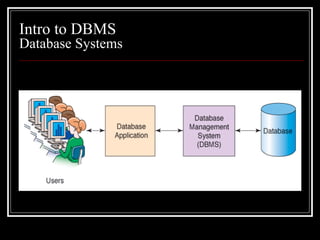
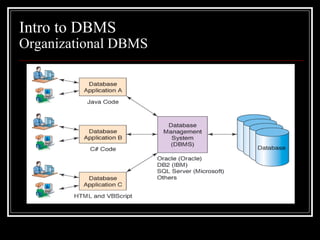
The document introduces databases and database management systems (DBMS). It discusses that a DBMS is software that allows users to create, access, and manage data and databases. A DBMS is made up of four main components: users, a database, database applications, and the DBMS itself. The DBMS controls access to the database and enforces rules like security and data integrity. It also discusses some advantages of using a DBMS like improved data sharing and consistency.