Embed presentation
Downloaded 50 times

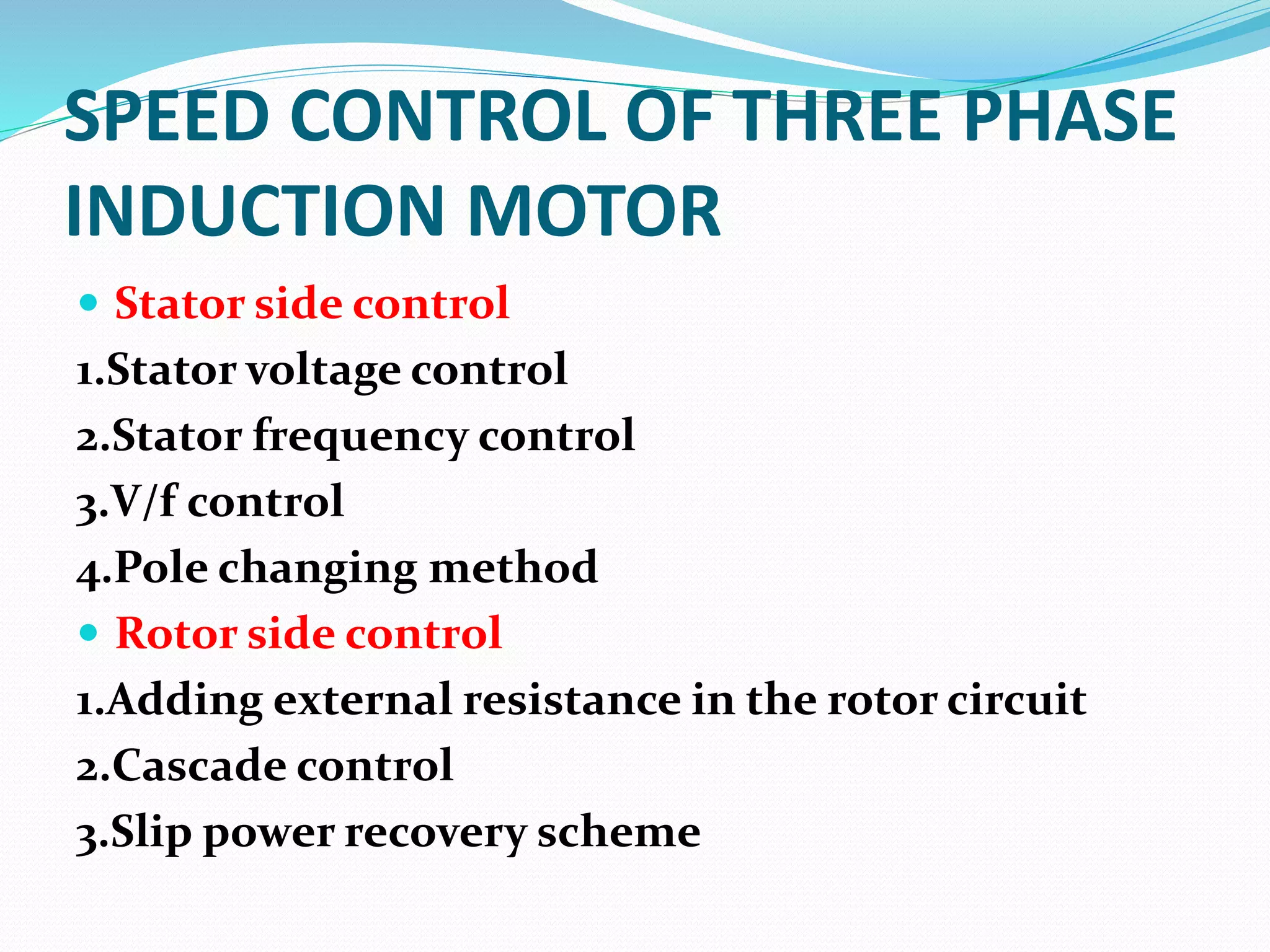
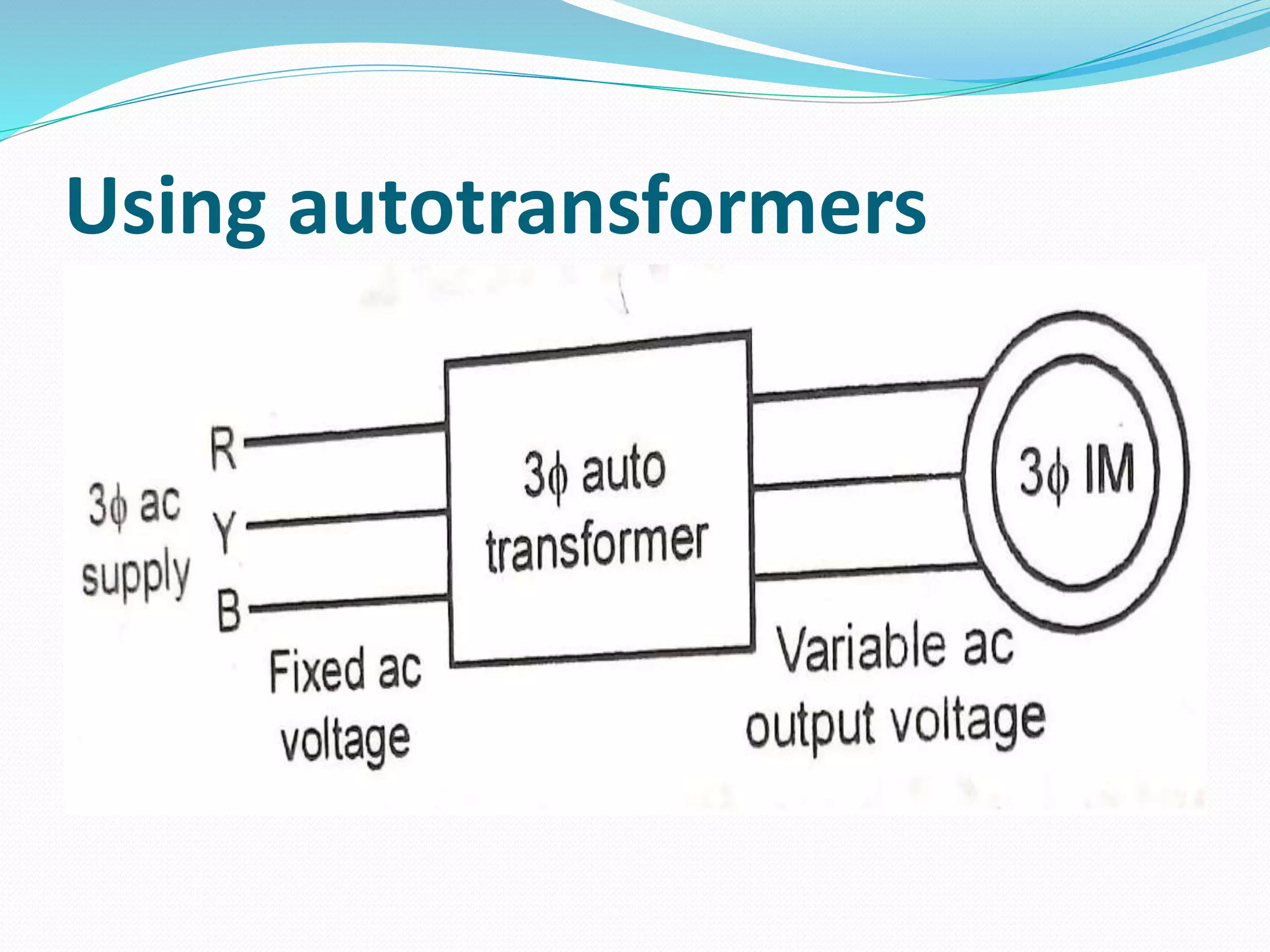
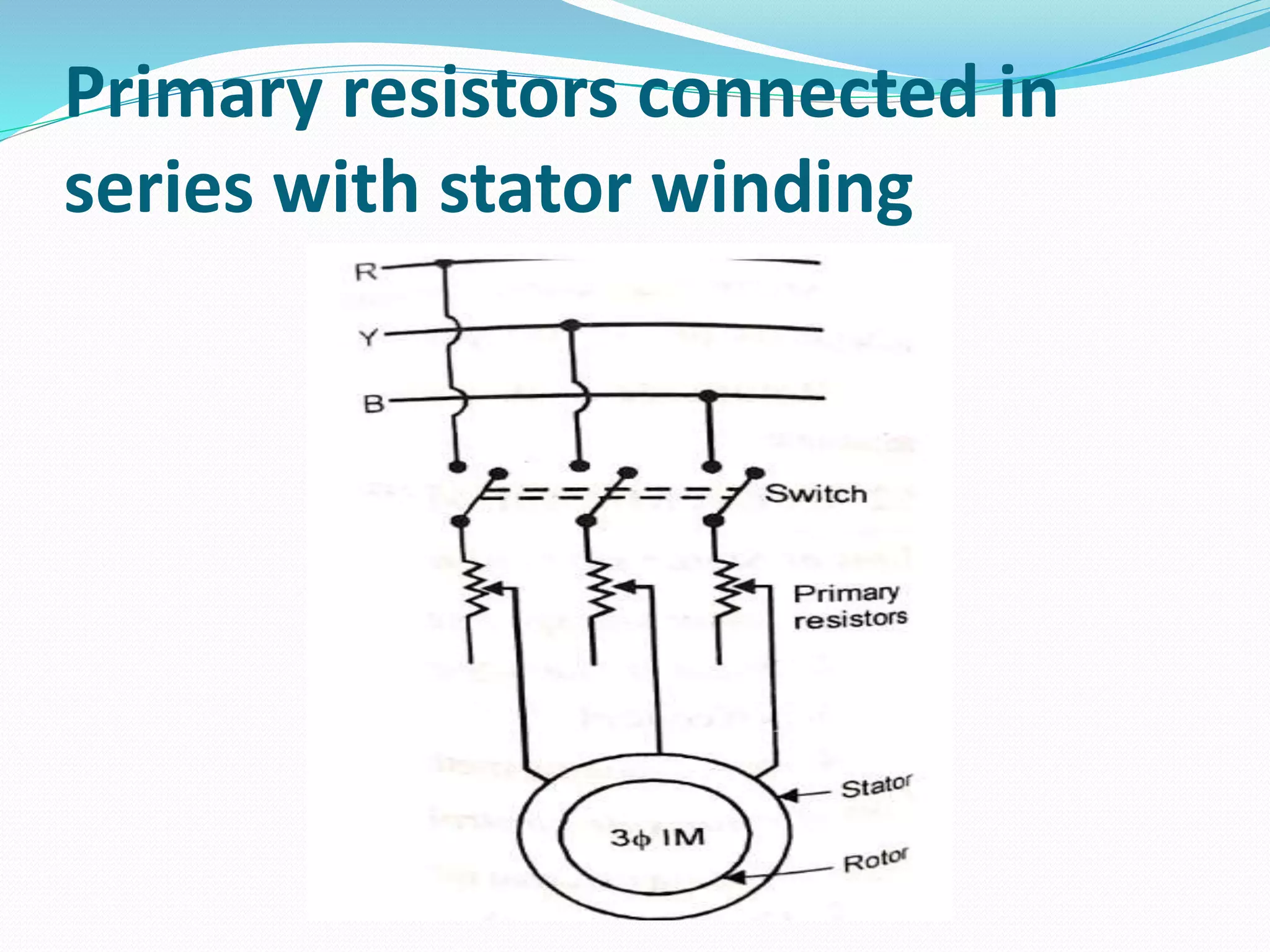
