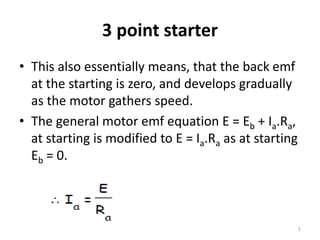
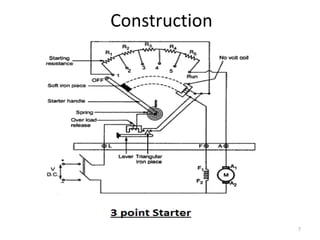
The 3 point starter is used to safely start shunt or compound wound DC motors. It works as a variable resistor to gradually reduce resistance in the armature circuit as the motor gains speed. This limits starting current. It has 3 main points - line (L), armature (A), and field (F) terminals. The no voltage coil holds the starter handle in the "RUN" position using electromagnetism so long as power is supplied, but the handle returns to "OFF" if power fails to protect the motor. The 3 point starter allows safe starting of DC motors by limiting high starting current.