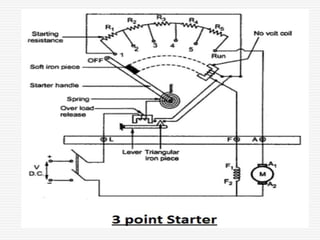
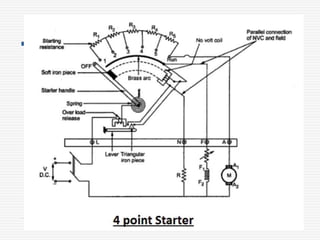
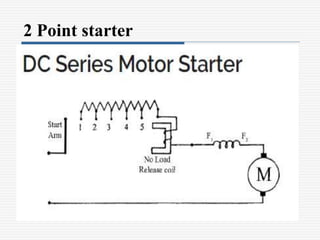
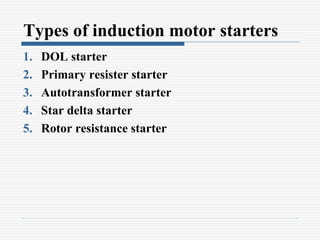
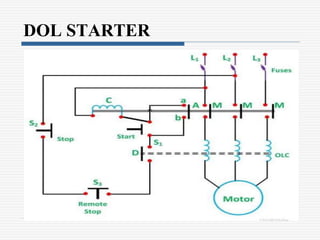
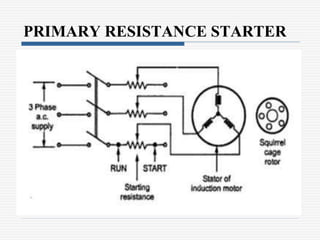
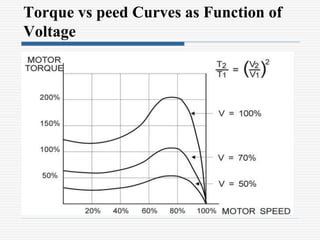
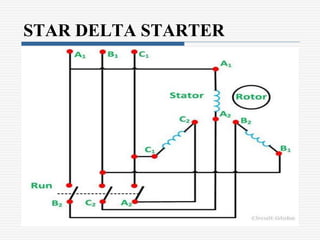
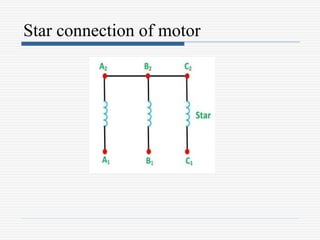
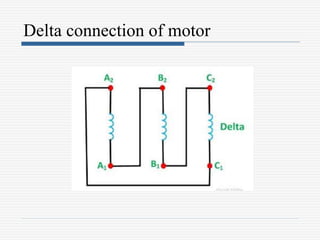
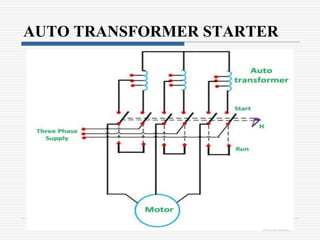
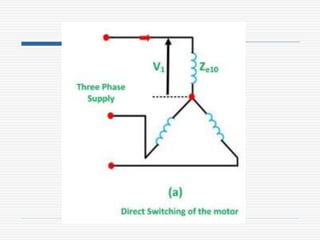
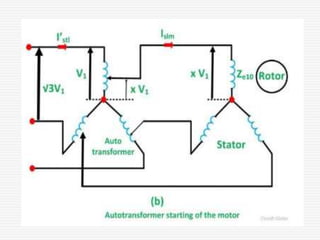
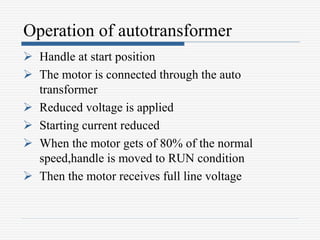
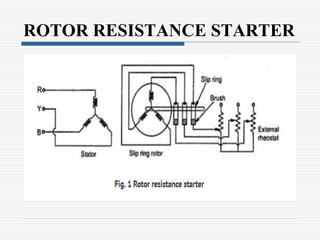
This document discusses different types of starters for DC motors and induction motors. For DC motors, it describes 3-point, 4-point, and 2-point starters. The 3-point and 4-point starters connect the armature, field, and supply. The 4-point adds a no-voltage coil terminal. The 2-point starter uses series resistance to reduce starting current. For induction motors, it discusses DOL, primary resistance, star-delta, autotransformer, and rotor resistance starters. The star-delta and autotransformer starters apply reduced voltage on start up to limit current. The rotor resistance starter connects external resistors to the rotor on start up. Assignment questions are provided to draw and explain examples of