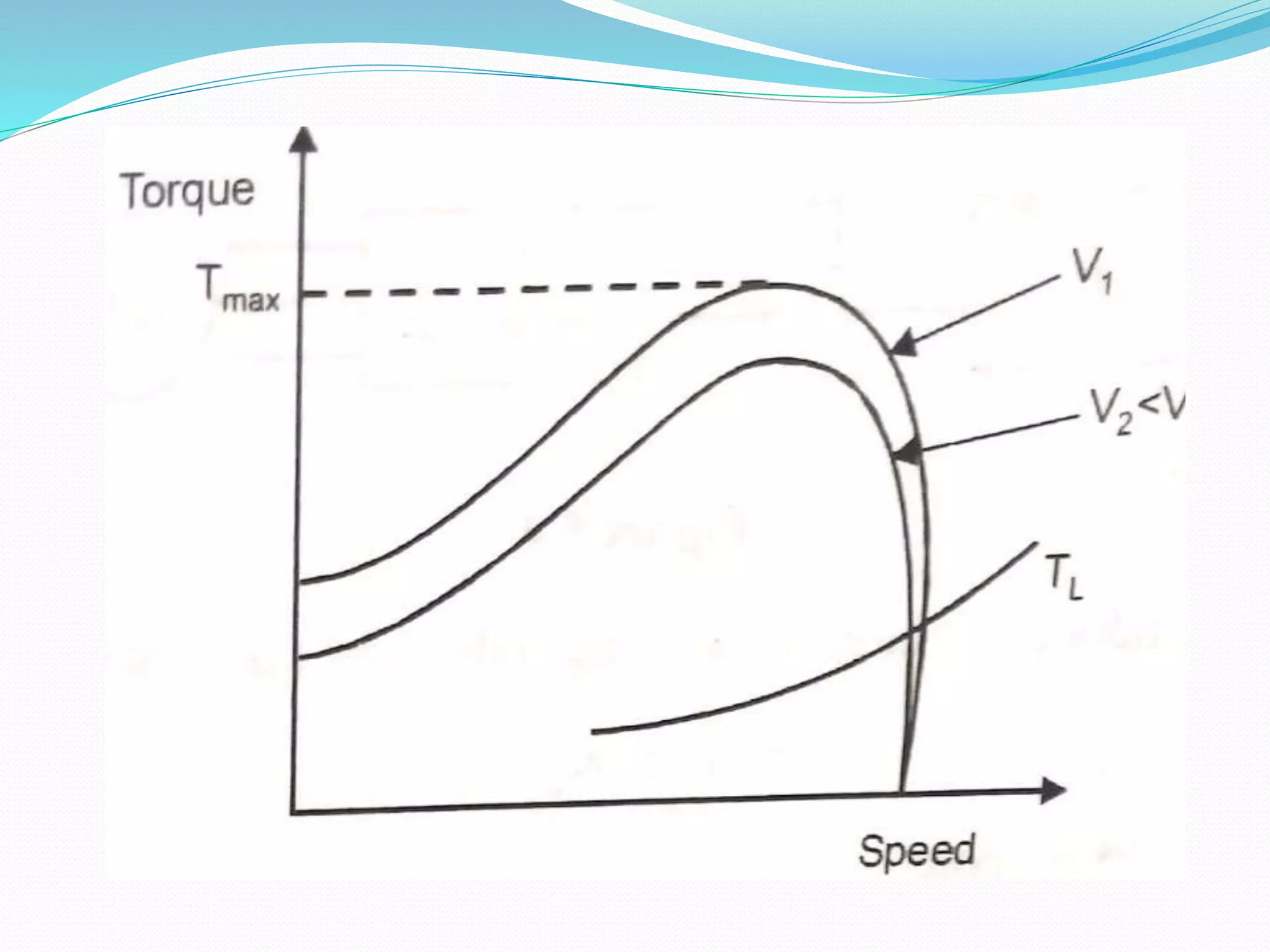

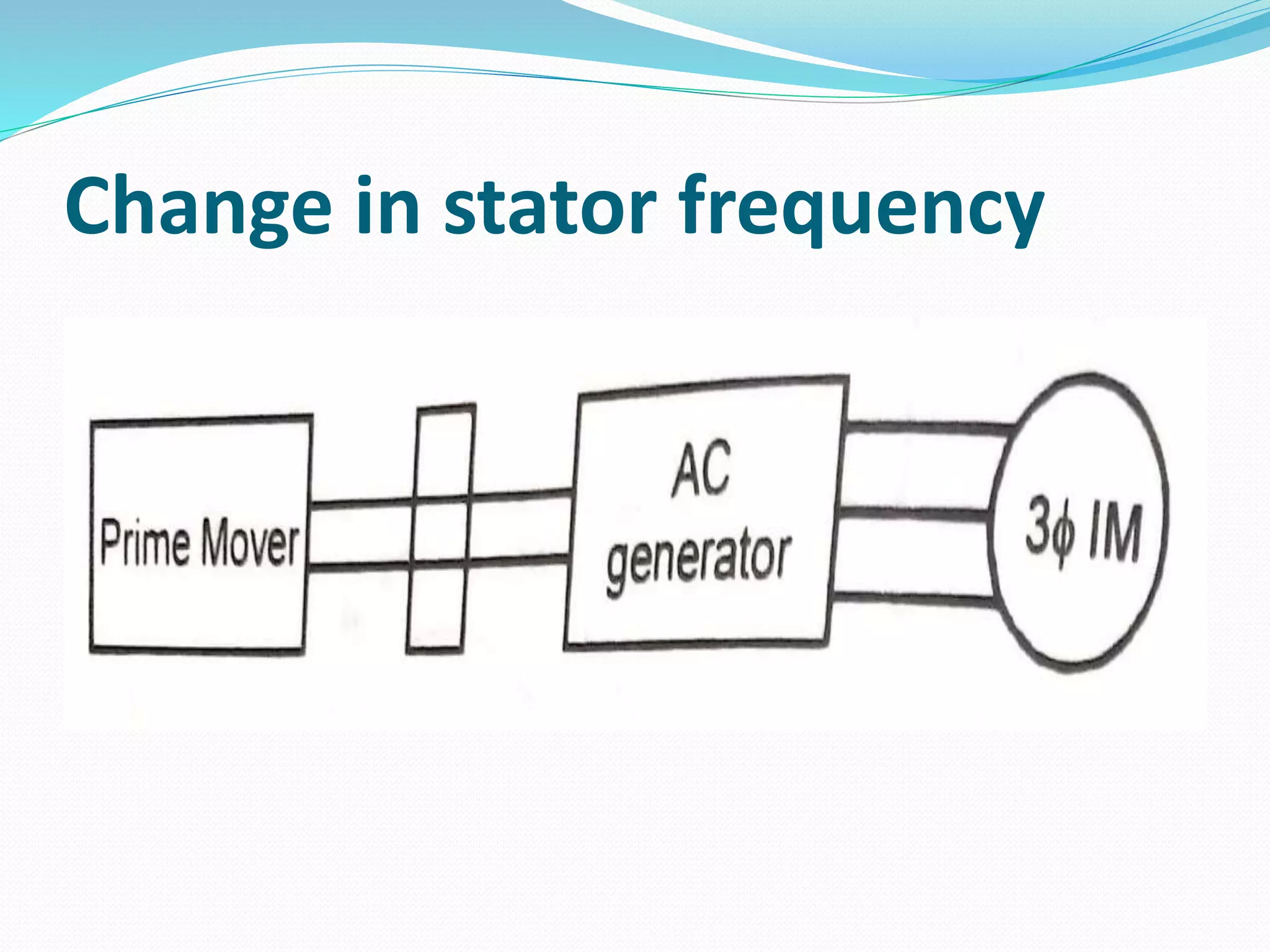
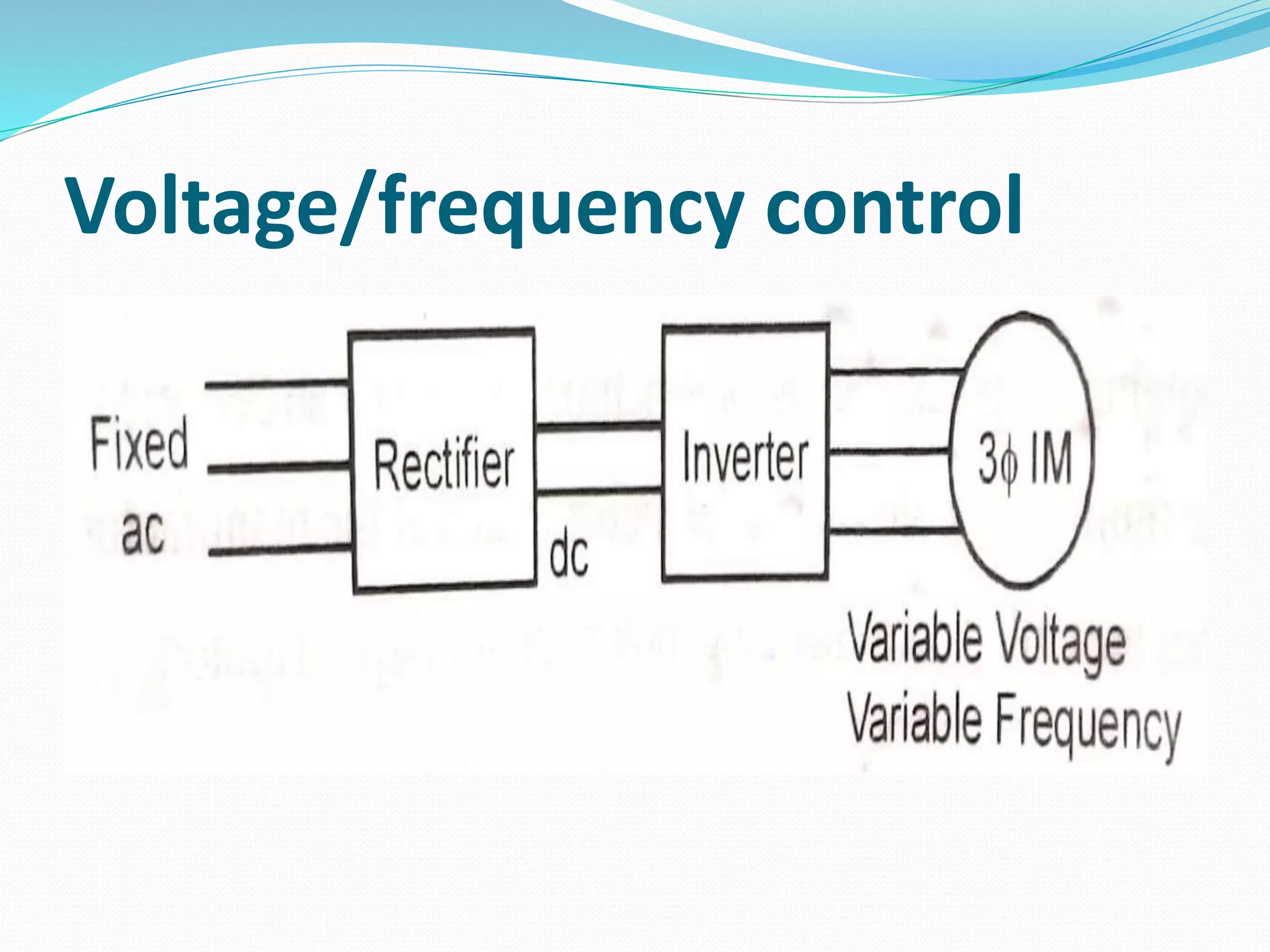
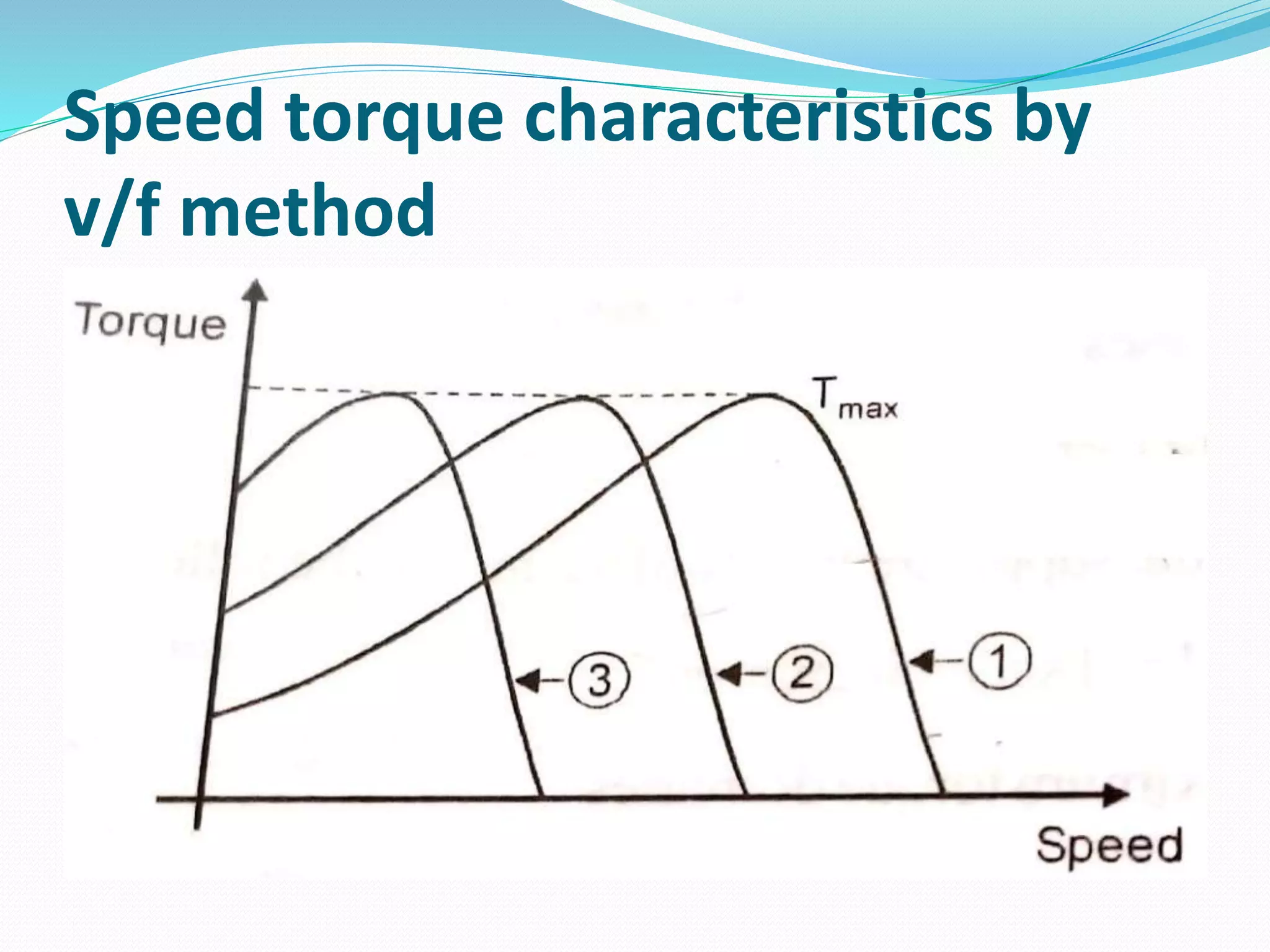

