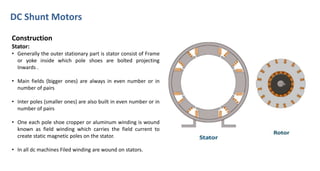
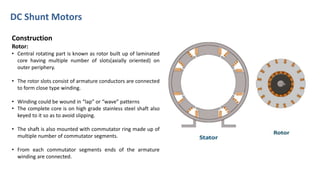
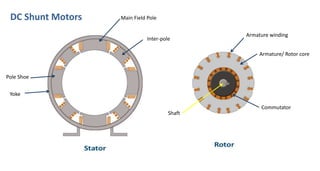
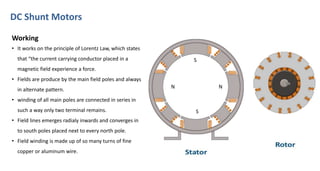
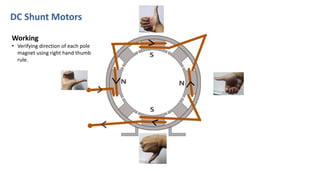
DC shunt motors are widely used in industrial applications due to their ability to maintain a constant speed under varying loads, making them ideal for devices like lathes and vacuum cleaners. Their construction involves a stator with field windings and a rotor featuring armature conductors, while operation is based on the Lorentz law where current-carrying conductors experience a force in a magnetic field. Key applications include various machines such as pumps, compressors, and woodworking tools.