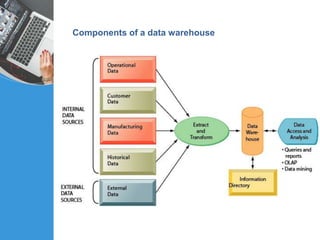
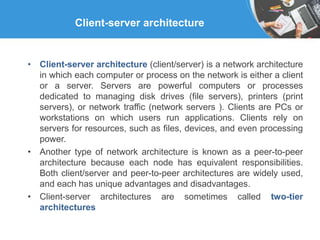
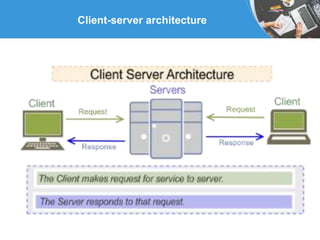
Businesses use databases to keep track of transactions, provide information to run more efficiently, and help managers make better decisions. A data warehouse stores current and historical data from operational systems for analysis but cannot be altered, while a data mart contains a focused subset of data for specific users. Client-server architecture divides computers into powerful servers that manage resources and client workstations that rely on servers, with each having distinct responsibilities.