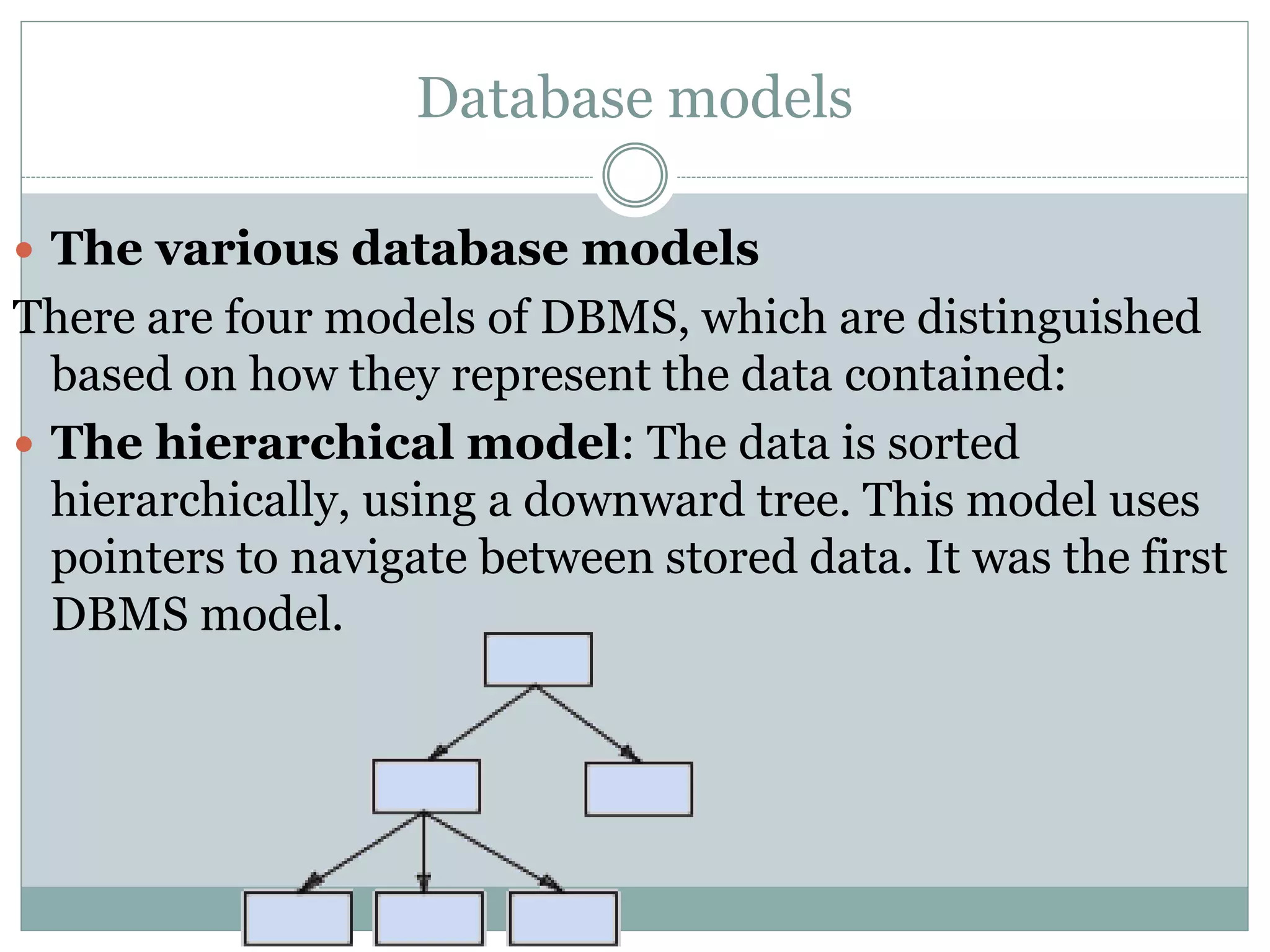
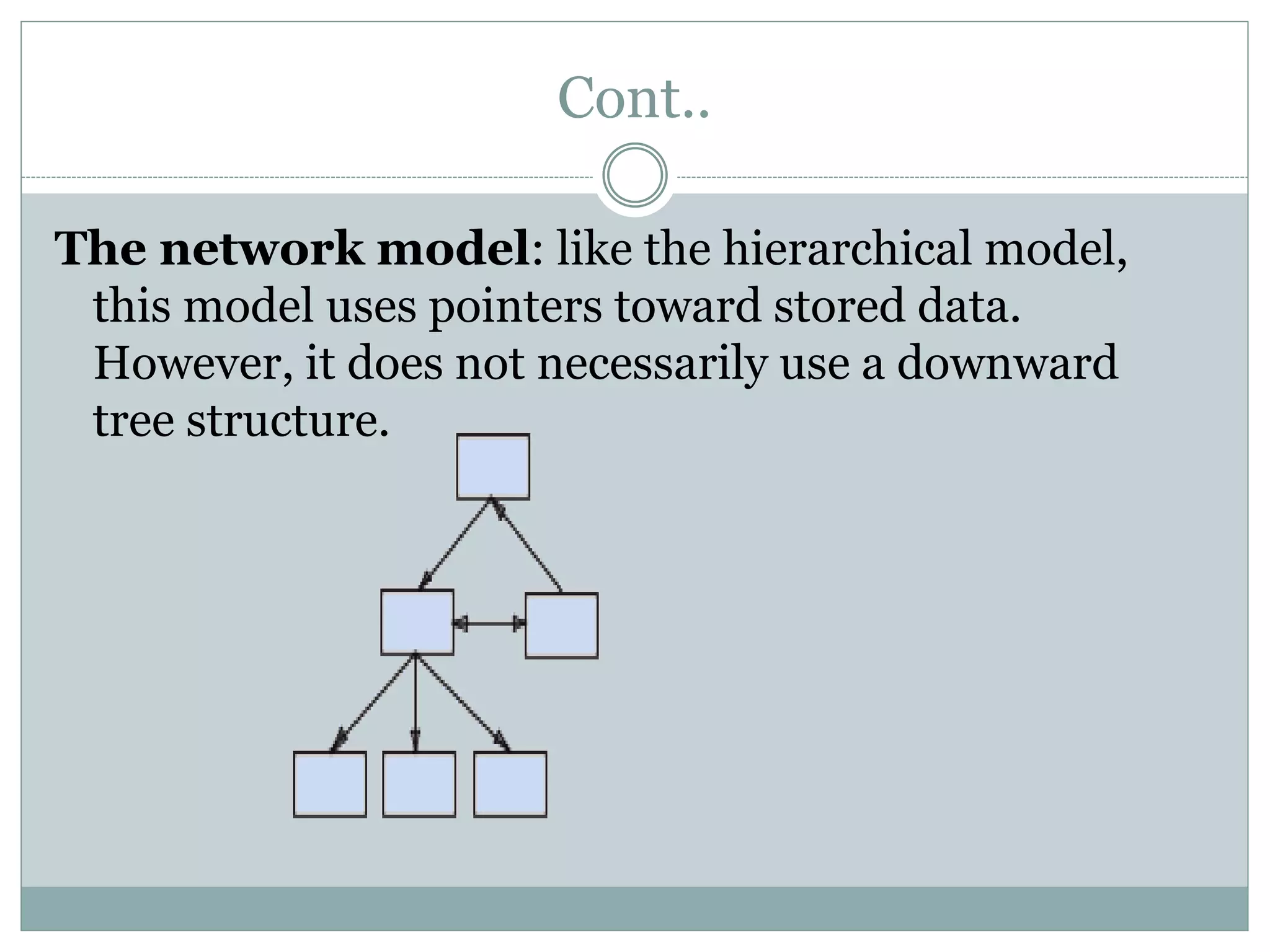
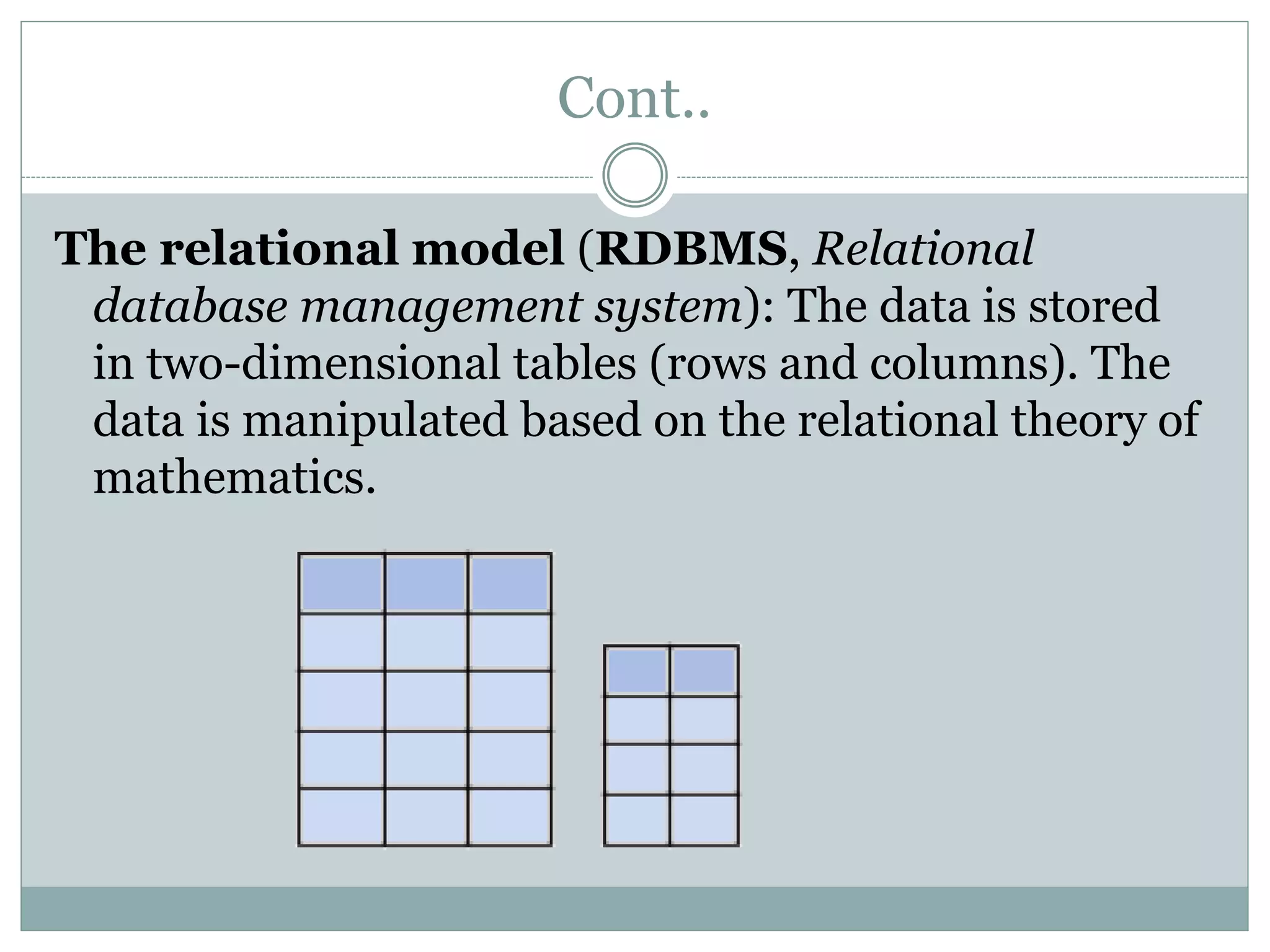
