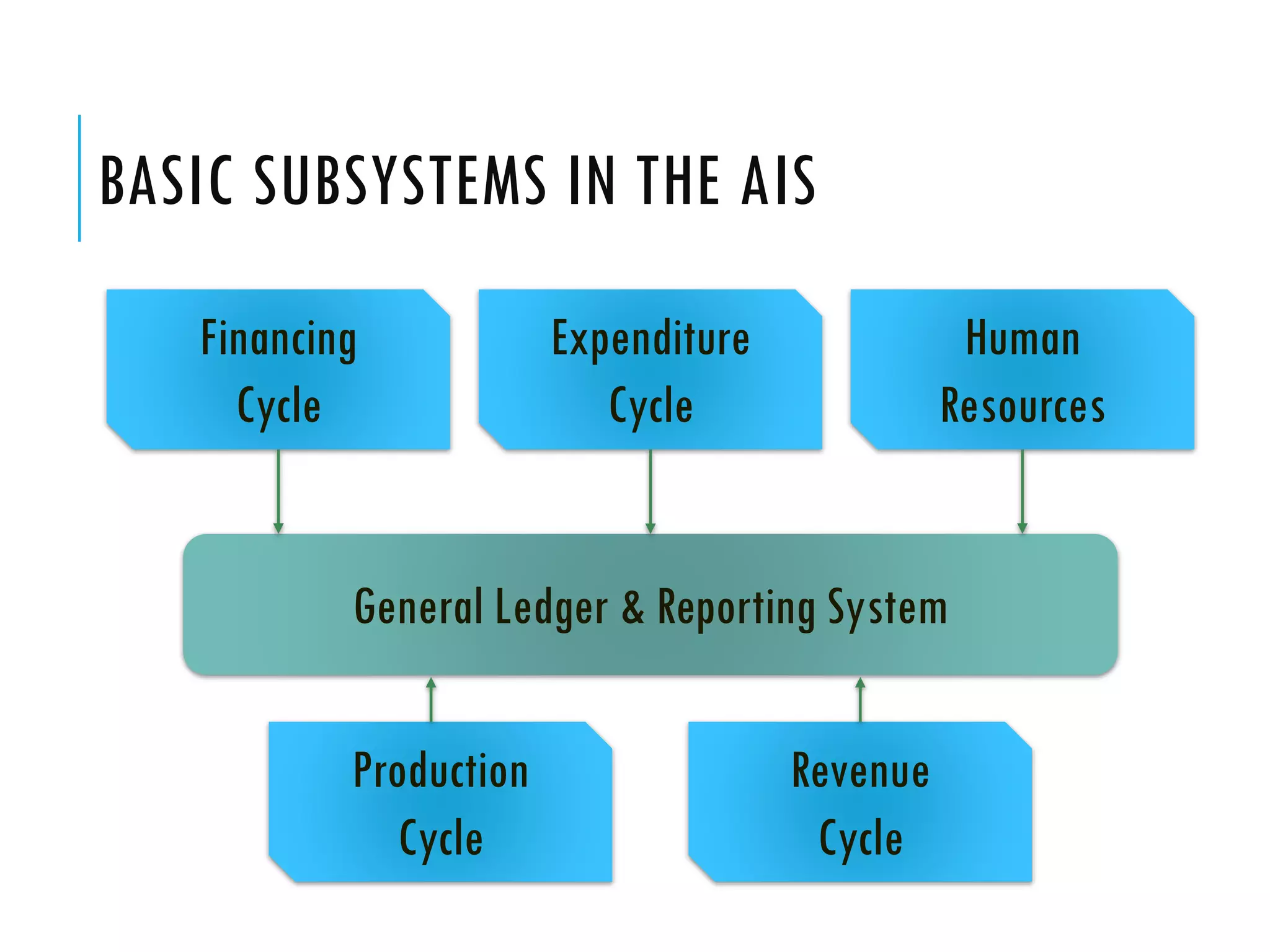
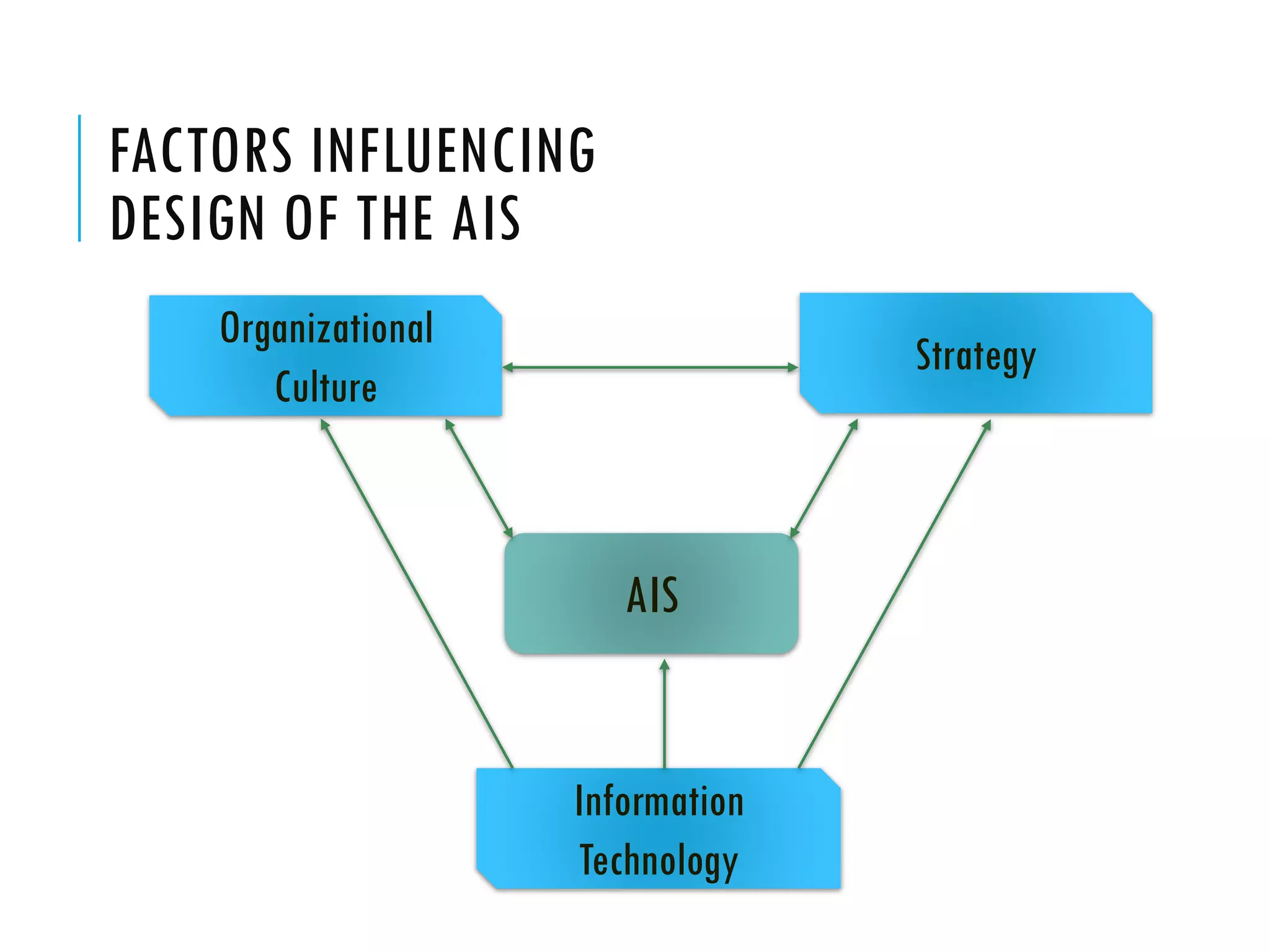
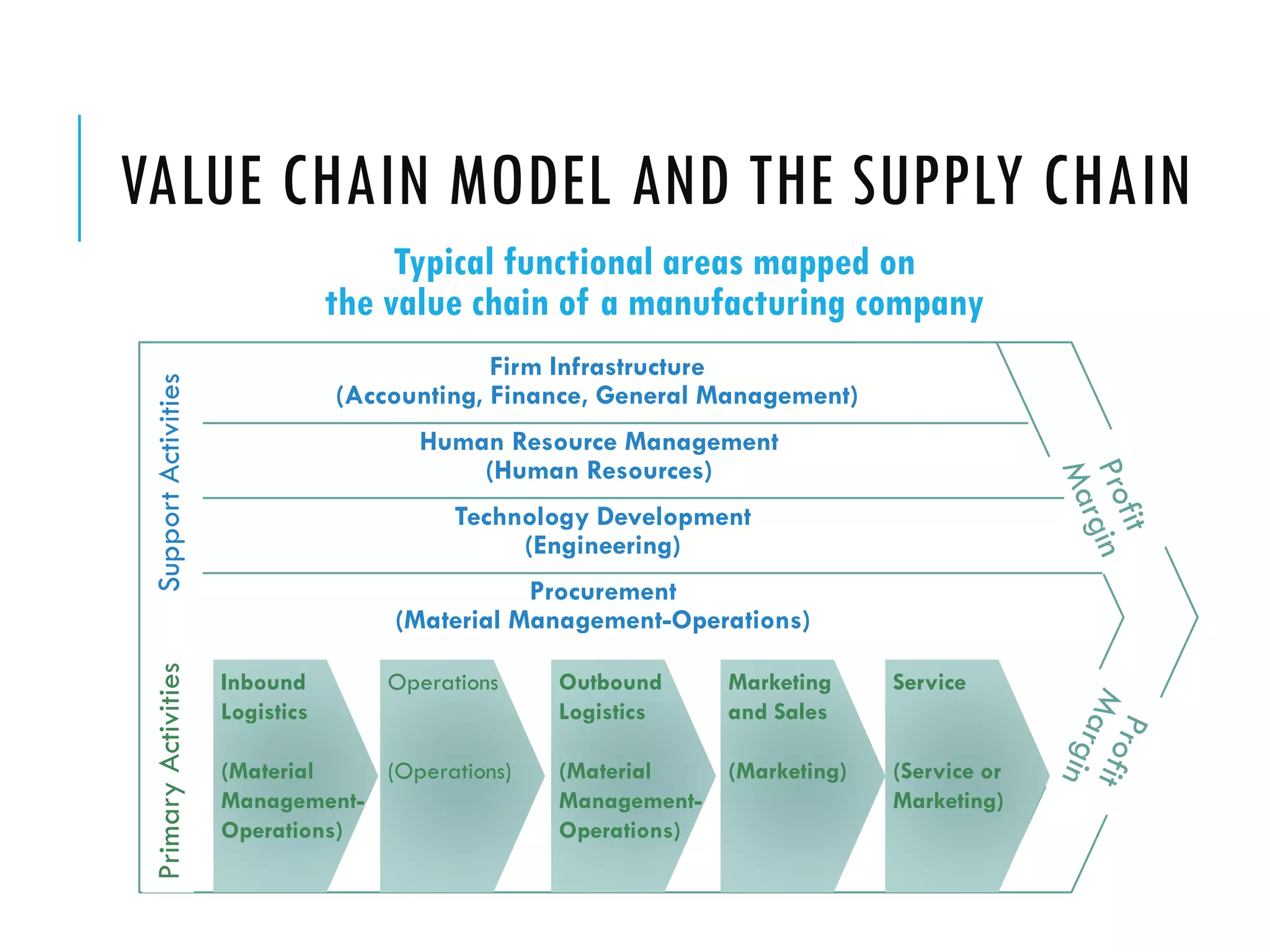
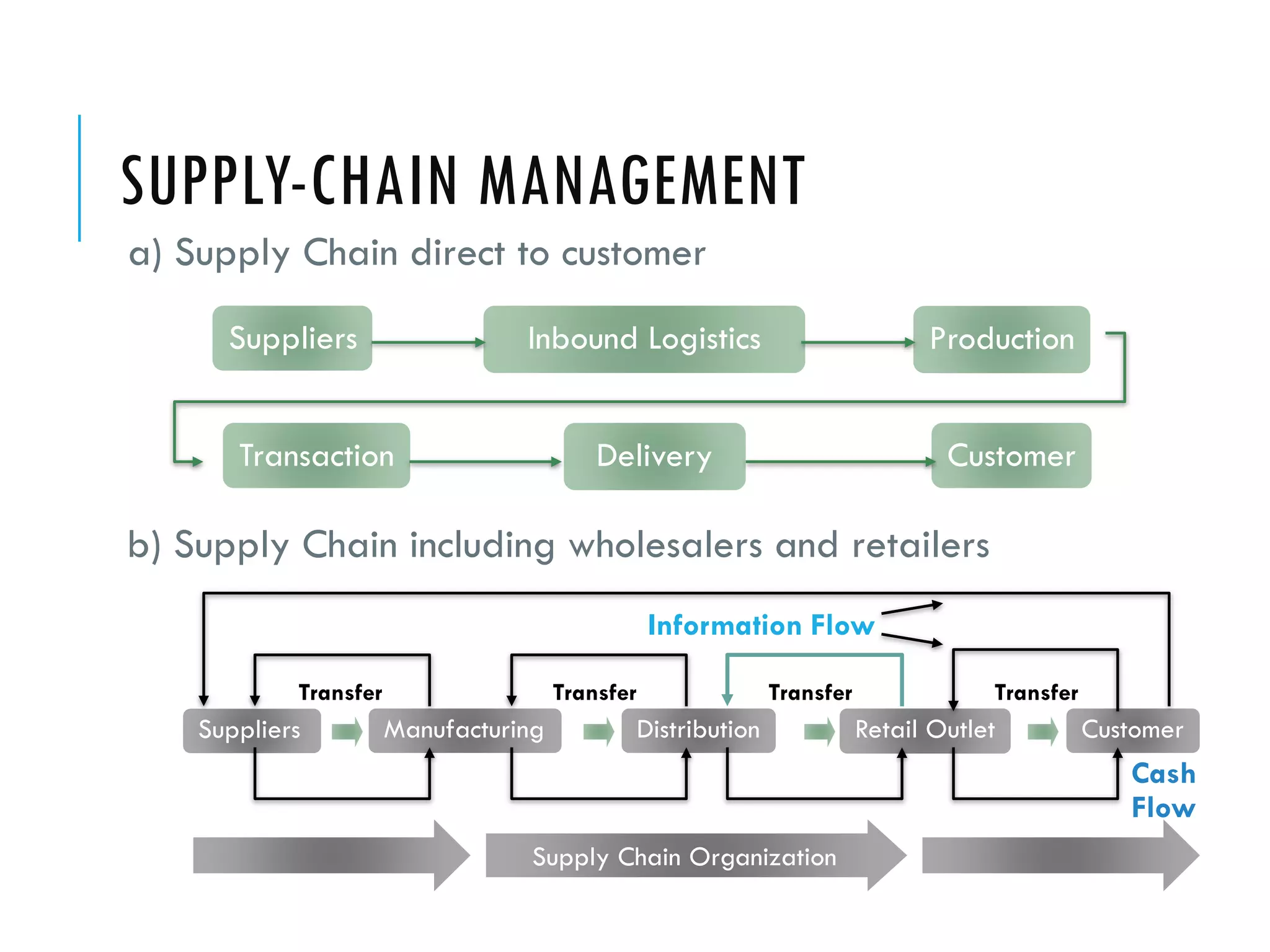
