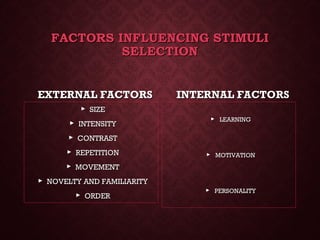
Perception involves receiving and interpreting sensory information from the environment through processes like sensation, attention, and interpretation. It is influenced by factors related to the perceiver, such as attitudes, as well as factors related to the target and situation being perceived. The perceptual process involves selecting stimuli to notice, organizing them into patterns, and assigning meaning. Accurate perception is important for decision making. Common perceptual distortions can occur from biases, expectations, and selective attention. Perception affects many organizational functions like performance appraisals, productivity, and job satisfaction.