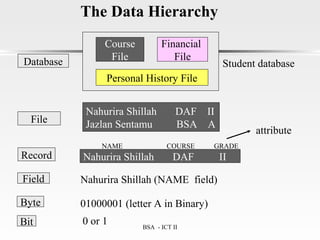
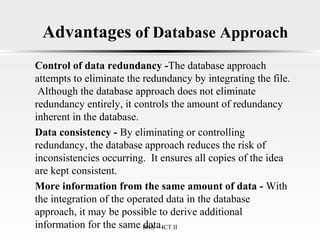
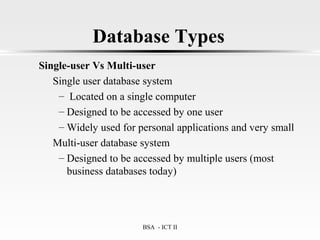
This document provides an introduction to data management. It discusses the importance of data management for making informed decisions and gaining a competitive advantage. It also outlines some key benefits of good data management, such as improved data quality and decision making, and costs of poor data management like wasted time and money. Additionally, it describes different approaches to data management like file-based and database management systems, and covers concepts such as data modeling, databases, and different database models.