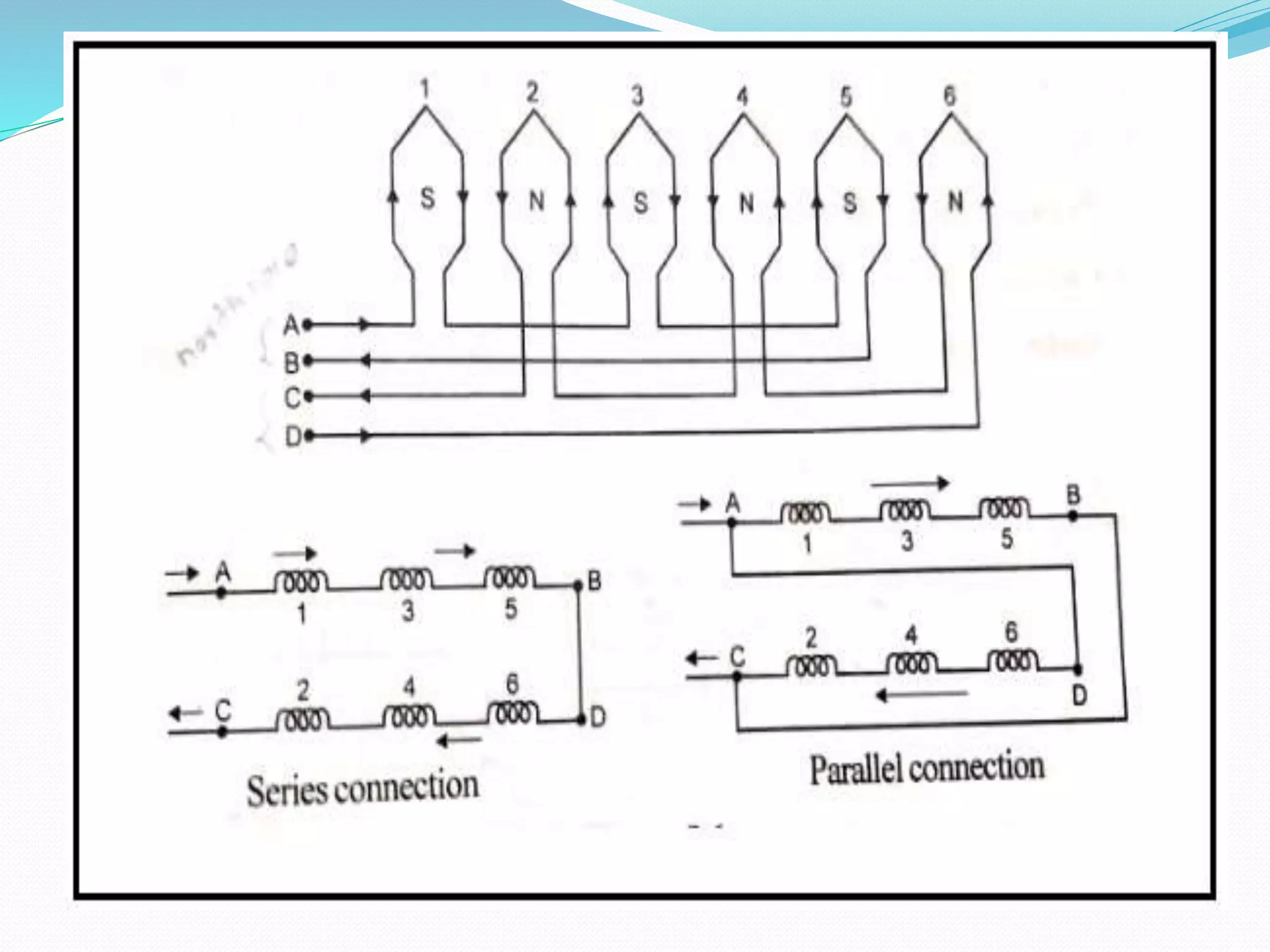
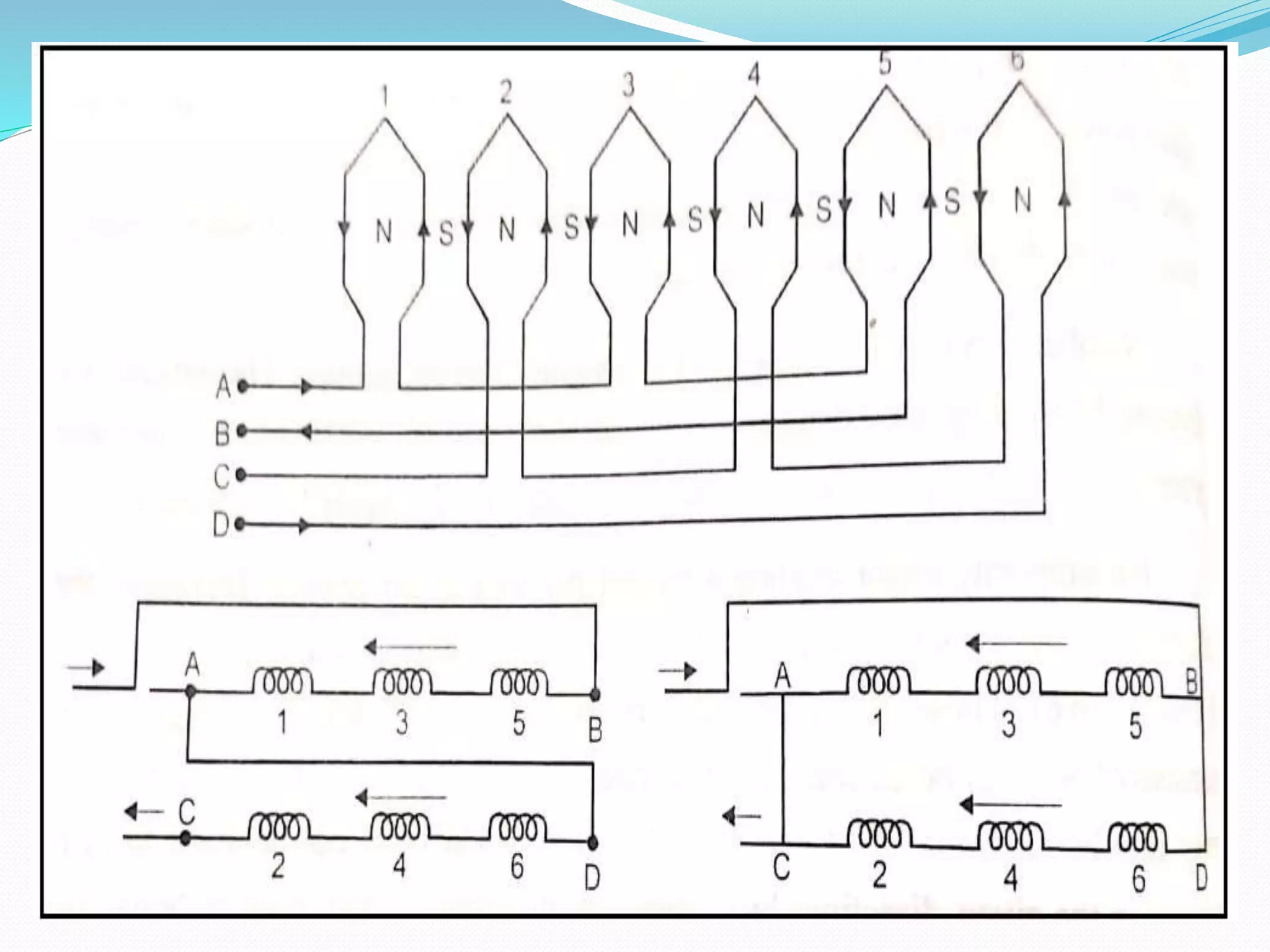

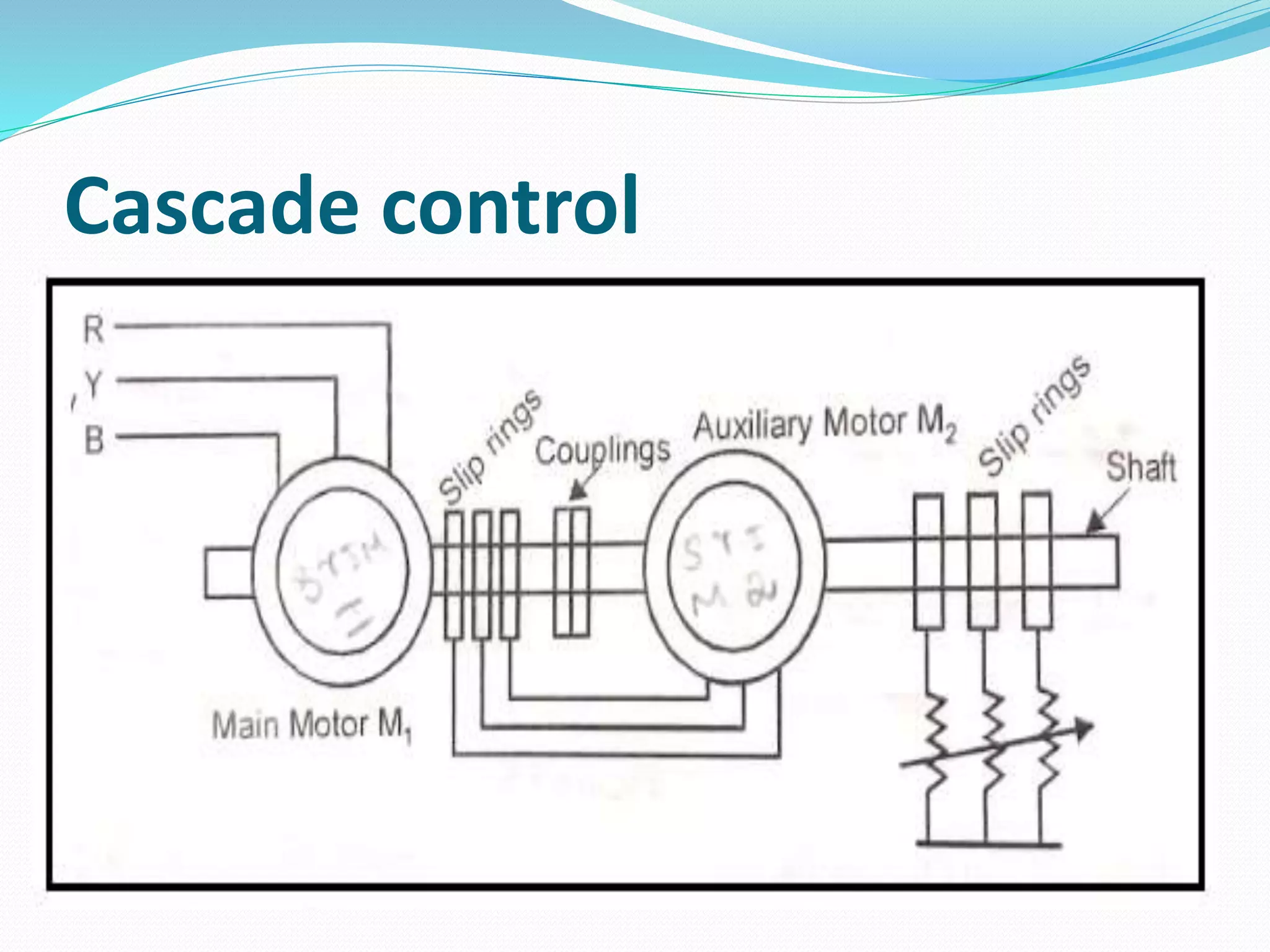

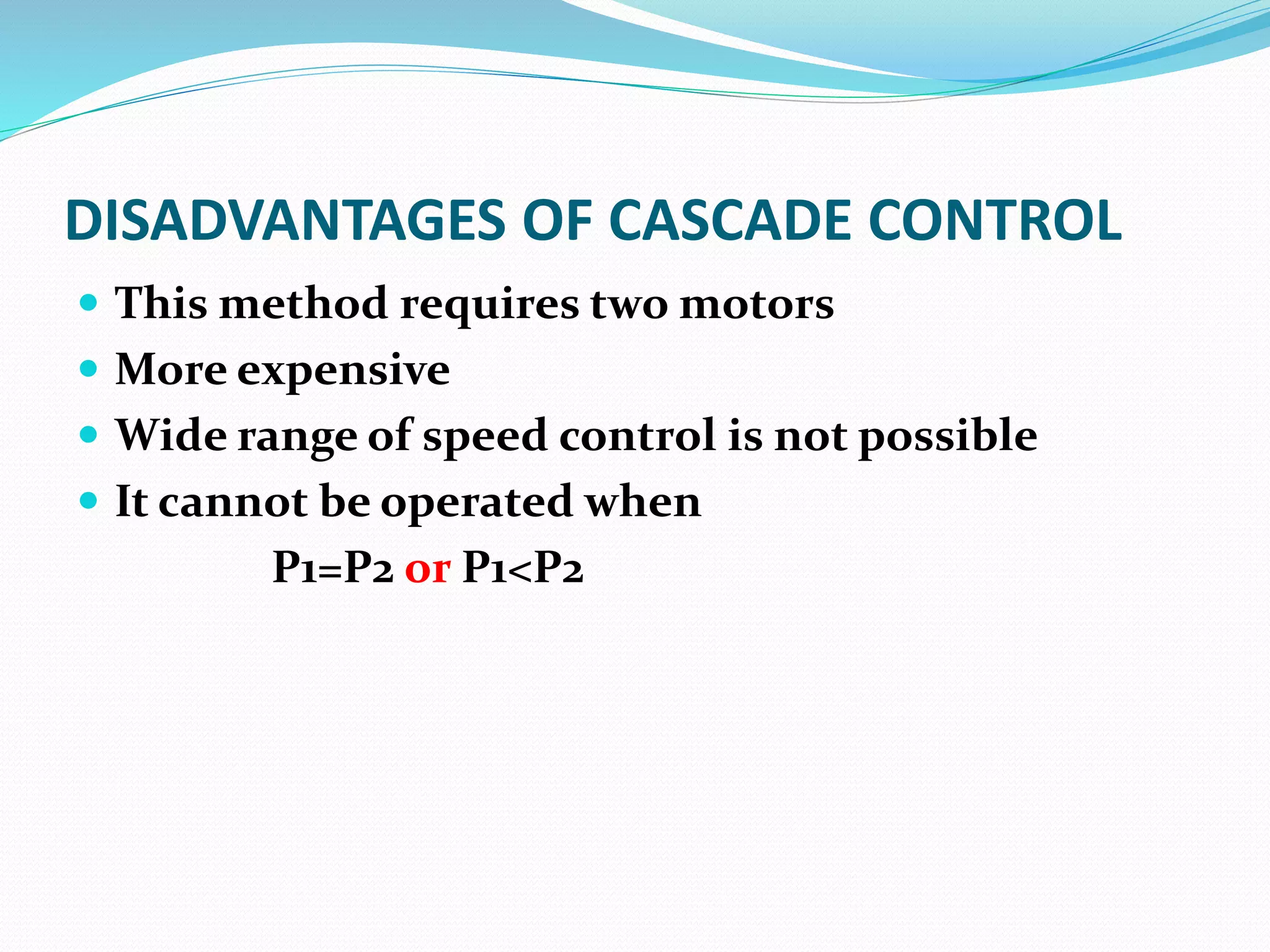
