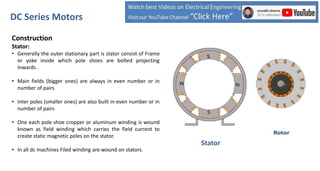
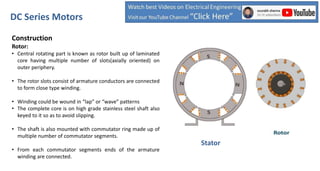
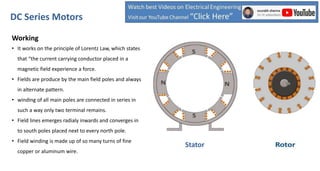
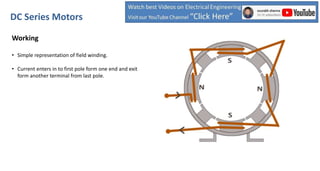
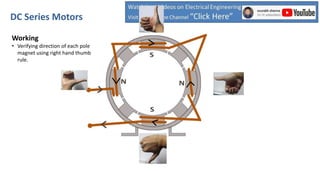
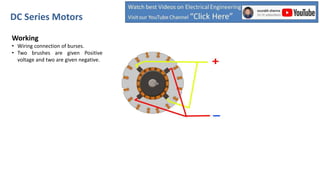
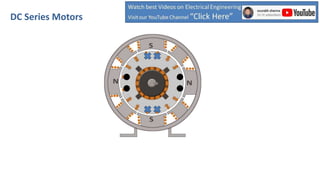
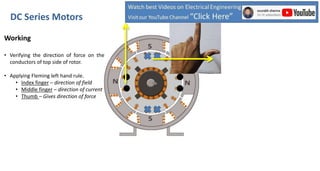
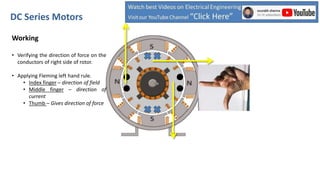
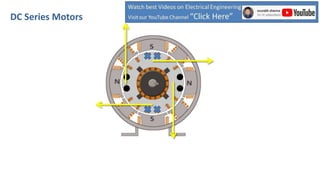
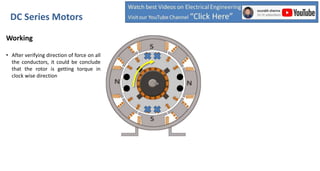
DC series motors are widely used in industrial applications due to their high starting torque, featuring a stator made of pole shoes and field windings, and a rotor with armature conductors. The motor operates on the Lorentz law, where current-carrying conductors in a magnetic field experience a force, allowing the rotor to turn. The rotor's rotation direction can be verified using Fleming's left-hand rule, which illustrates the relationship between magnetic field direction, current flow, and force exerted.