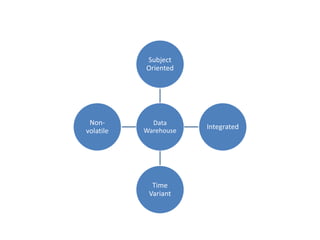
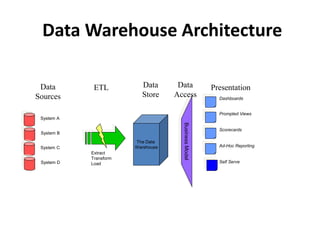
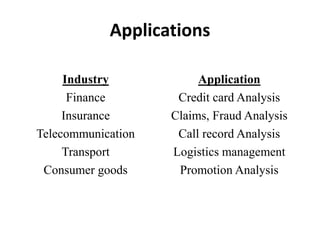
This document provides an overview of data warehousing. It defines a data warehouse as a central database that includes information from several different sources and keeps both current and historical data to support management decision making. The document describes key characteristics of a data warehouse including being subject-oriented, integrated, time-variant, and non-volatile. It also discusses common data warehouse architectures and applications.