The document discusses the evolution of management thought from classical to modern theories. Classical theories included scientific management, administrative management, and bureaucratic management. Neoclassical theories arose in response to the human relations movement and Hawthorne experiments. Modern theories include quantitative approaches, systems approaches, and contingency approaches. Recent developments discussed are total quality management and the search for excellence framework.
















![BUREAUCRATIC MANAGEMENT
Max Weber [1864-1920 ].
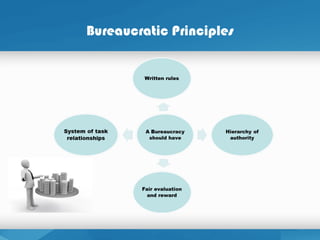
Rules and regulations to eliminate managerial inconsistencies.
Authority is the power to hold people accountable for their actions.
Positions in the firm should be held based on performance not social
contacts.
Position duties are clearly identified. People should know what is expected
of them.
Lines of authority should be clearly identified. Workers know who reports to
who.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/evolutionofmanagementthought-160824121013/85/Evolution-of-management-thought-18-320.jpg)