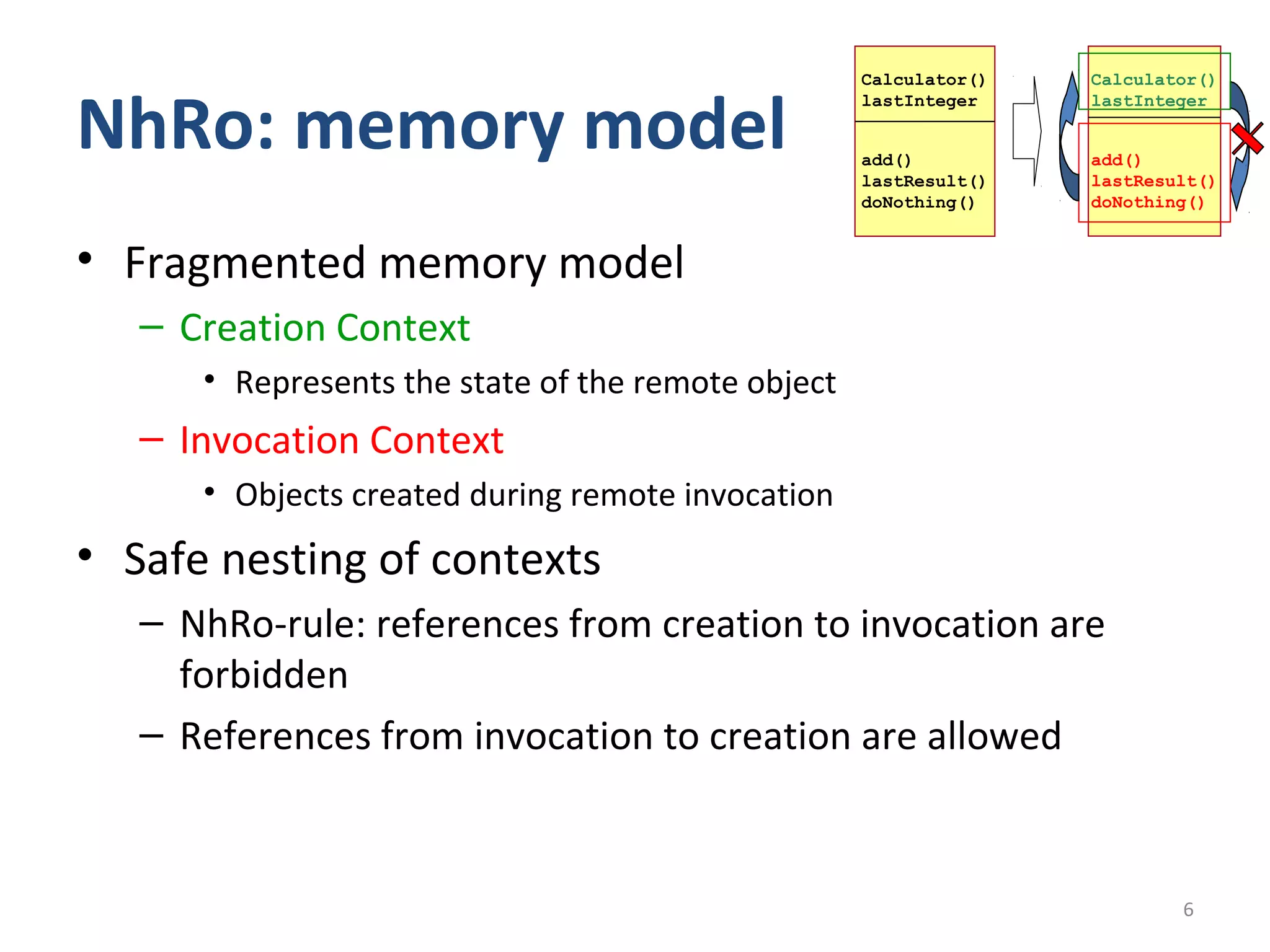
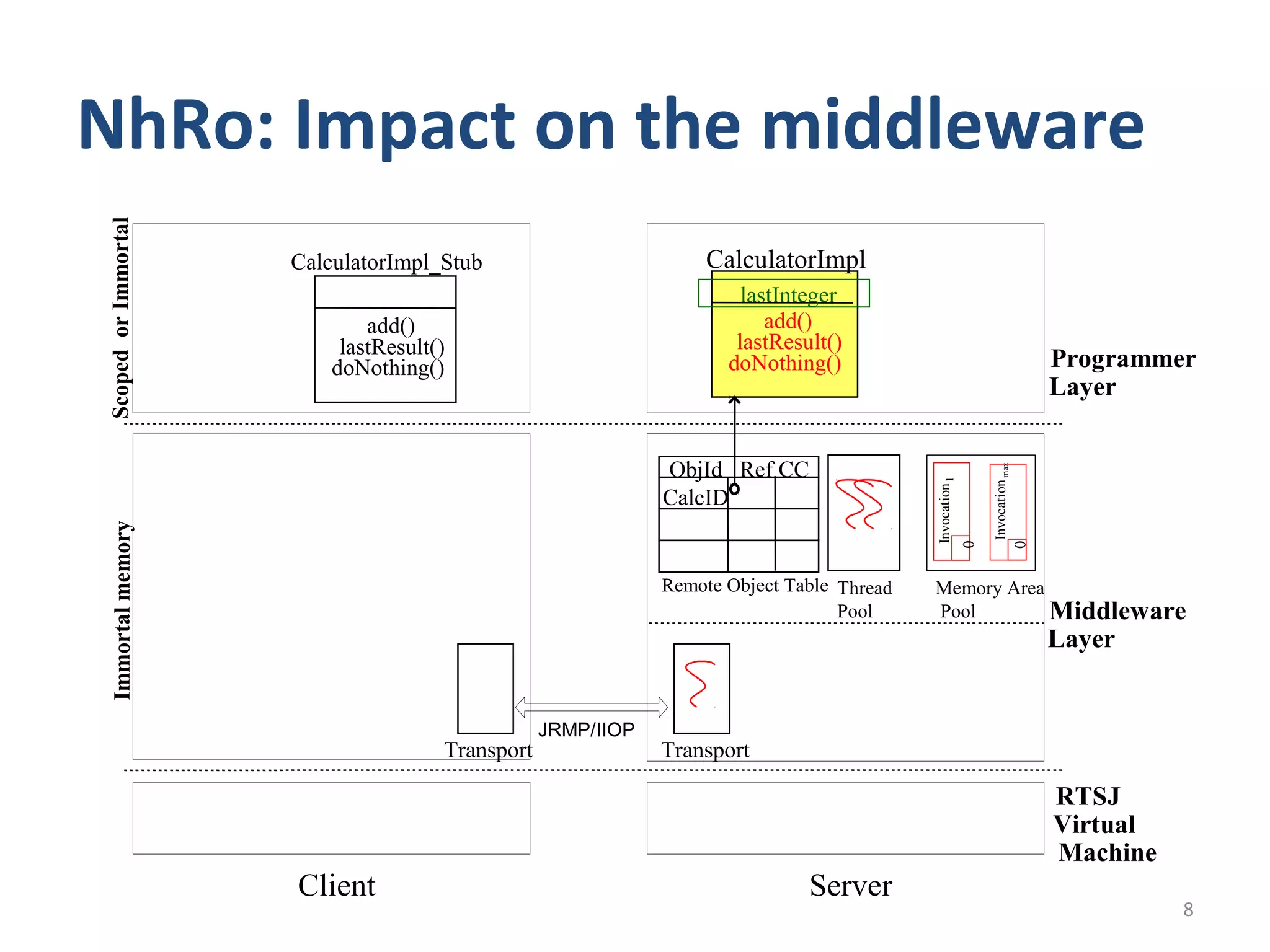
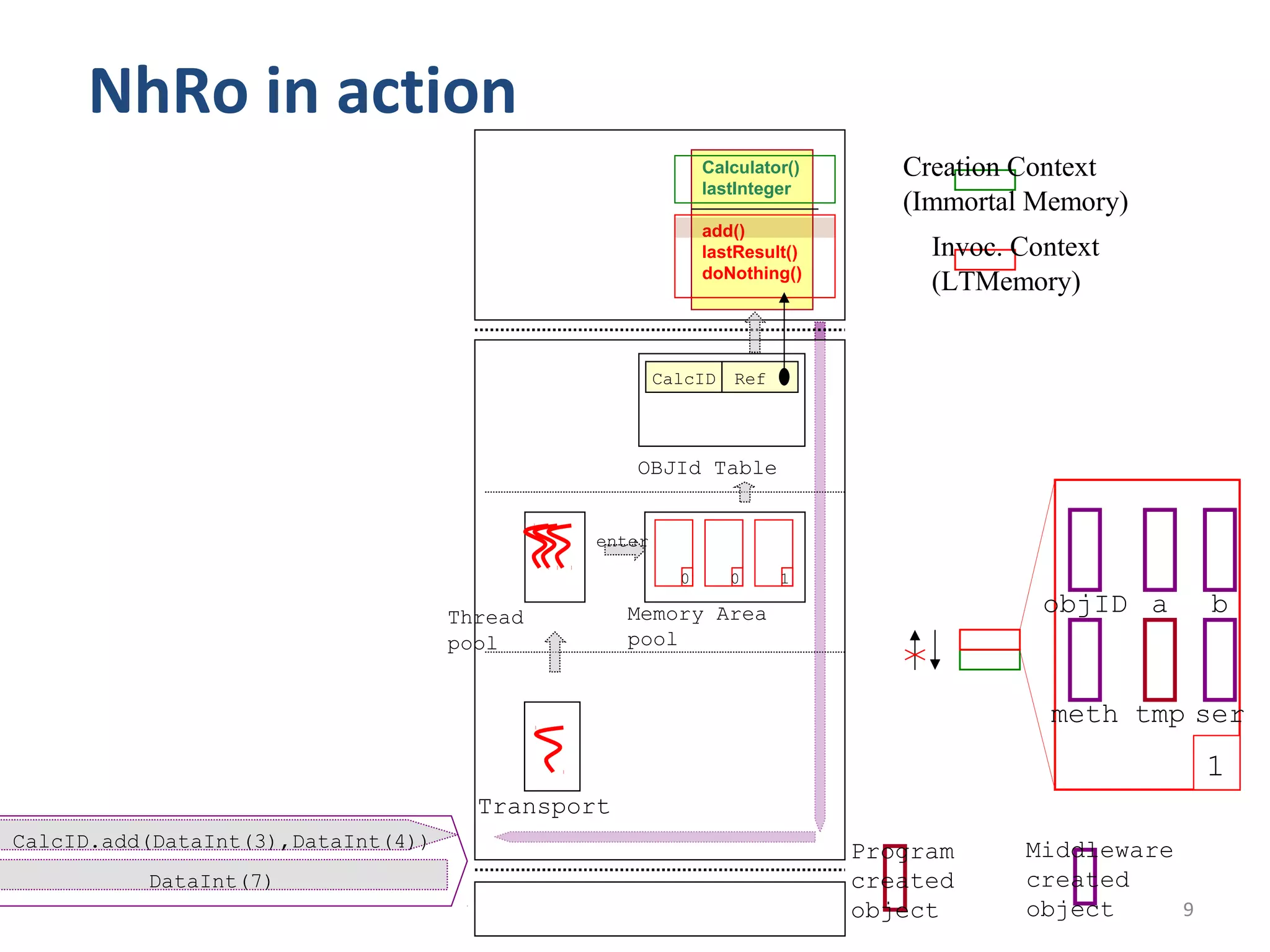
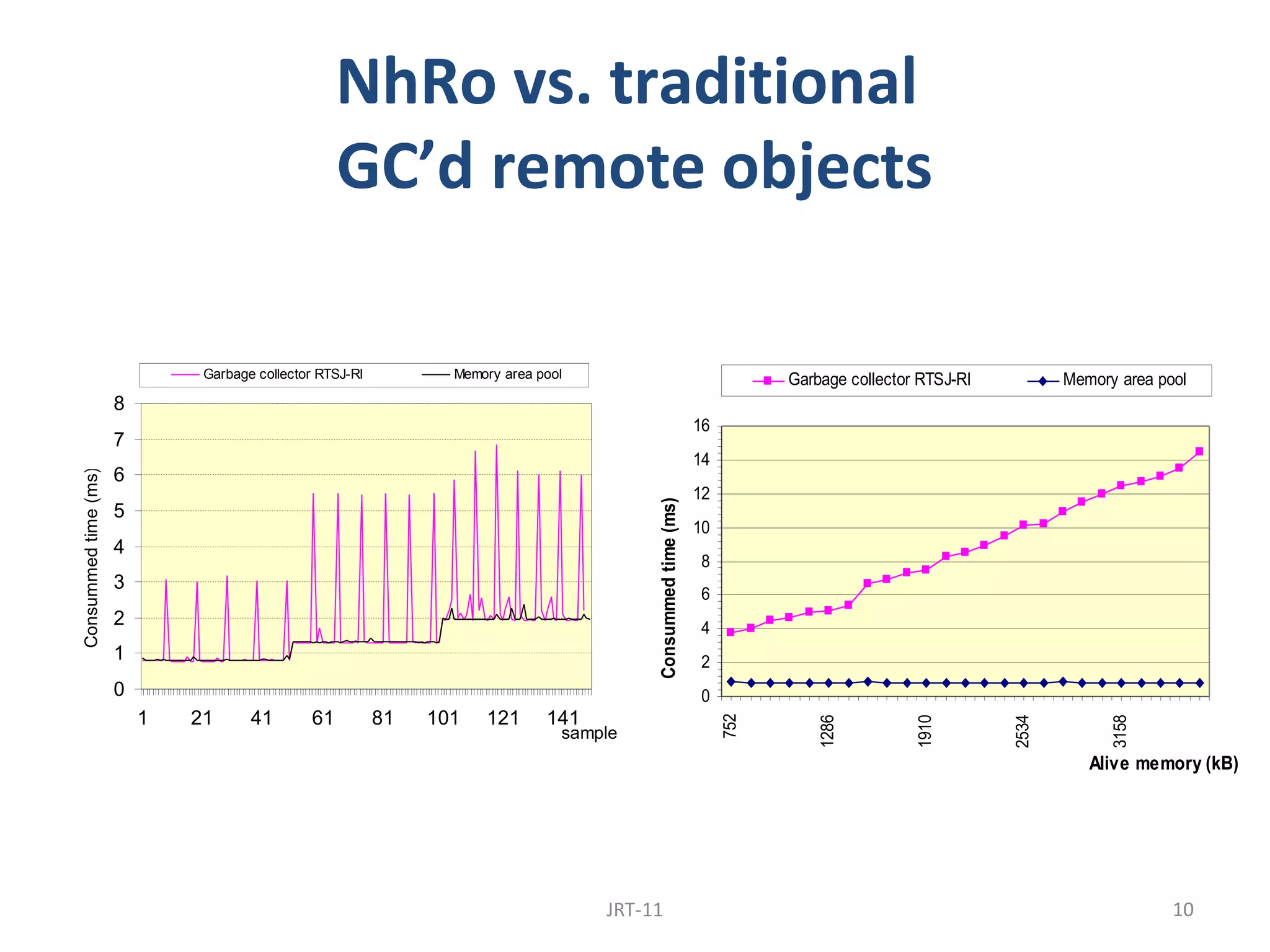
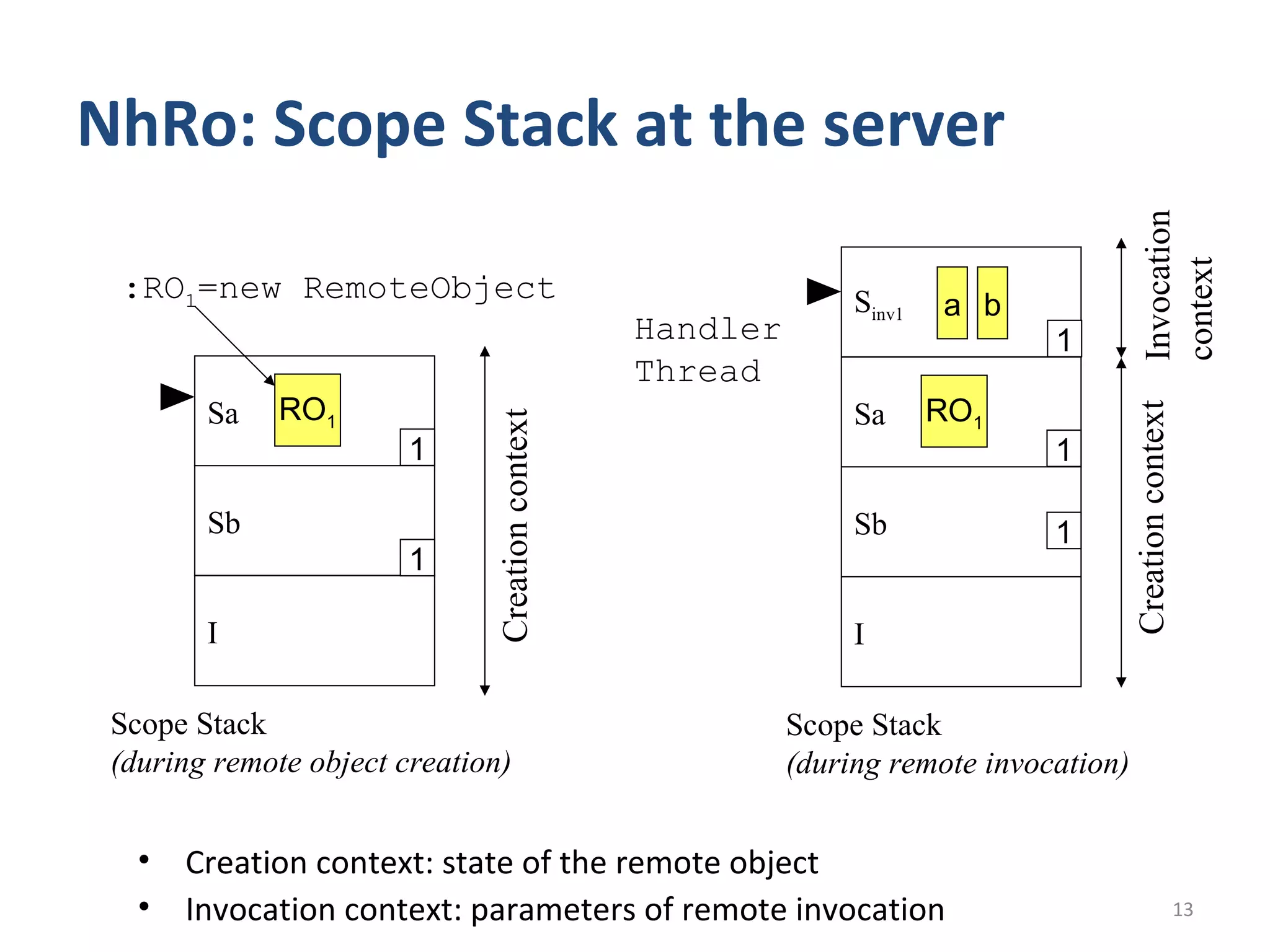
This document proposes a No Heap model for remote objects in distributed real-time Java systems. The model avoids garbage