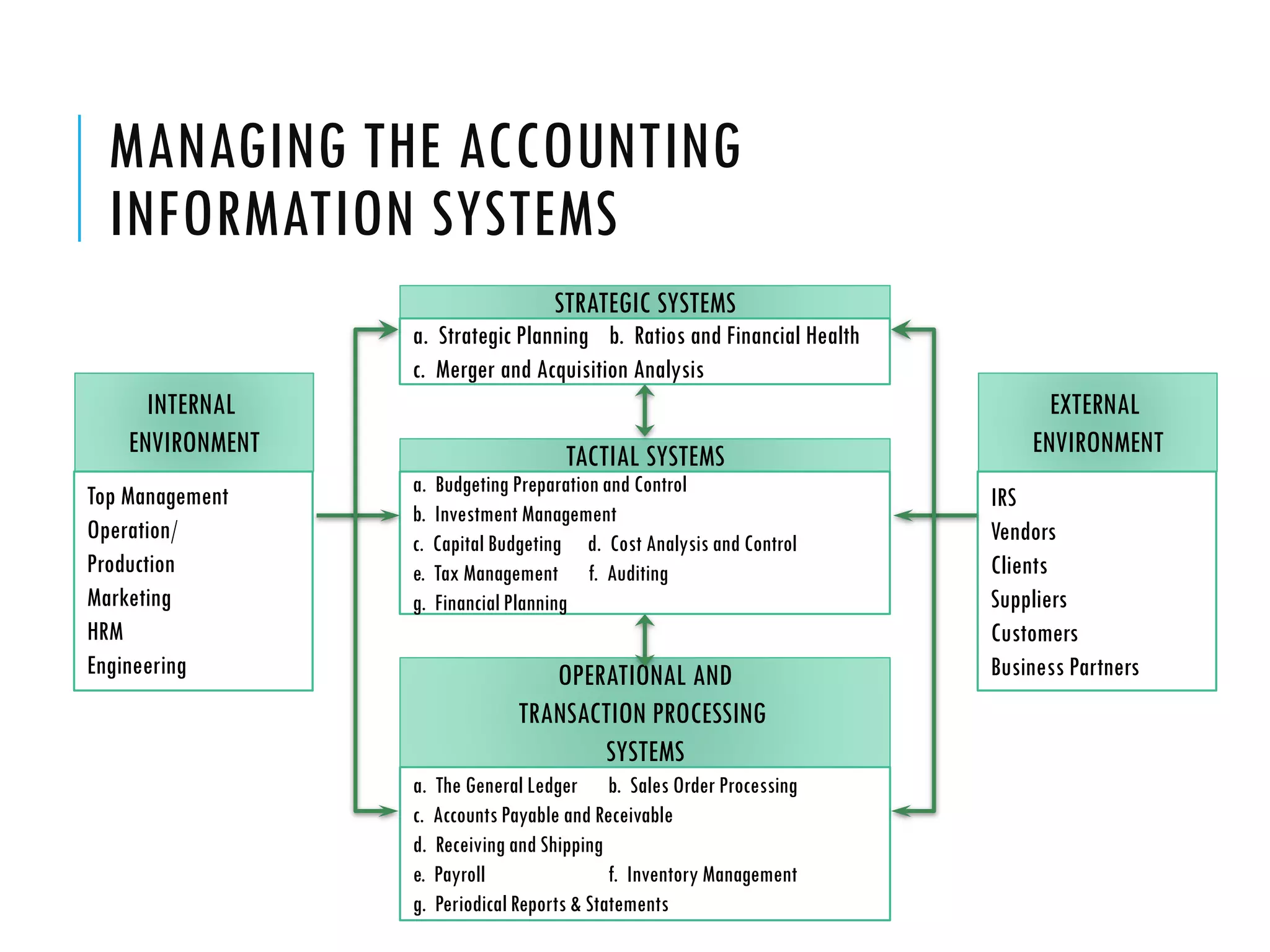
The document discusses accounting information systems (AIS). It defines an AIS as consisting of people, procedures, data, software, and IT that perform important functions for an organization, including collecting and storing transaction data, processing data into useful information, and providing adequate controls. The document outlines five learning objectives, which are to explain what an AIS is, why studying AIS is important, how an AIS adds value in a company's value chain, the three basic functions of an AIS, and the types of information an AIS can provide.