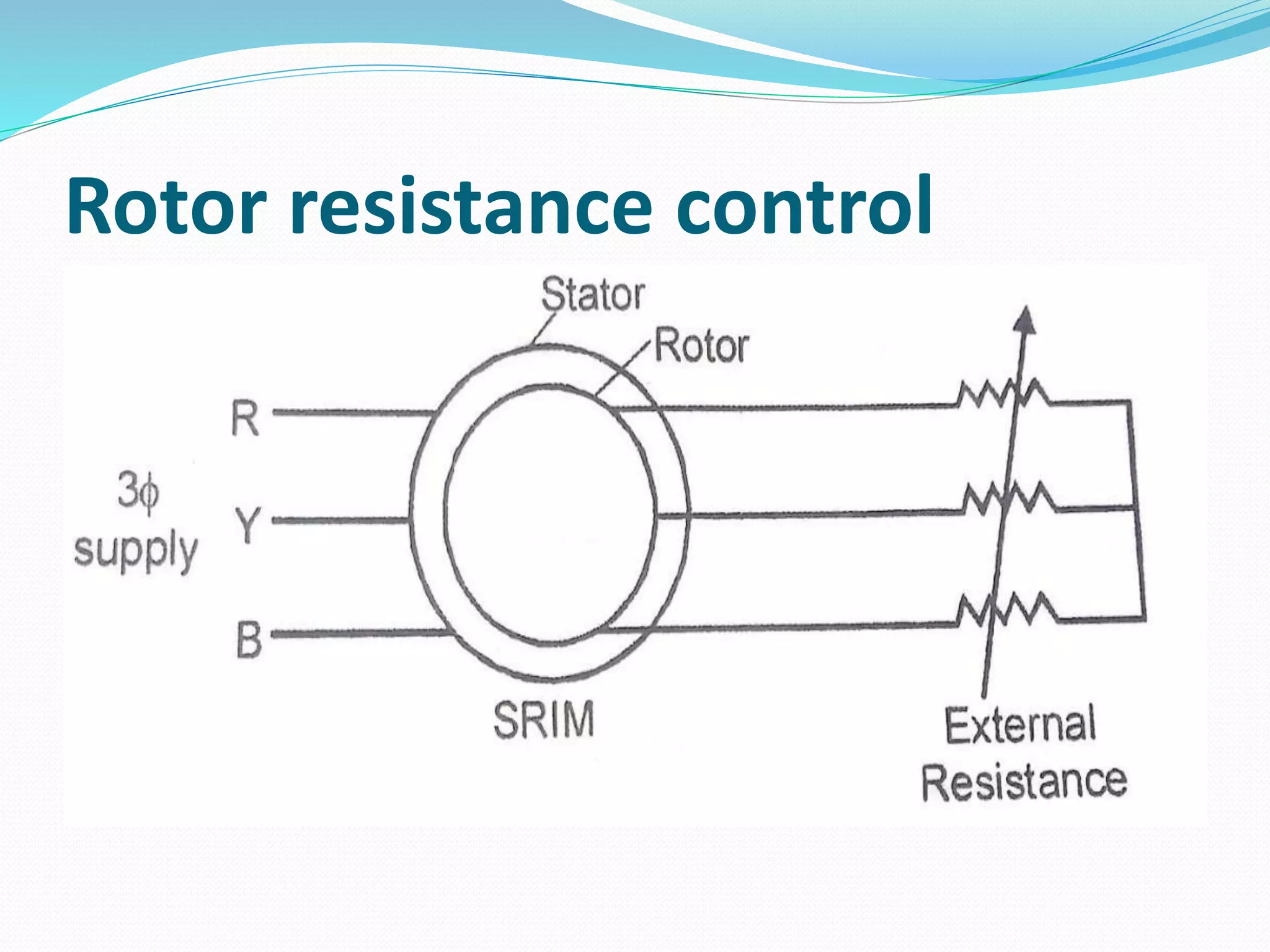
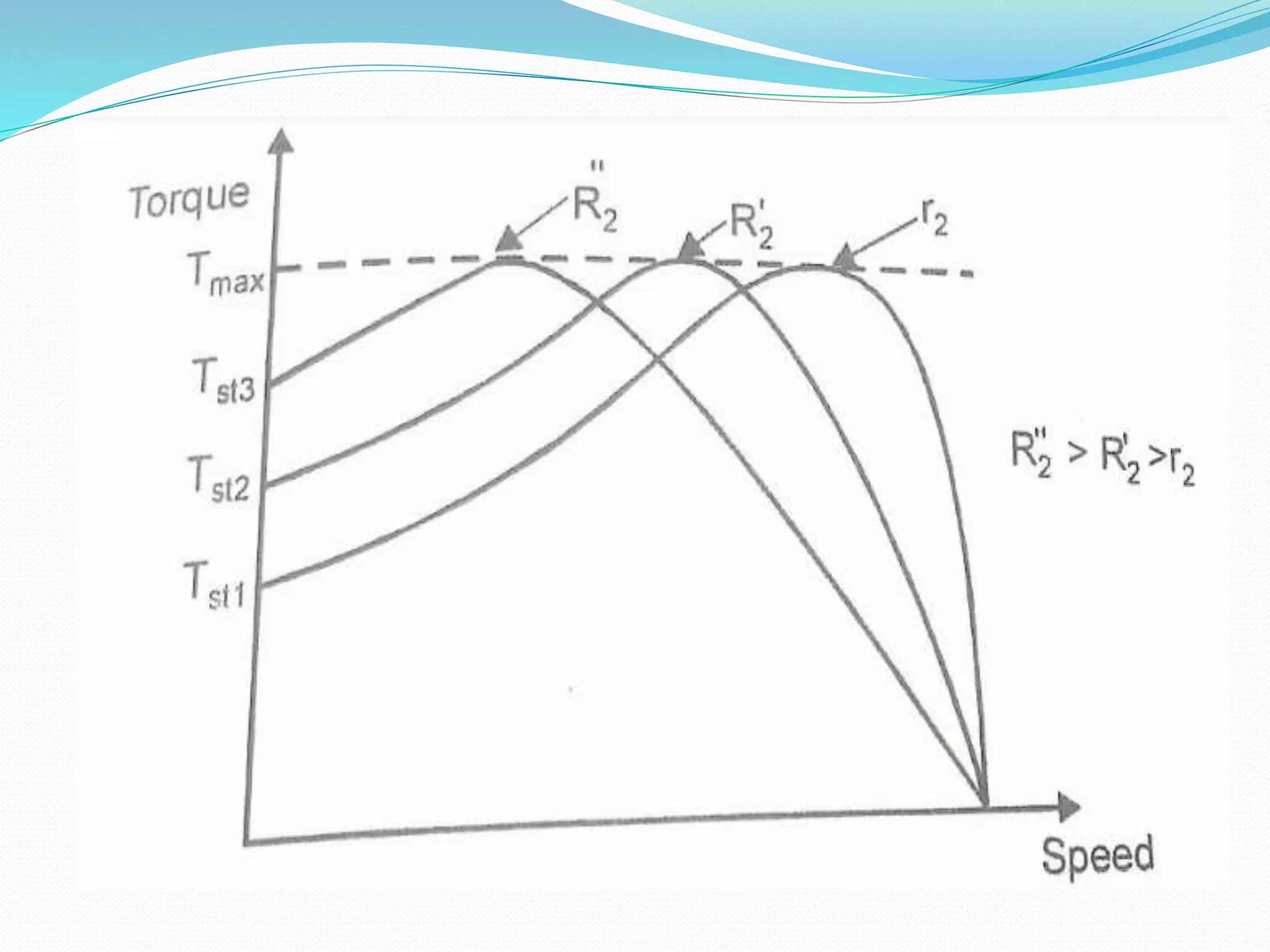


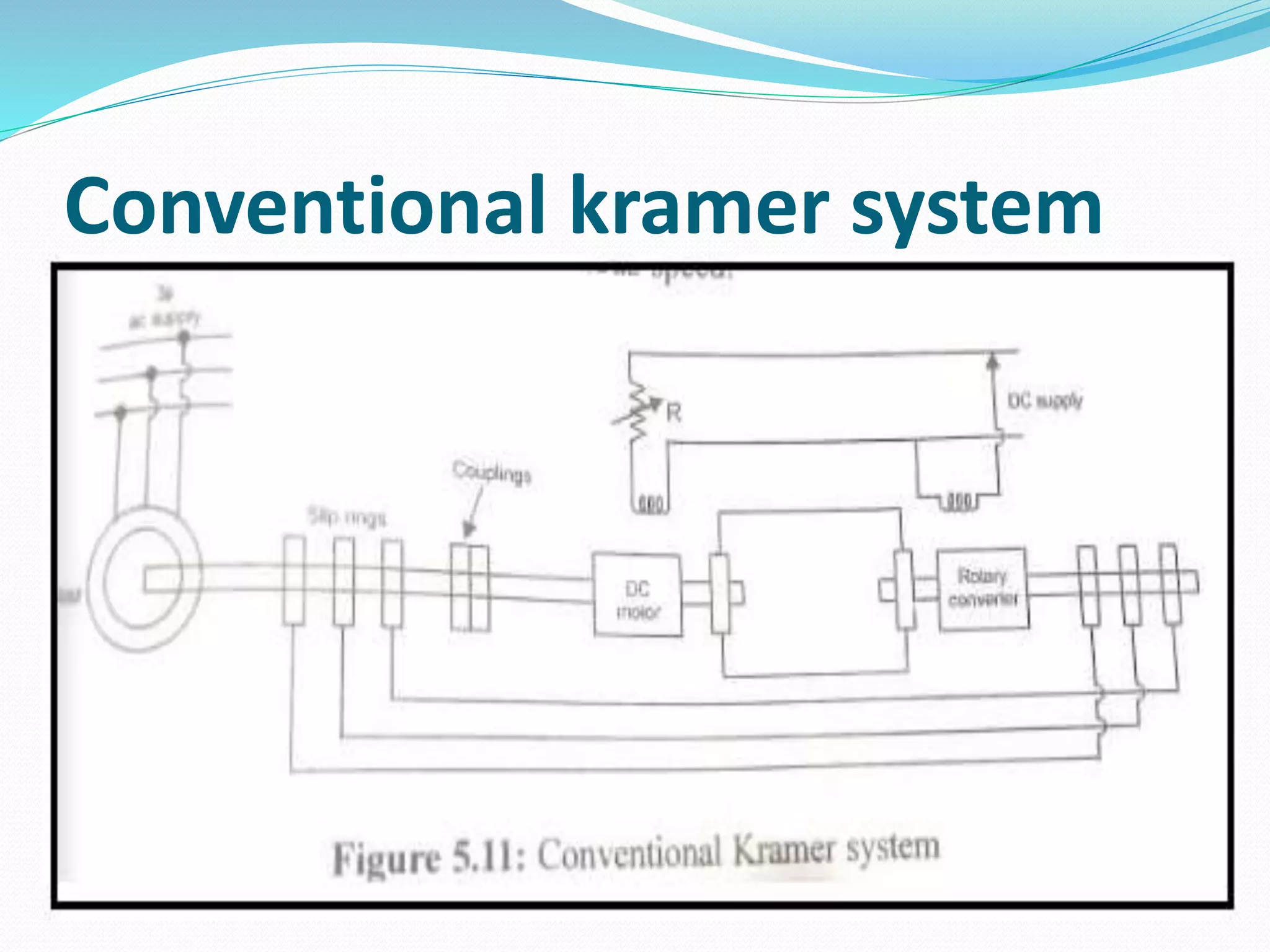
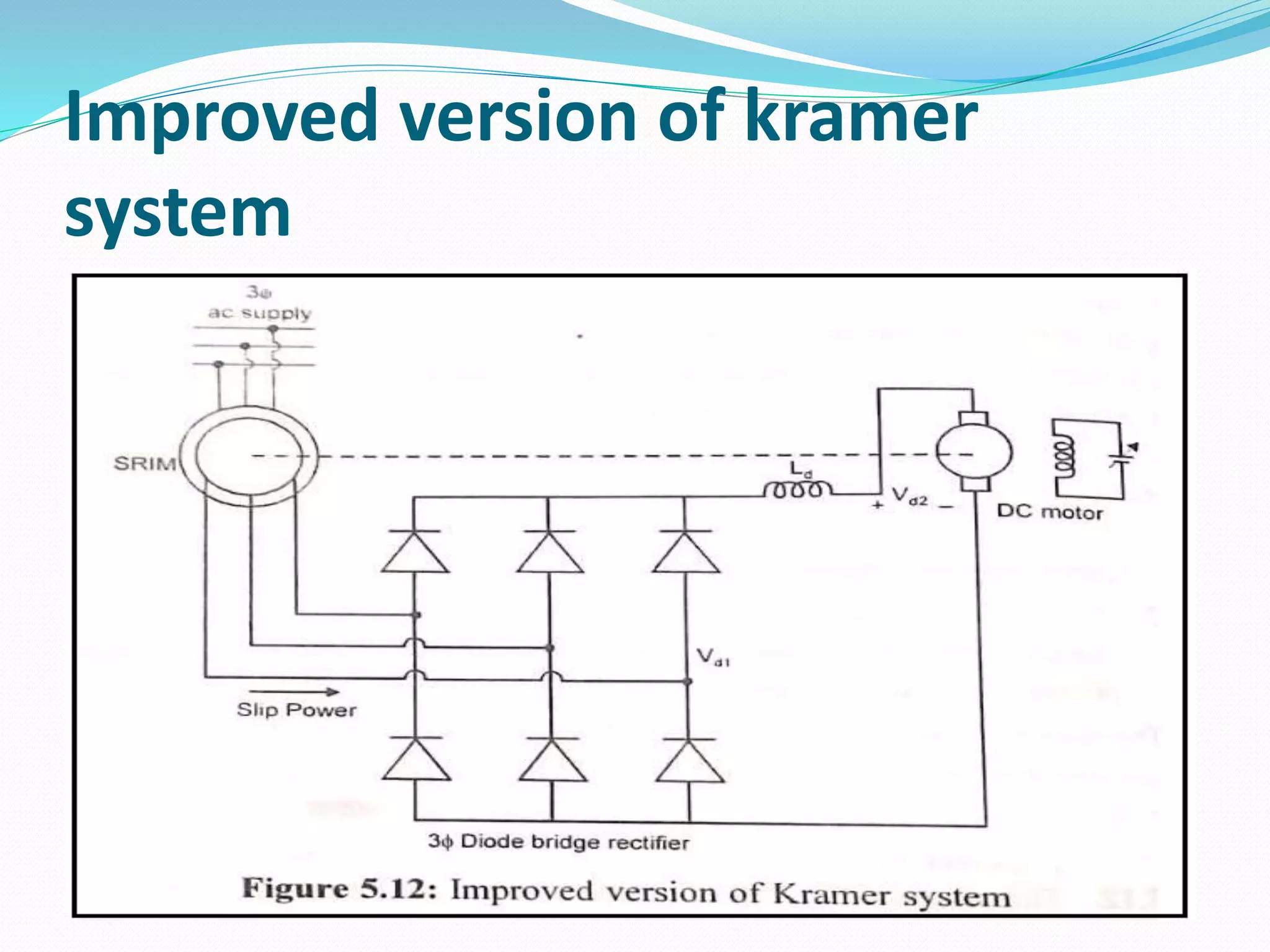
