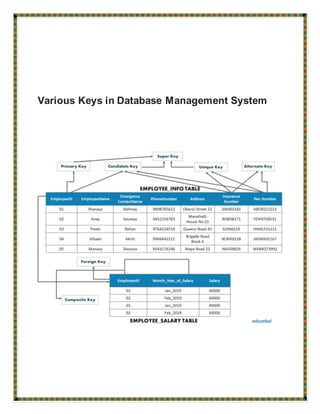
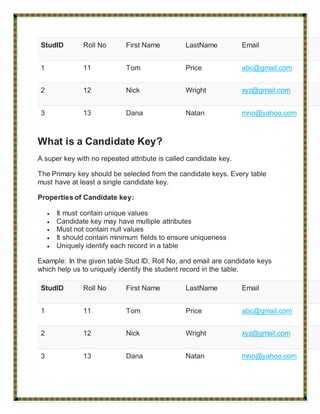
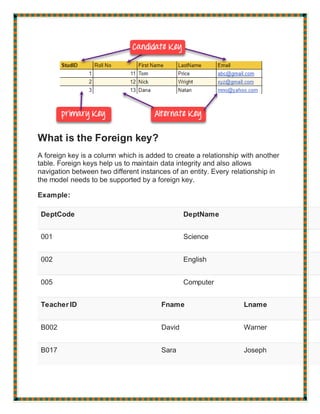
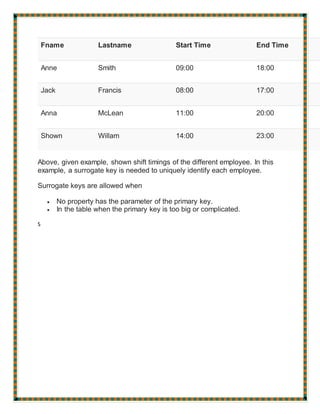
The document defines and provides examples of various types of keys used in database management systems, including super keys, primary keys, candidate keys, alternate keys, foreign keys, compound keys, composite keys, and surrogate keys. It explains that primary keys uniquely identify rows, foreign keys create relationships between tables, and surrogate keys are artificial keys used when no natural key exists.