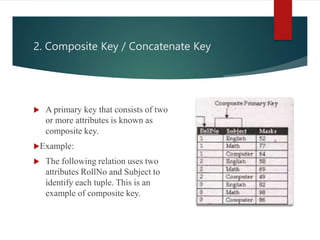
The document discusses various types of keys used in databases, defining a key as an attribute that uniquely identifies a tuple in a relation. It outlines seven types of keys: primary key, composite key, candidate key, alternate key, foreign key, secondary key, and sort/control key, explaining their unique characteristics and functions. Each key plays a critical role in data organization and relationships within database relations.