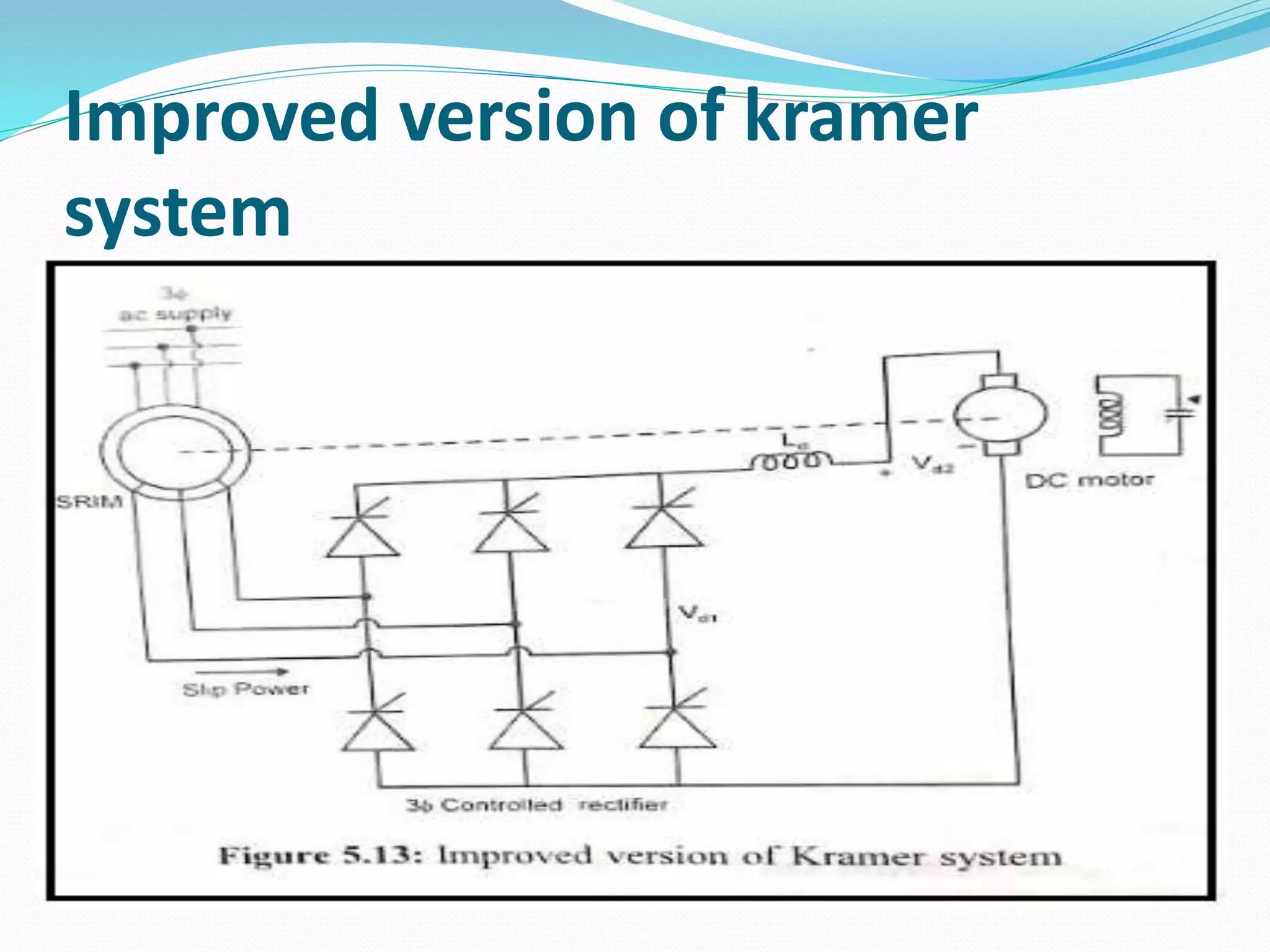
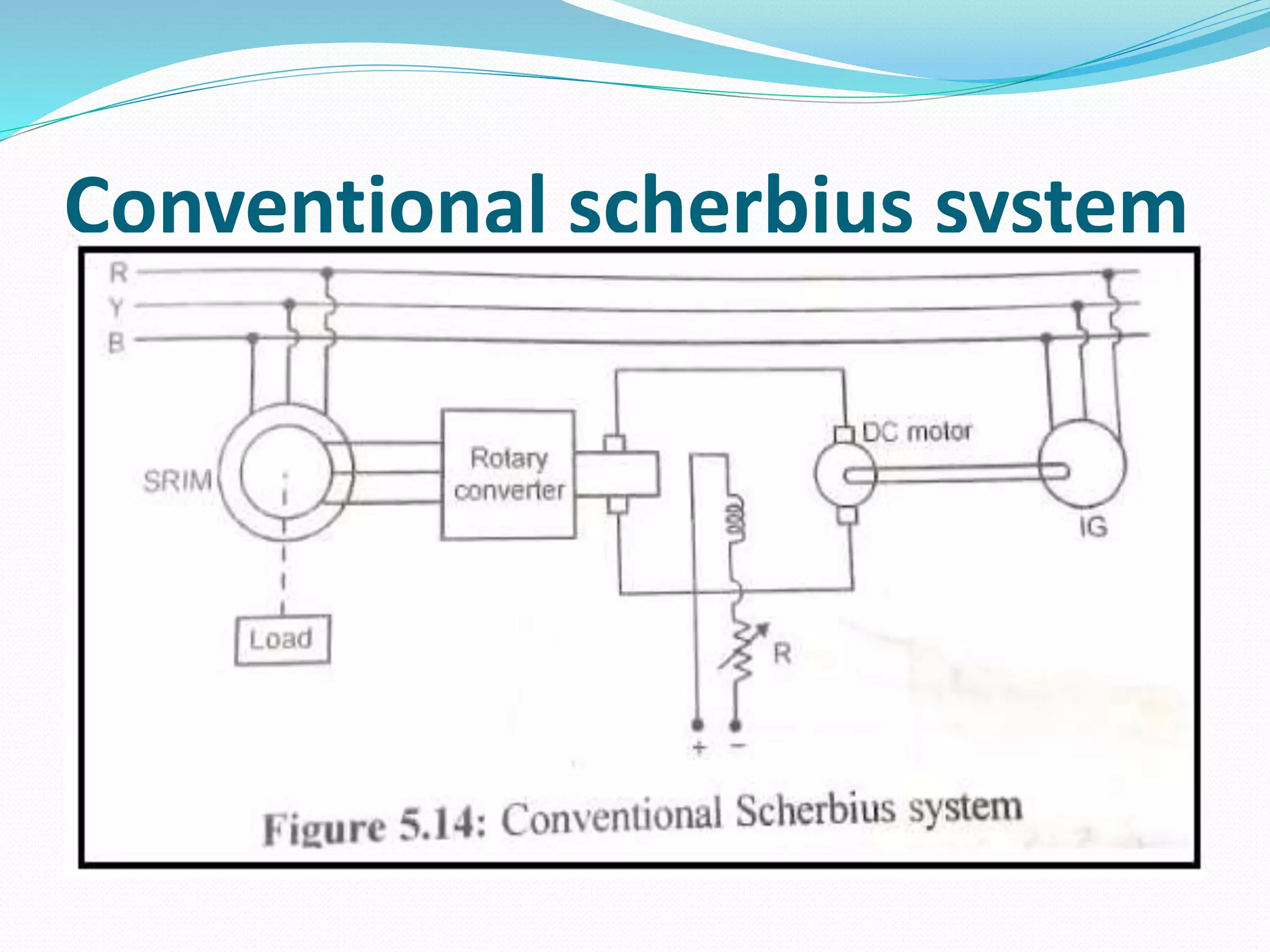

This document discusses various methods for controlling the speed of AC induction motors, including stator-side control by varying voltage or frequency, and rotor-side control using cascade control, adding rotor resistance, or slip power recovery schemes. Stator-side control involves changing the stator voltage using autotransformers or resistors, or changing the frequency which varies the synchronous speed. Rotor-side control techniques include cascade control using two motors, adding external resistance in the rotor circuit, or recovering slip power using Kramer or Scherbius systems.
























