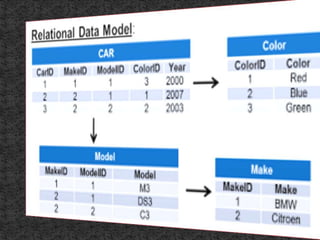
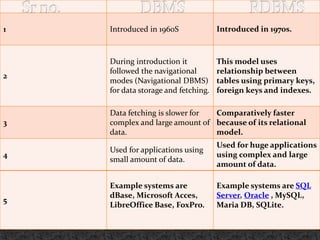
This document provides an introduction to database management systems (DBMS) and relational database management systems (RDBMS). It defines a database as a collection of related data organized for easy access, management, and updating. A DBMS is software that allows users to create, define, and manipulate databases. It provides protection and security. RDBMS introduced the relational model, using relationships between tables via primary keys, foreign keys, and indexes. This made data fetching and storage faster compared to earlier navigational models. RDBMS is widely used by enterprises for complex, large datasets.