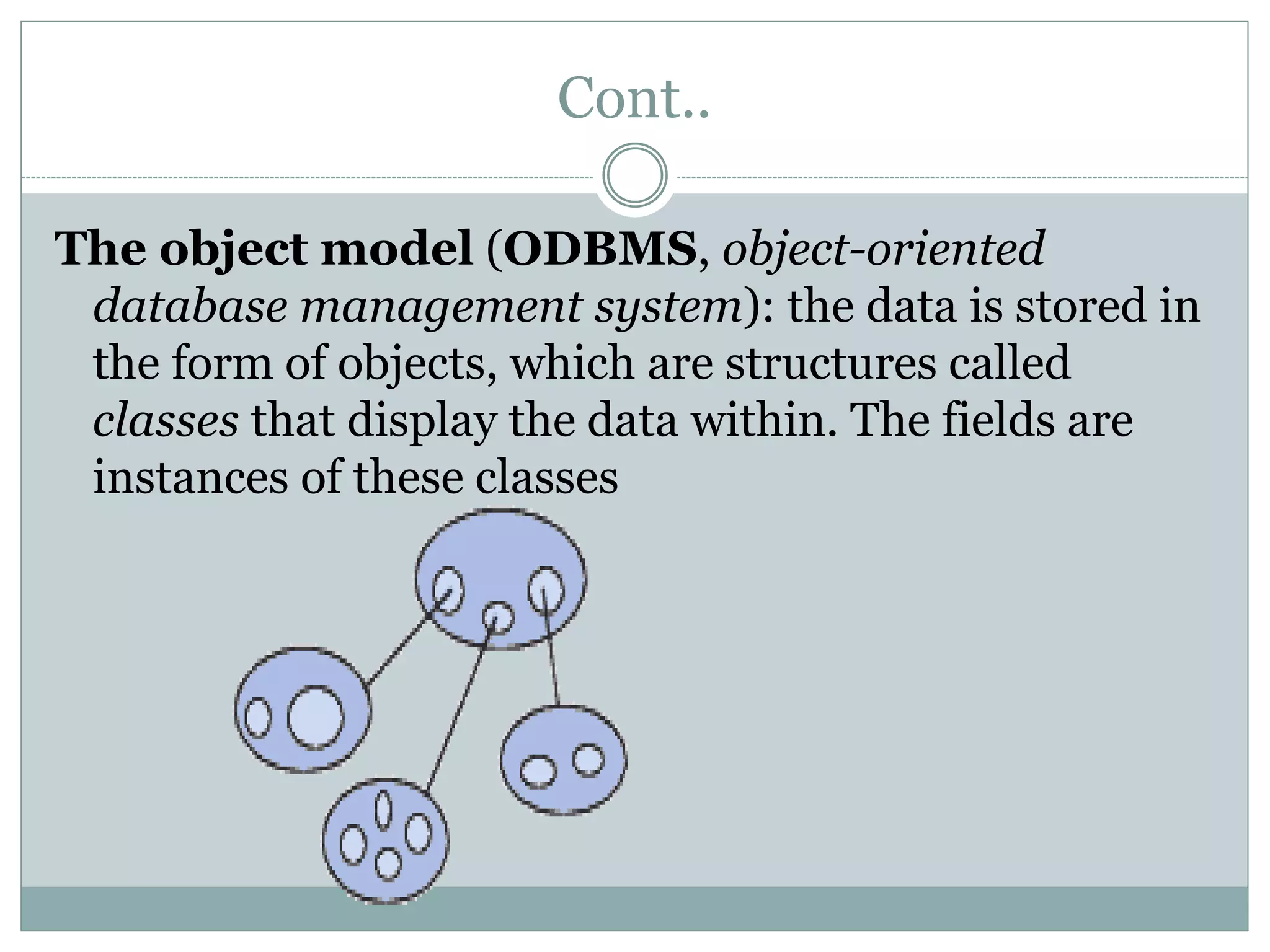
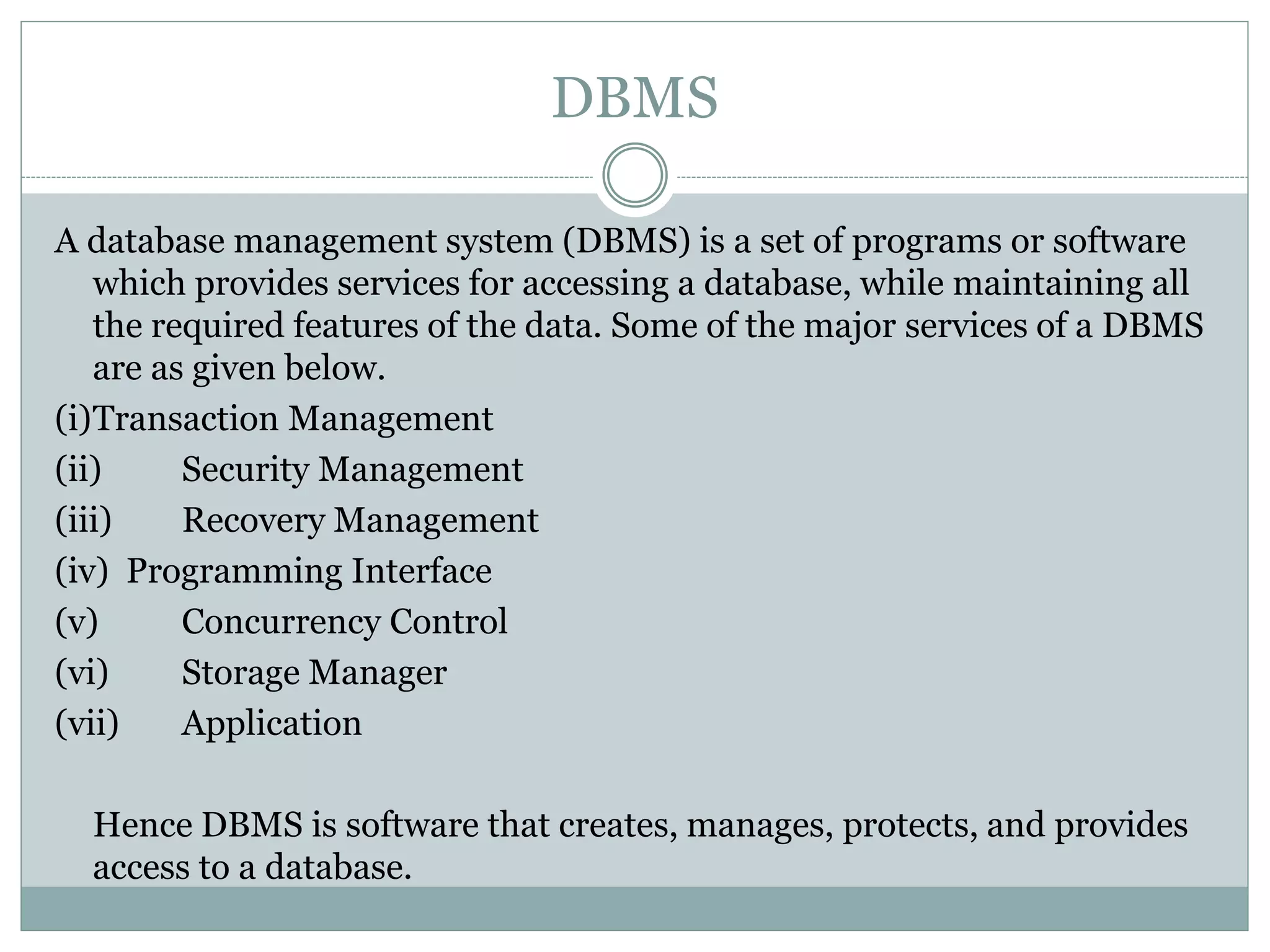
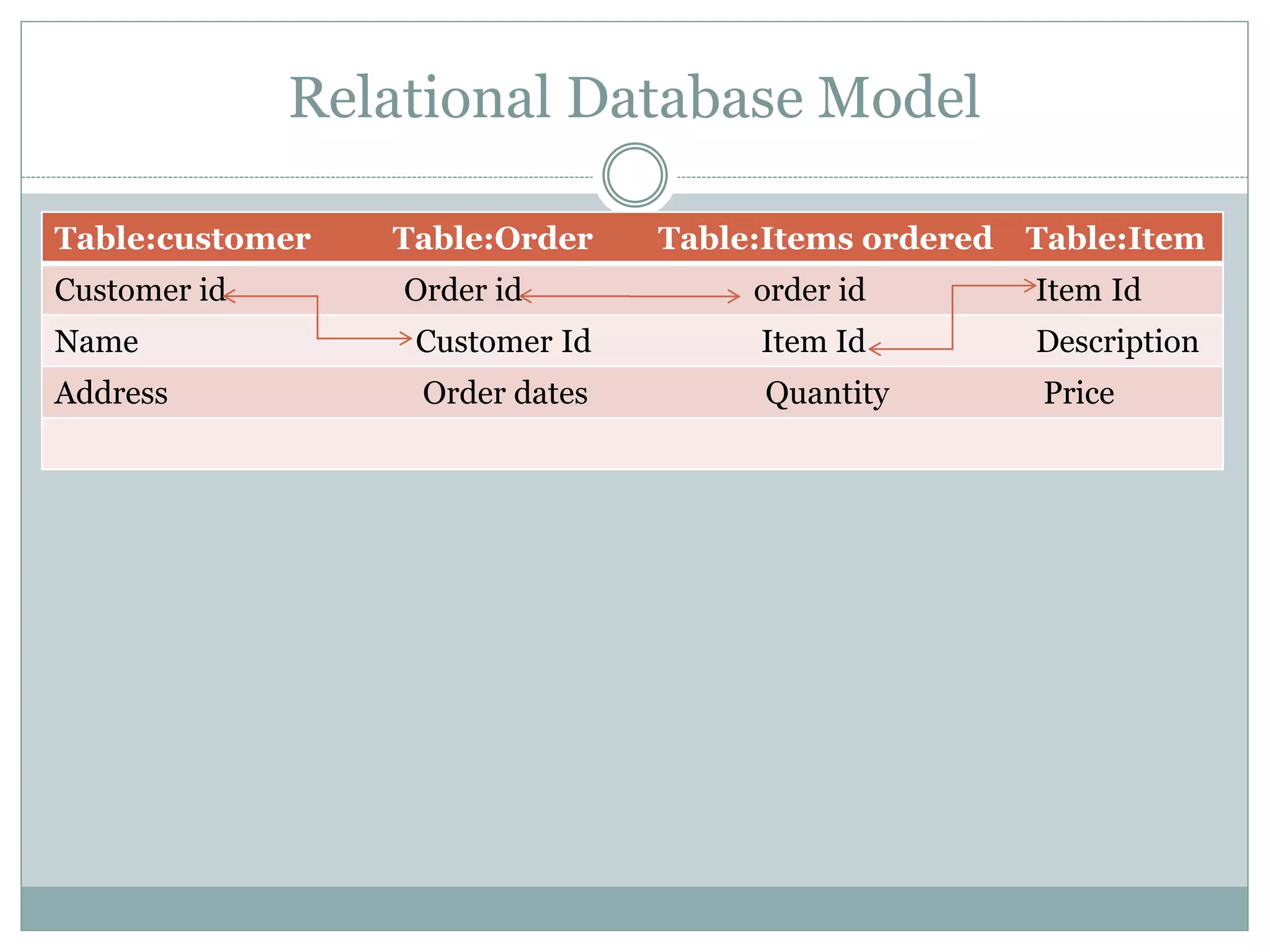
A database management system (DBMS) is a collection of software programs that manage data stored in a database. It allows for data storage, organization, manipulation, and retrieval. Popular DBMS programs include MS Access, Oracle, MySQL, and SQL Server. The relational database model organizes data into tables with rows and columns and defines relationships between tables. A relational database management system (RDBMS) uses this model and provides security, concurrency control, and other features to make database access and management easier.