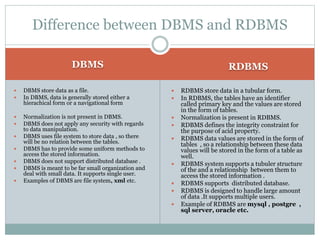
This document summarizes DBMS and RDBMS. It defines DBMS as a software system that allows management of a database. RDBMS is a type of DBMS that is based on the relational model introduced by Dr. Edgar Frank Codd. The key differences between DBMS and RDBMS are that RDBMS stores data in tables with relationships, supports normalization, distributed databases and multiple users, while DBMS stores data in files without relationships. Views and keys like super keys, candidate keys, primary keys and foreign keys are also explained.