collection by containing objects within scoped memory areas. Remote objects have a creation context in immortal memory and invocation contexts in local temporary memory areas. This allows safe nesting of contexts by forbidding references from creation to invocation contexts while allowing references the other way. The model is compared to traditional garbage collected remote objects, showing it uses less time as it avoids garbage collection overhead.




![bytes
5000
0
10000
15000
20000
25000
30000
void
boolean
byte
char
short
int
long
float
double
null
Byte
Short
Integer
Long
Float
Double
Character
X
Boolean
RtUnRemOb
String()
JRT-11
String(10)
and LTMemory size
String(25)
String(50)
String(100)
Object[0]
Object[10D]
Object[25D]
Object[50D]
Object[100D]
Vector(0)
Vector(10D)
Vector(25D)
Vector(50D)
Vector(100D)
Remove invocation parameters
X echo(X)
X doNothing()
void doNothing(X)
16](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2011-jtr-pbasanta-noheap-130123023152-phpapp01/75/No-Heap-Remote-Objects-for-Distributed-real-time-Java-16-2048.jpg)
![NhRos vs. (RT*) Garbage Collectors [new]
JRT-11 17](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2011-jtr-pbasanta-noheap-130123023152-phpapp01/75/No-Heap-Remote-Objects-for-Distributed-real-time-Java-17-2048.jpg)