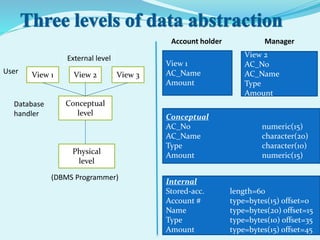
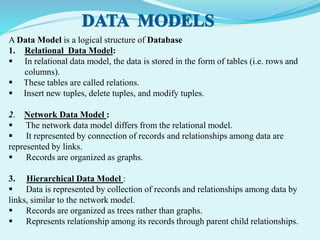
The document discusses database management systems (DBMS). It defines key concepts like data, databases, and DBMS. It explains that a DBMS is software that manages databases and makes data storage and retrieval easier. The document also covers database models like relational, network and hierarchical, different types of DBMS languages, purposes of DBMS, advantages and disadvantages. It provides examples of database usage in domains like banking, airlines, universities etc.